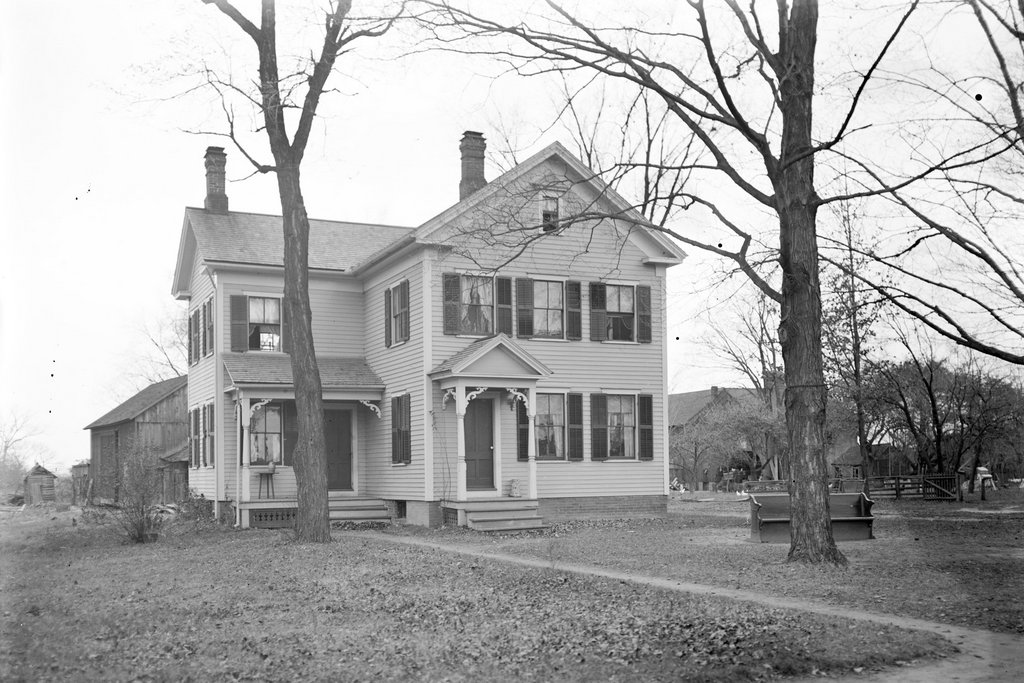
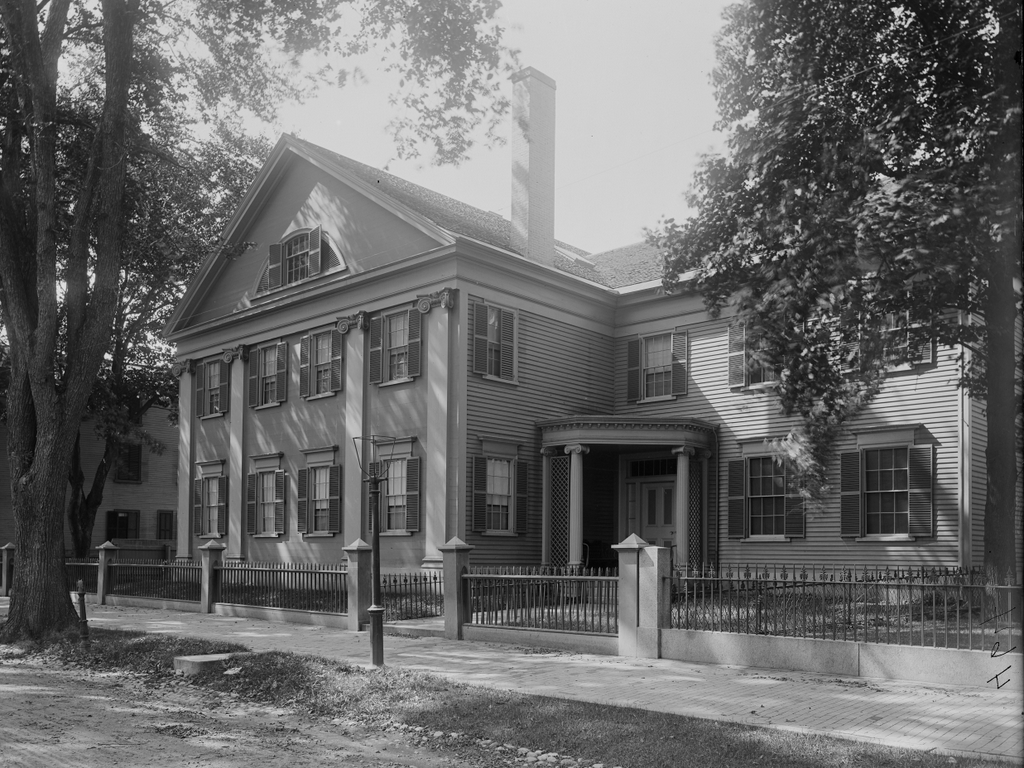
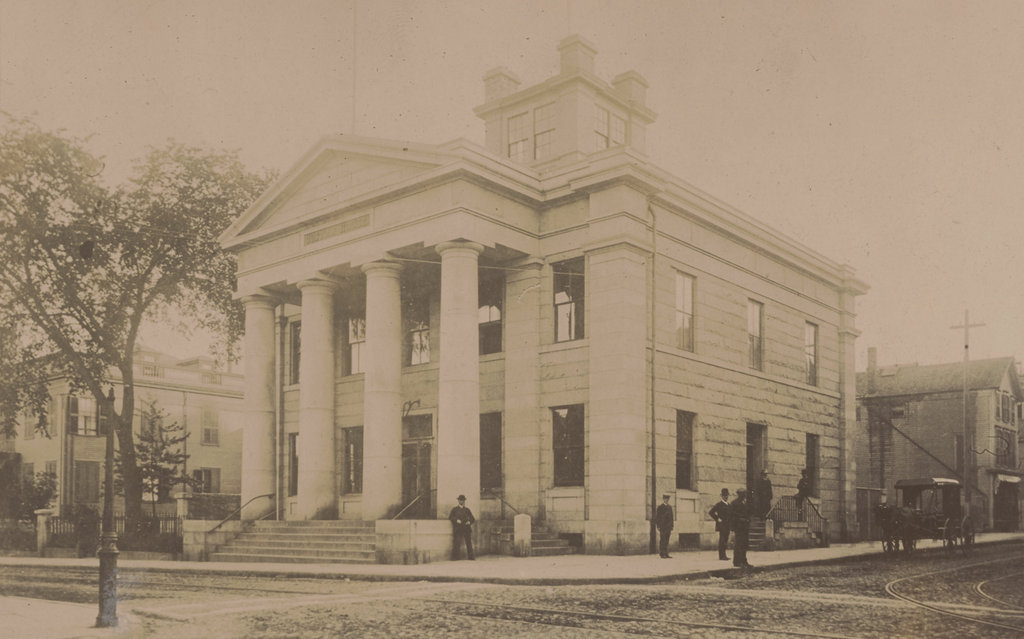
The house at the southwest corner of Longmeadow Street and Emerson Road in Longmeadow, Massachusetts, in November, 1910. Image courtesy of the Longmeadow Historical Society, Paesiello Emerson Collection.
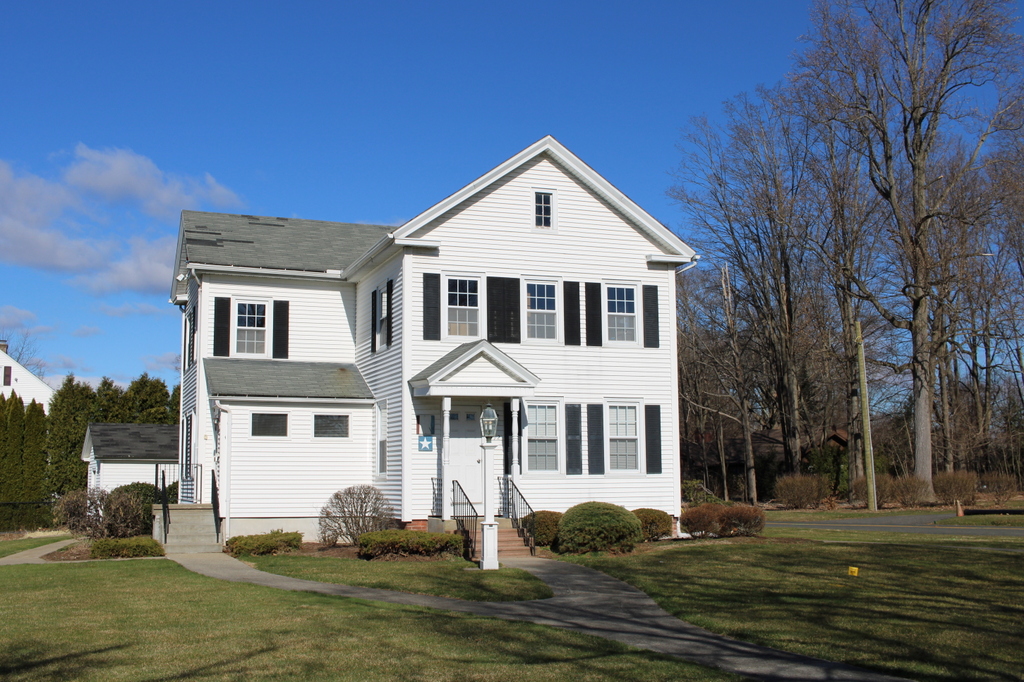
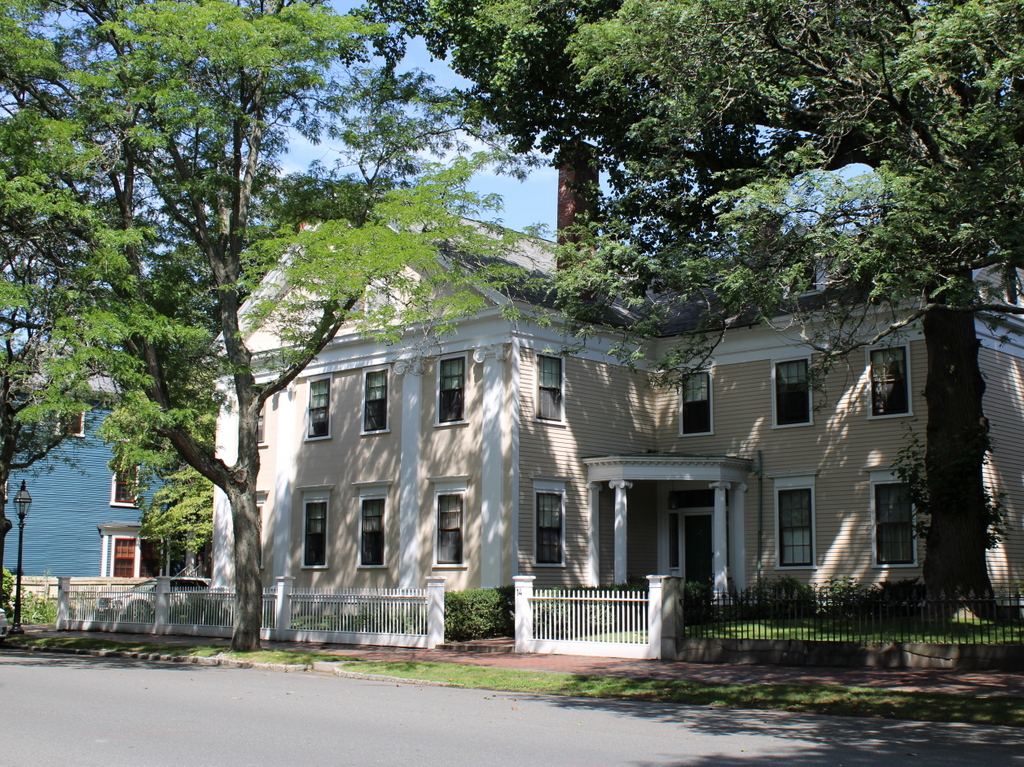
The scene in 2024:
The exact date of construction of this house seems uncertain, and the MACRIS inventory form for the house estimates that it was built around 1830 as the home of David Hale. However, it might be several decades older, because the 1831 town map shows David Hale living here at the time, although it is unclear whether it was in this particular house or an earlier house on the same site. Either way, the architecture of the house suggests that it was probably built sometime around 1830 to 1850, when Greek Revival style architecture was prevalent throughout much of New England.
