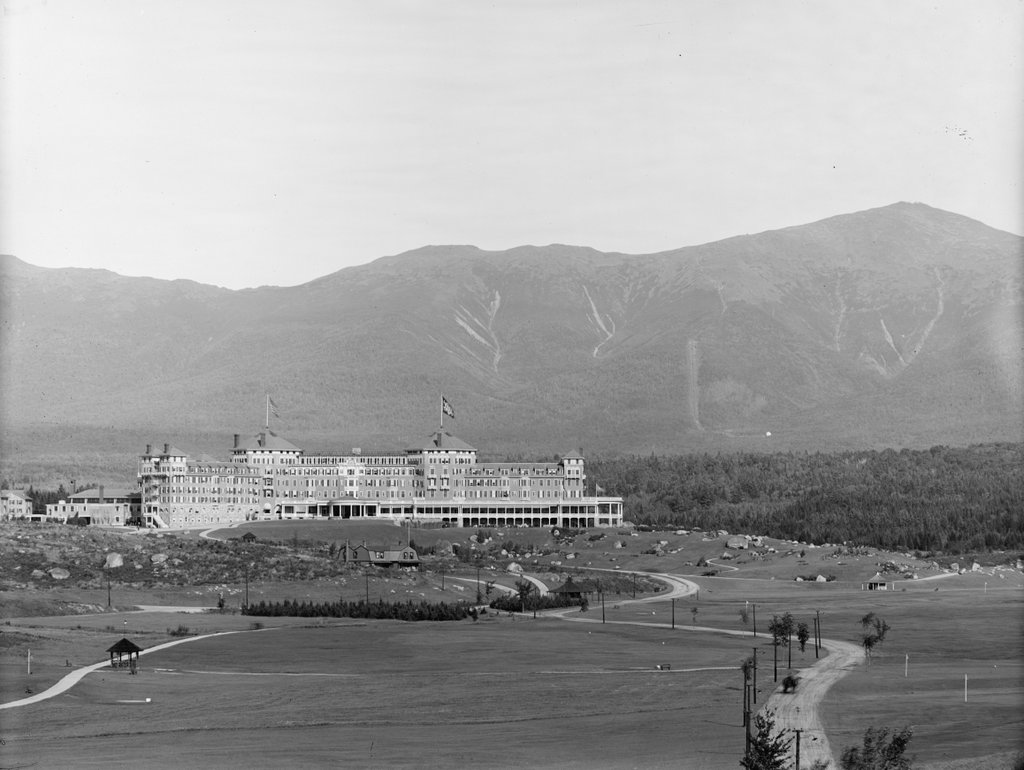
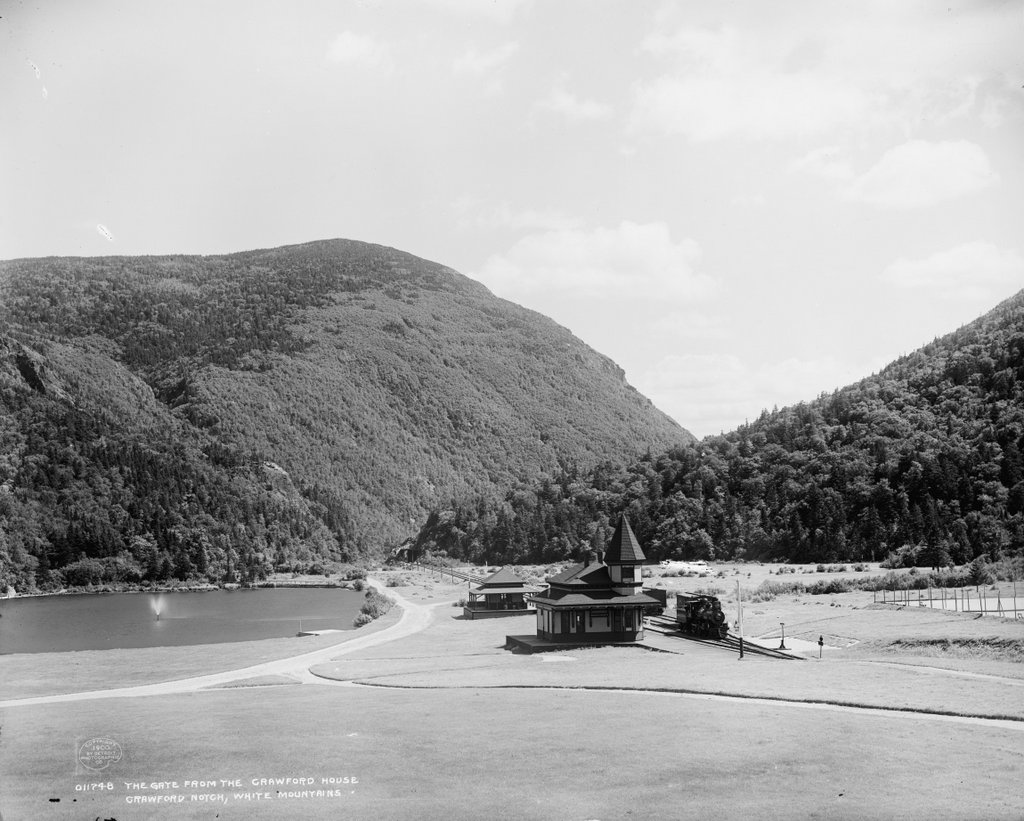
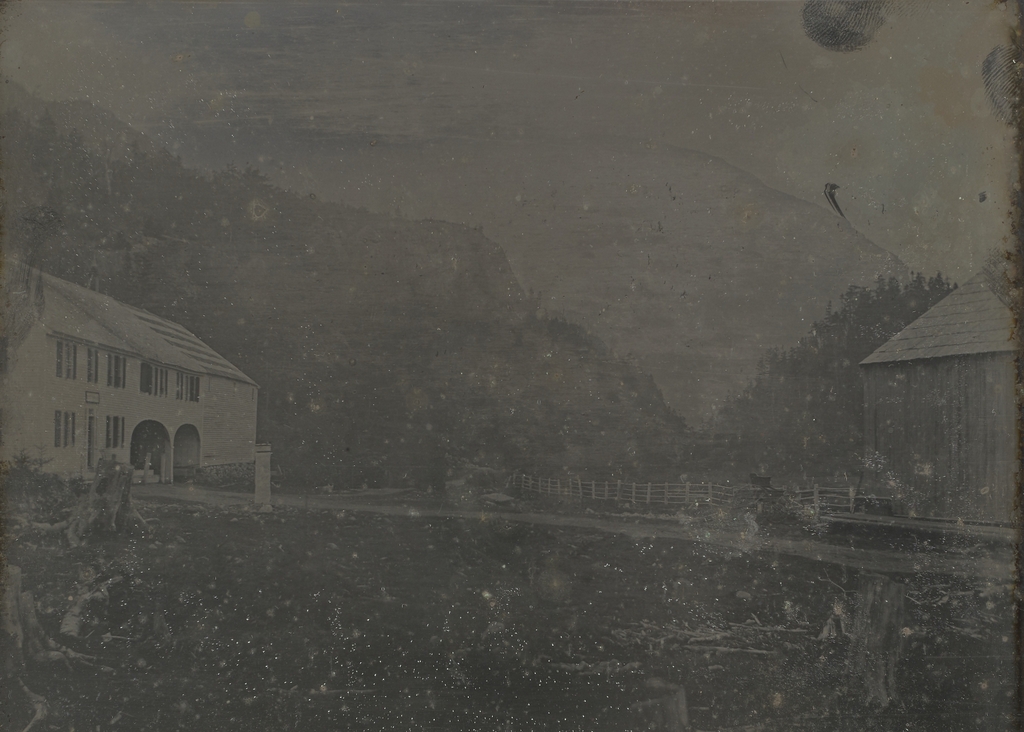The Crawford House at Crawford Notch in the White Mountains of