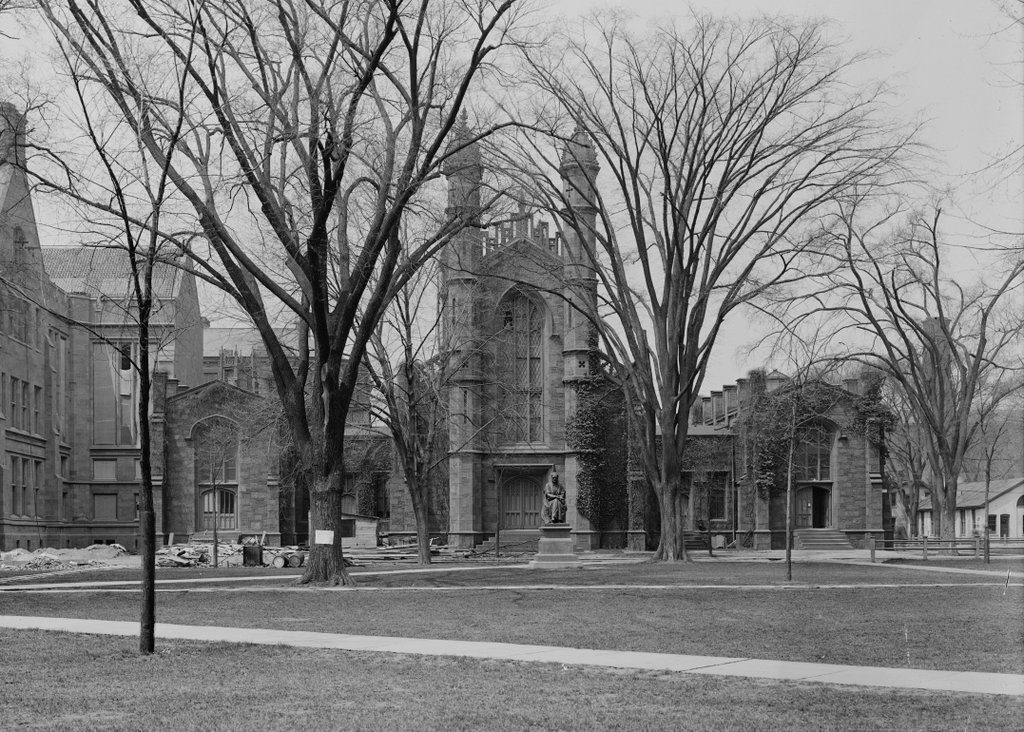
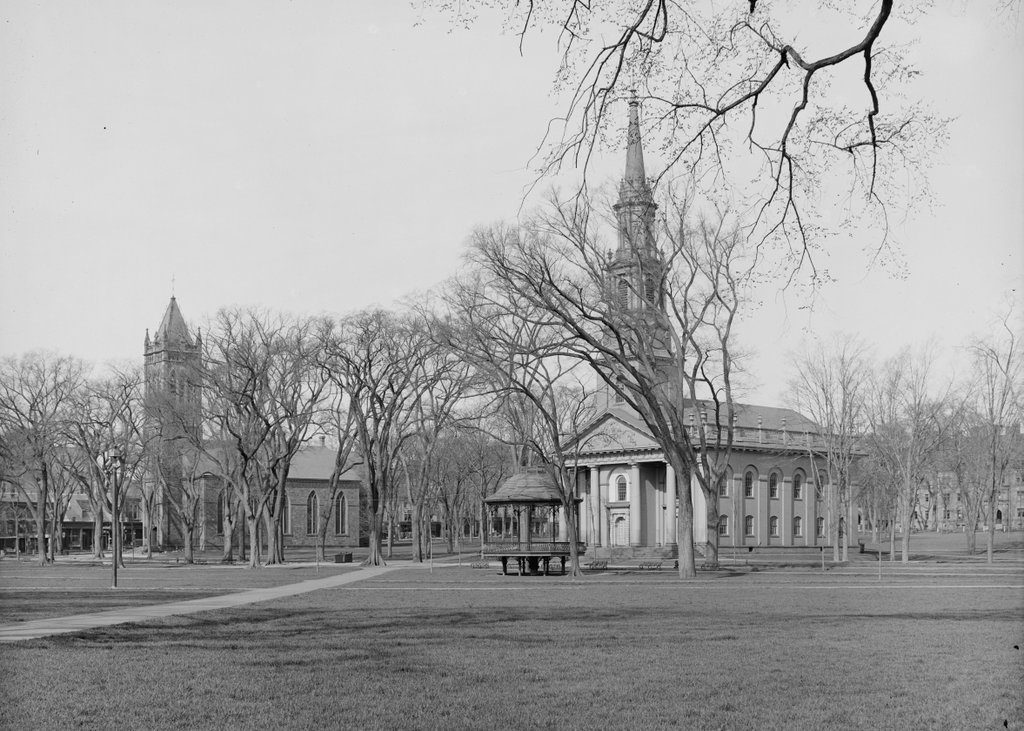Dwight Hall on the campus of Yale University in New Haven, around 1905-1915. Image courtesy of the Library of Congress, Detroit Publishing Company Collection.