During the 1850 census, David Hale and his wife Rebecca Woolworth were living here with their youngest child, Fanny. They had eight children in total, seven of whom lived to adulthood, and by 1850 all the other children had apparently moved out and started families of their own. The 1850 census lists David as a farmer, and in the 1860 census he is a shoemaker, with a personal estate of $150 and real estate valued at $1,000. Fanny was still living here in 1860, with her occupation listed as “Domestic.” She may have been the primary caretaker for her parents as they aged, and she did not marry until 1865, less than a year before her father’s death.
After David’s death in 1865, the heirs subsequently sold the property to Michael Kinney. He and his wife Ellen were born in Ireland, as were their two older children, Mary and Jerry. They evidently came to America by around 1860, because their two younger children, Eddy and Thomas, were born in the United States. The 1870 census listed Michael’s occupation as being a farm laborer, but by 1880 he was listed as working on the railroad.
Michael died in either the 1880s or 1890s, and Ellen died in 1897. Their son Jerry died two years later from liver cancer, and Thomas also died relatively young. Thomas was living here in the house when the top photo was taken in 1910, along with his wife Mary; their children Edward, Thomas, Ellen, Jeremiah, and Francis; and a boarder named Thomas Evans. However, Thomas died just three years later, in December 1913, from pneumonia at the age of 45. Mary was pregnant at the time, and five months later she gave birth to another son, Charles.
Mary and Charles were still living here in 1930, and she was working as a manager at a dry goods store. She apparently sold the house at some point in the 1930s, though, because by 1940 she was living a few blocks away on Westmoreland Avenue with her daughter Ellen and Ellen’s family.
The house changed hands several times in the mid-20th century, and in 1966 it was purchased by Bay Path Junior College—now Bay Path University—and was used as a nursery school. The house is still part of the Bay Path campus today, and it is now used for administrative offices. At some point during this time, the exterior of the house was altered, including enclosing the porch on the left side and installing vinyl siding, windows, and shutters. The scene behind the house has also changed since then. What had once been farmland extending along both sides of Emerson Road has since been subdivided into house lots.