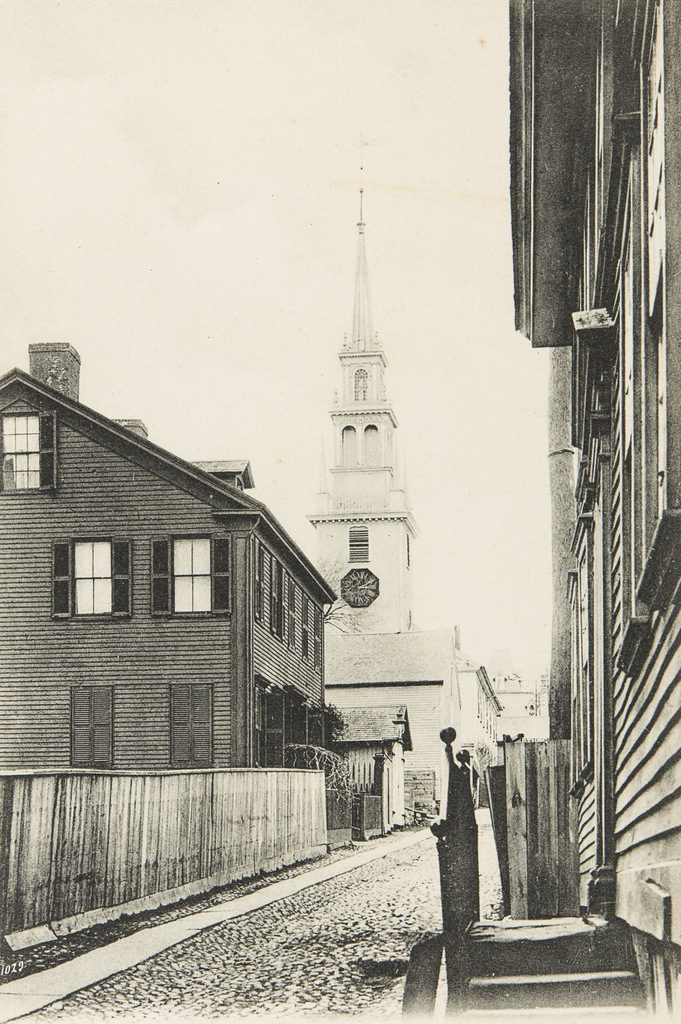
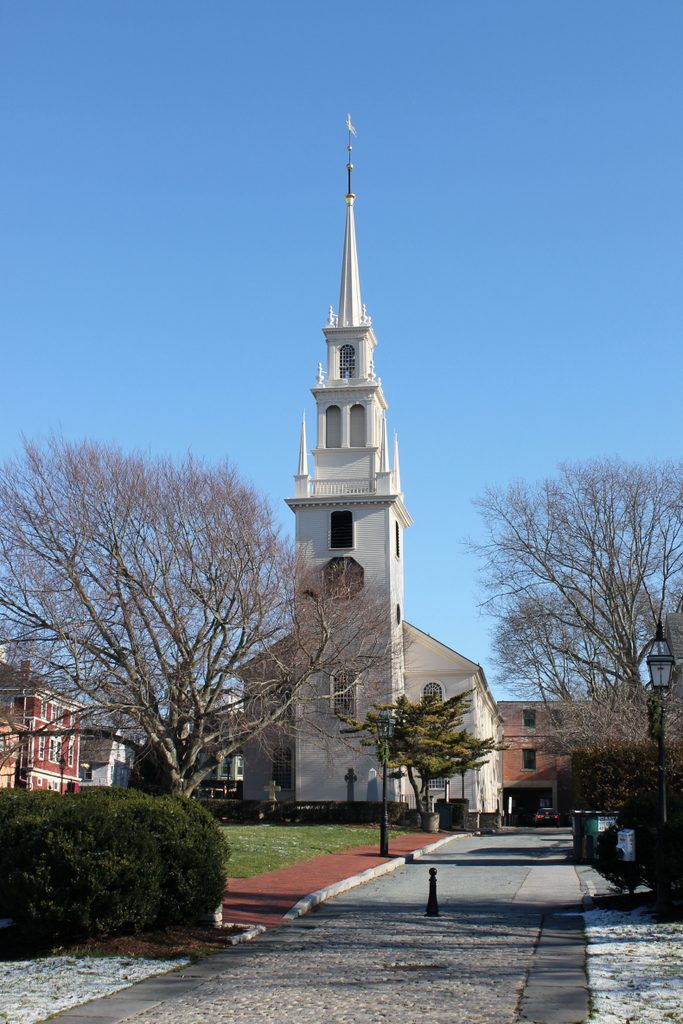
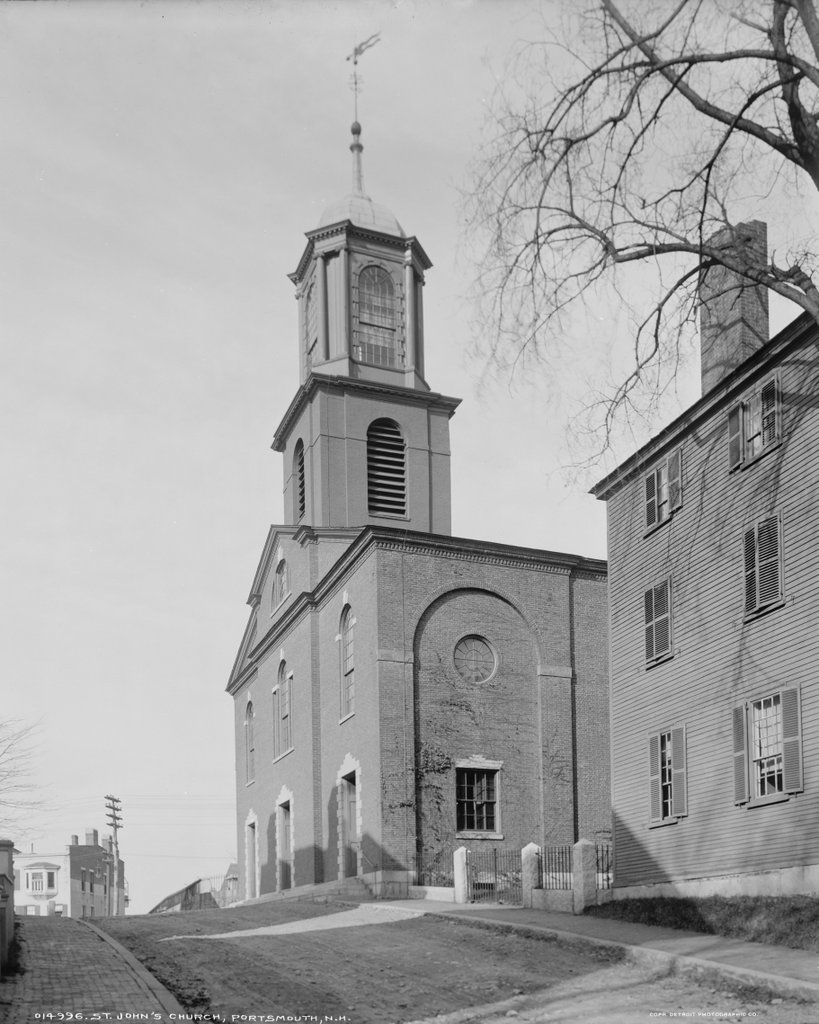
Trinity Church, seen looking east along Frank Street in Newport, around 1901. Image courtesy of the Providence Public Library.