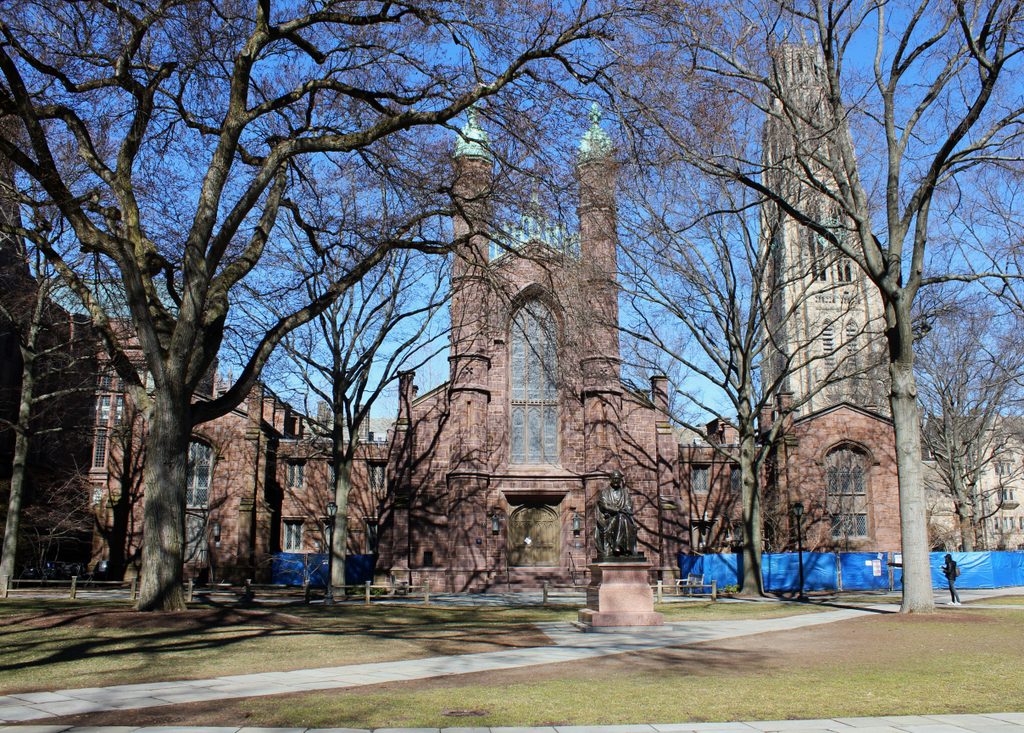
The scene in 2018:
During the first half of the 19th century, the most prominent feature on the Yale campus was the Old Brick Row, a group of seven buildings that ran parallel to College Street on what is now known as the Old Campus. Constructed in the 18th and early 19th centuries, these brick buildings included dormitories, along with academic buildings that housed recitation rooms, laboratories, chapels, and a library. The Old Brick Row served the school well for many years, but one of the first significant additions to the campus came in the 1840s, with the construction of a new library building. Located away from the Old Brick Row, on the High Street side of the block, the new library was both physically and architecturally set apart from the older buildings. It featured an ornate Gothic Revival-style design, which contrasted sharply with the older, more plain Federal-style buildings, and its style also foreshadowed the future development of a Gothic-style quadrangle that would eventually displace the Old Brick Row.
The library building, which was later named Dwight Hall after former presidents Timothy Dwight IV and Timothy Dwight V, was constructed between 1842 and 1846. It was the work of noted New Haven architect Henry Austin, and it was among the first major commissions of his career. Prior to its construction, the library had been located in several different Old Brick Row buildings, including the Atheneum from 1763 to 1804, the Lyceum from 1804 to 1824, and then in the Second Chapel starting in 1824. However, this building was the first on campus to be built specifically as a library, and its design was intended, at least in part, to protect the school’s rare books and archival materials from fire. Its location, far from the Old Brick Row, would have kept it safe in the event of a fire in the older buildings, and the library itself was built to be as fireproof as possible, with features such as a brownstone exterior, tin roof, and internal firewalls.
