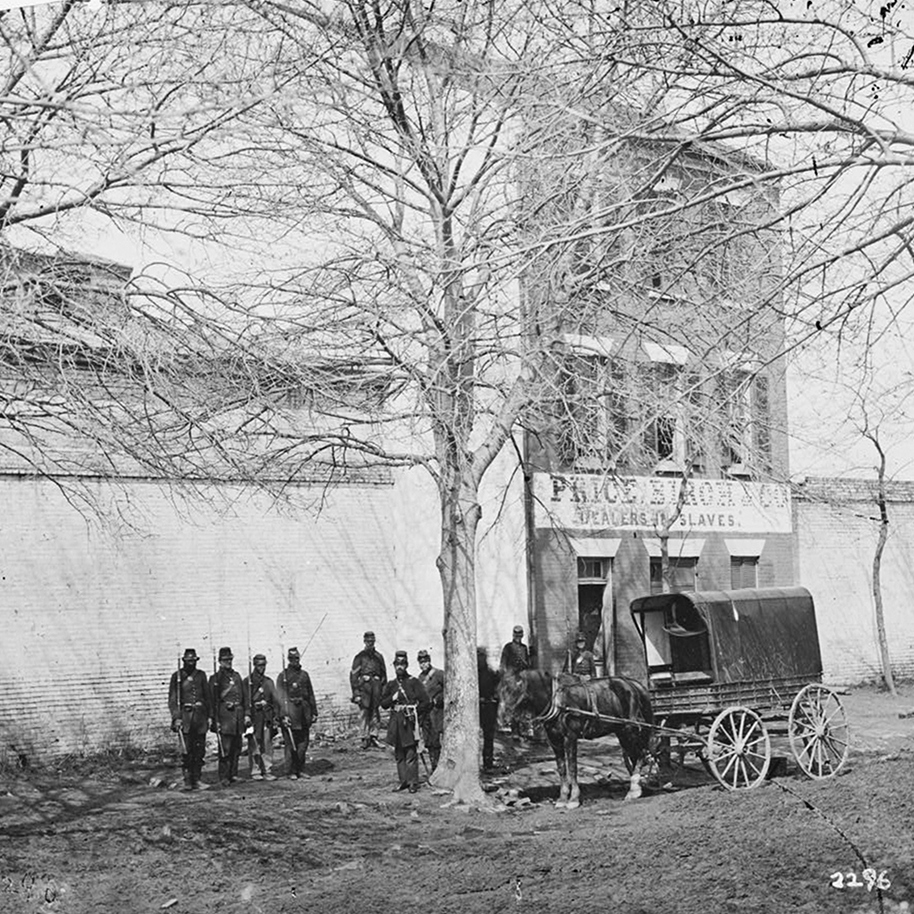
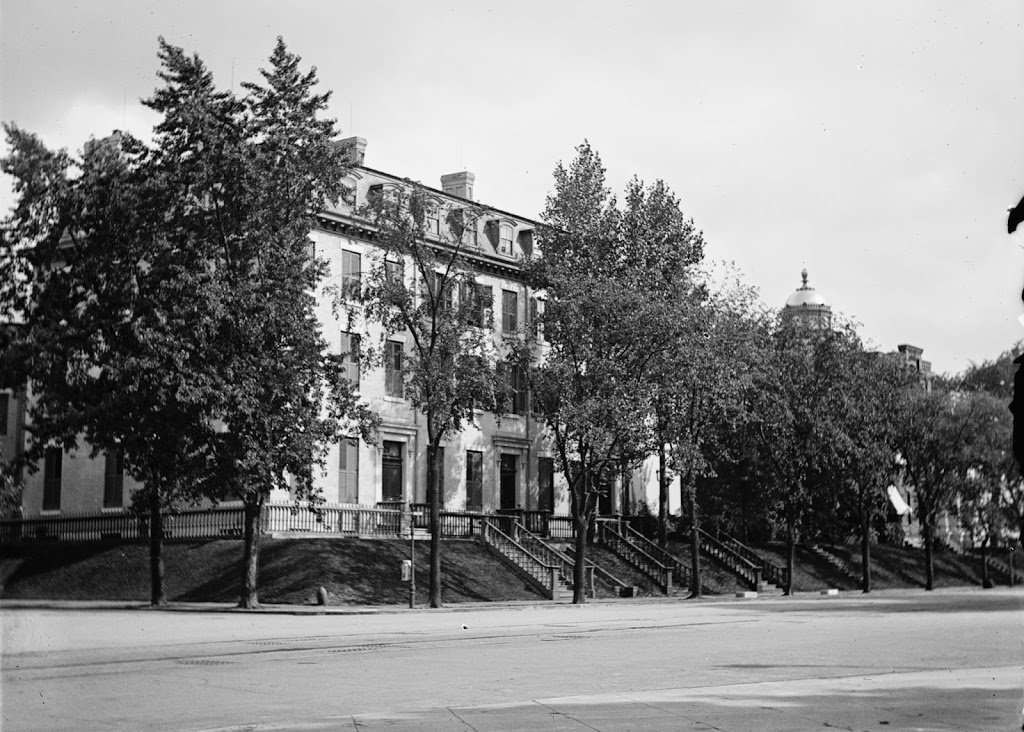
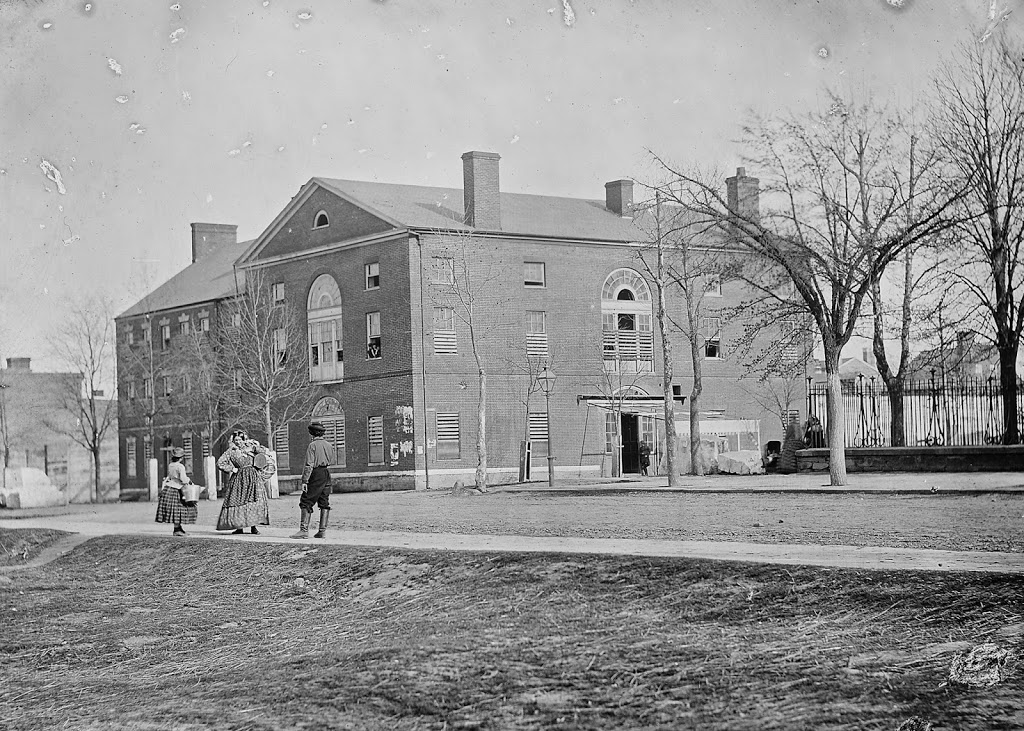The Franklin and Armfield Office at 1315 Duke Street in Alexandria, around the early 1860s. Image courtesy of the Library of Congress, Civil War Collection.
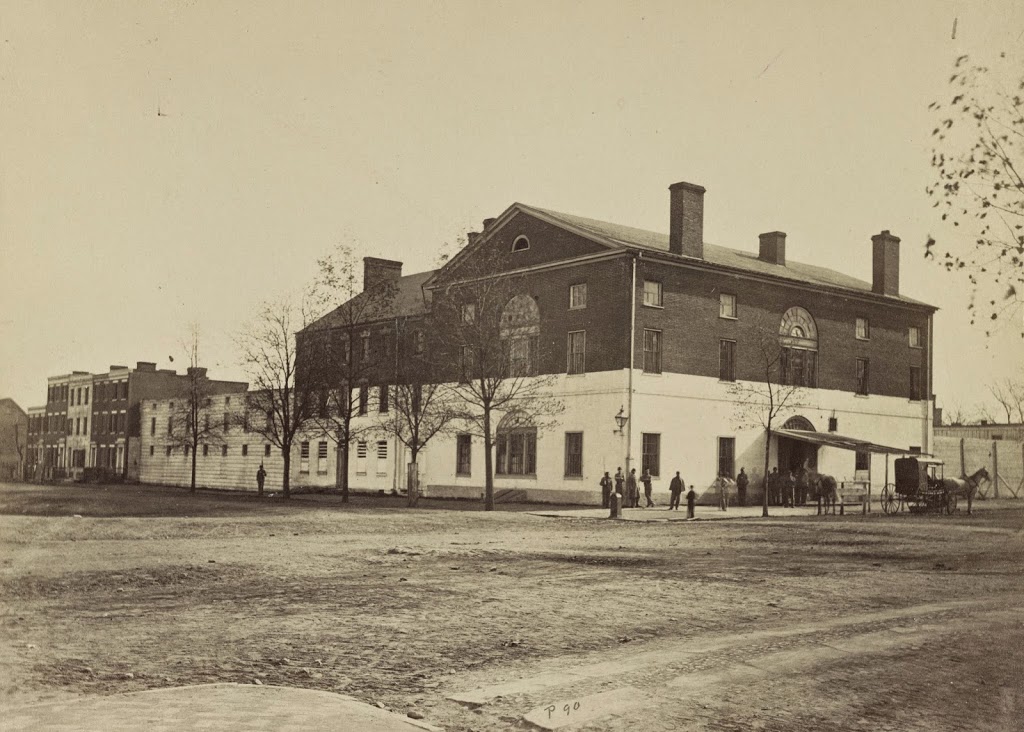
The scene in 2021:
The Franklin and Armfield Office at 1315 Duke Street in Alexandria, Virginia was built in 1810. It was originally built as a private residence for Brigadier General Robert Young of the Second Militia of the District of Columbia, but he was forced to sell the home in 1820 due to financial problems. By 1828, the home was leased, and eventually bought by infamous slave traders, Isaac Franklin and John Armfield. Franklin and Armfield were the largest slave traders in the United States between 1828 and 1836, and the Duke Street home was turned into their main office.
Since the transatlantic slave trade was banned in 1808, Franklin and Armfield would send agents across Virginia, Maryland, and Delaware in search of slave owners who were willing to part with their slaves for relatively cheap prices. The enslaved people would then be shipped back and held in the high-walled courtyards surrounding the offices (Seen to the left and right of the house in the top picture). In these courtyards, the enslaved people were subject to brutal beatings, rapes, and countless other forms of cruel control. Rapes were so frequently done by Franklin and Armfield to their slaves, that they bragged about them in letters between each other, and both men would father children to