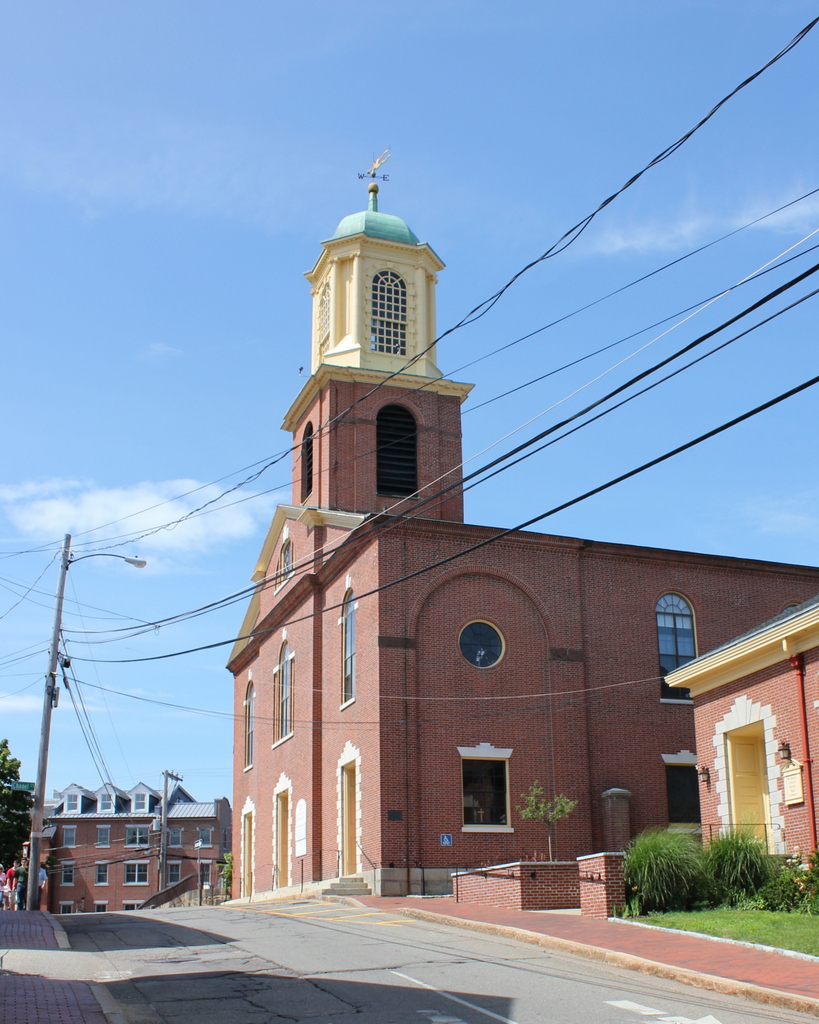
The scene in 2017:
Newport features an impressive collection of colonial-era buildings that have survived to the present day, but one of the most significant of these is Trinity Church, which is seen in these two photos. It was built in 1725-1726 as an Anglican church, replacing an earlier building that the congregation had previously used, and it was the work of local architect and builder Richard Munday. His design was based on the churches of London architect Christopher Wren, and it also bears a strong resemblance to Old North Church, which had been built just a few years earlier.
Although the building itself was completed in 1726, the spire was not added until 1741, and it had to be rebuilt in 1768. Another change came in 1762, when the church was expanded by 30 feet. In order to do this, the building was divided in half, the rear section was moved back, and the addition was built in the middle of the two halves. However, it has seen few significant changes since then, and it remains remarkably well-preserved, both on the exterior and interior.
Unlike in most other New England towns, Newport’s colonial-era churches were not built at the head of large public squares. This was an effect of Rhode Island’s legacy of religious tolerance, in order to avoid showing preference to one denomination over another. Because of this, houses of worship tended to have less prominent locations. Here, Trinity Church was situated on a narrow lot bounded by Spring, Church, and Frank Streets. The church building itself filled up most of the lot, with just enough room for a small churchyard on the north and west sides. As the first photo shows, this left the church crowded on all sides, and nearly hidden from view by an assortment of modest houses and commercial buildings.
This situation continued for much of the 20th century. However, a fire in 1973 destroyed the building at the corner of Thames and Frank Streets. This loss helped to spur the redevelopment of the entire block, and during the 1970s the Newport Restoration Foundation acquired properties in the two-block area between Mill and Church Streets. This project was led by the Newport Restoration Foundation’s founder, the tobacco heiress Doris Duke, and it eventually involved the removal of all the buildings here on Frank Street. These buildings held little historical or architectural value, and they were replaced by Queen Anne Square, a public park that stretches from the front of Trinity Church down to Thames Street.
Today, the narrow, cobblestoned Frank Street is still there, although the western end of it is now a pedestrian walkway through Queen Anne Park. With the street no longer cluttered with buildings, Trinity Church is now easily visible from Thames Street and the waterfront area, and it stands as the only surviving structure from the first photo. The nearly 300 year old church is now one a contributing property in the Newport Historic District, a National Historic Landmark district that encompasses much of downtown Newport. However, it is also individually listed as a National Historic Landmark, making it one of 18 buildings in Newport to be recognized as such.