Within a few decades of the library’s completion, the Old Campus began to undergo a major transformation. The buildings of the Old Brick Row were steadily demolished, and the entire block was eventually encircled by late 19th and early 20th century Gothic-style buildings, creating an open quadrangle where the old buildings had once stood. The library was spared demolition, and was incorporated into this new campus plan, as was South Middle College, a part of the Old Brick Row that had been built in 1752. Later renamed Connecticut Hall, it is the oldest building on the Yale campus, and the library is now the second oldest.
This building served as the Yale library for many years, although it eventually became too small for the school’s growing collections. The library was expanded with the construction of Chittenden Hall in 1890 and Linsly Hall in 1906, and the latter is partially visible on the left side of both photos. However, even this arrangement proved inadequate over time, and in 1931 the library moved into the newly-completed Sterling Memorial Library. The old library was then converted into a chapel, and was renamed Dwight Hall. Over the years, the building has also served as the headquarters and namesake of Dwight Hall at Yale, a community service organization that is comprised of a wide variety of advocacy groups, charities, and related service-based campus groups.
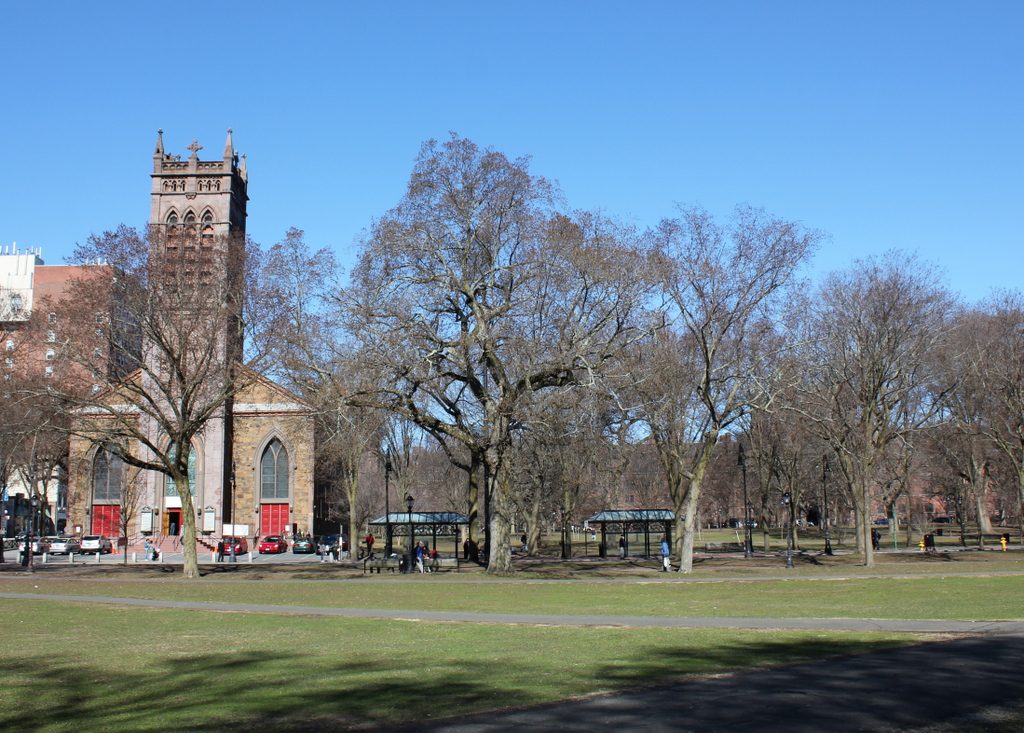
Today, aside from changes in its use, Dwight Hall is not significantly different from its appearance in the first photo, taken more than a century ago. Linsly Hall, which is now combined with the adjacent Chittenden Hall, is still standing on the left side as well, and other features from both photos include the statue of Theodore Dwight Woolsey, who became president of the college in 1846, the same year that Dwight Hall was completed. This statue has become somewhat of a Yale landmark, as rubbing Woolsey’s left foot is said to bring good luck. This has resulted in a foot that is significantly shinier than the rest of the statue, a phenomenon that has even been referenced on the television show Gilmore Girls.
Overall, the only major difference between these two photos is the Harkness Tower, which is visible in the distance on the right side of the 2018 photo. Completed in 1922, this 216-foot tower was named in honor of Yale graduate and prominent Standard Oil investor Charles William Harkness, and was donated by his family after his death in 1916. The 2018 photo also shows some of the work that has recently been done on Dwight Hall. The building temporarily closed in 2017, and underwent its first major renovation since its conversion from a library to a chapel. This work was still in progress when the first photo was taken in the spring of 2018, but it was completed several months later, and the building reopened in the fall of 2018.