enslaved women in their captivity. Franklin would later go on to sell the woman he raped and the child he fathered with her. A two-story extension was added to the back of the building to serve as jail cells. These cells could be used to isolate certain slaves but were more often rented out by travelling slave owners who wanted to keep their slaves on the Virginia side of the Potomac.
Due to a surplus of enslaved people in the Upper South, slaves did not fetch high prices in Alexandra. The enslaved people were typically kept in the home’s courtyards until enough of them were bought for them to all be shipped together or marched to their offices in Natchez and New Orleans. Once in the Deep South, they could be sold at much higher prices than they were bought for in Virginia. It’s estimated that Franklin and Armfield sold between 1,000-2,000 people each year, transporting all of them by way of cramped slave ships or forced marches across the South.
By 1836, Franklin decided to retire, and his partner Armfield decided to sell off most of the business. He sold the Duke Street offices to another slave trader, George Kephart. He would continue the practice of selling slaves until he sold it to yet another slave trading firm, Price, Birch & Co. in 1858.
Price, Birch & Co. would become infamous not for their volume of slaves sold, but rather for one particular man that they enslaved. Solomon Northup, a freed slave from Saratoga Springs, New York was kidnapped in Washington, DC in 1841. He was shipped down to New Orleans where we was bought by a planter and re-enslaved. It would take Solomon 12 years before he would once again gain his freedom with the help of Samuel Bass. A Canadian working on the plantation, Samuel was able to get word back to New York about Solomon’s re-enslavement. After an appeal to the Governor of New York, Solomon was granted his freedom in 1853. Solomon would later go on to write his famous memoirs, 12 Years a Slave. In his memoirs, Solomon named his kidnapper as “Burch”, but it’s largely been accepted that the man he was talking about was James H. Birch, of Price, Birch & Co. in Alexandria. It should be noted though that Solomon Northup does not appear to have actually passed through the Alexandria slave pens, only that Birch used the building as his offices. Price, Birch & Co. would go on to own the building until the Civil War, when it was occupied by Union Forces in 1861. During the Civil War the slave pens were ironically, used as jail cells for captured Confederate soldiers.
After the Civil War, a railroader by the name of Thomas Swann bought the property in 1870 and tore down the slave pen extension. The buildings exterior also underwent changes that give it its modern appearance, such as the fourth story windows being added as well as the arches over the windows on the front façade. The property changed hands multiple times over the last century, serving as apartments for most of that time before being sold in 2017 to the Northern Virginia Urban League. Today, the building has been re-named the Freedom House, and features a museum to the building’s history on the first floor, and offices for the Northern Virginia Urban League on the upper floors.