New Hampshire, seen from across Saco Lake, around 1891-1910. Image courtesy of the Library of Congress, Detroit Publishing Company Collection.
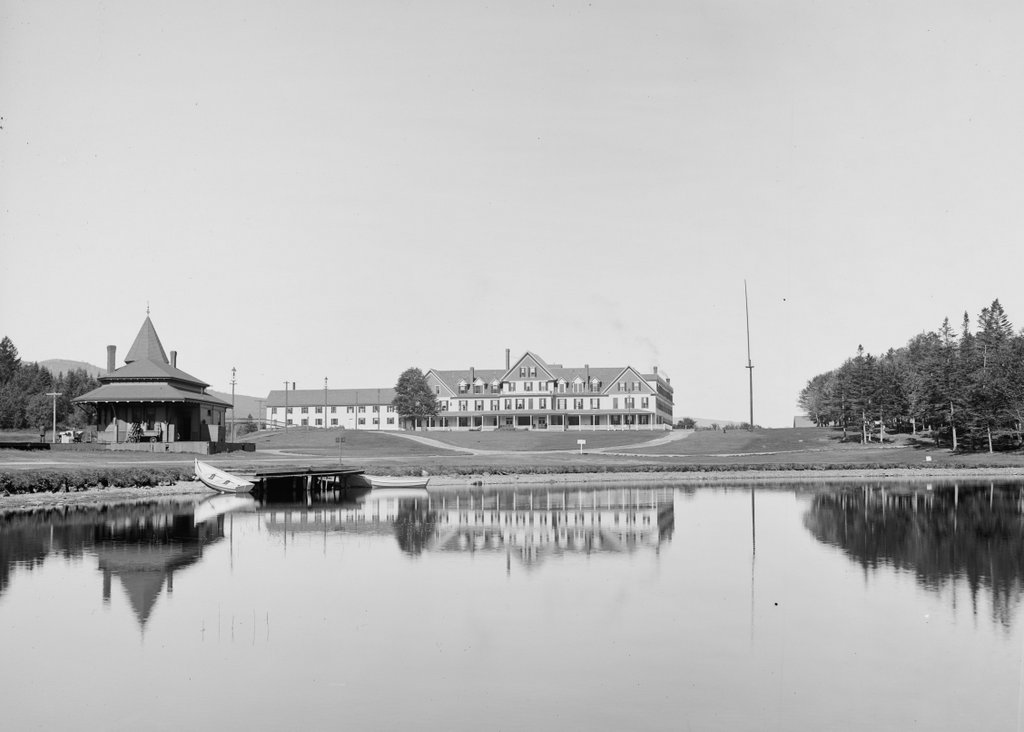

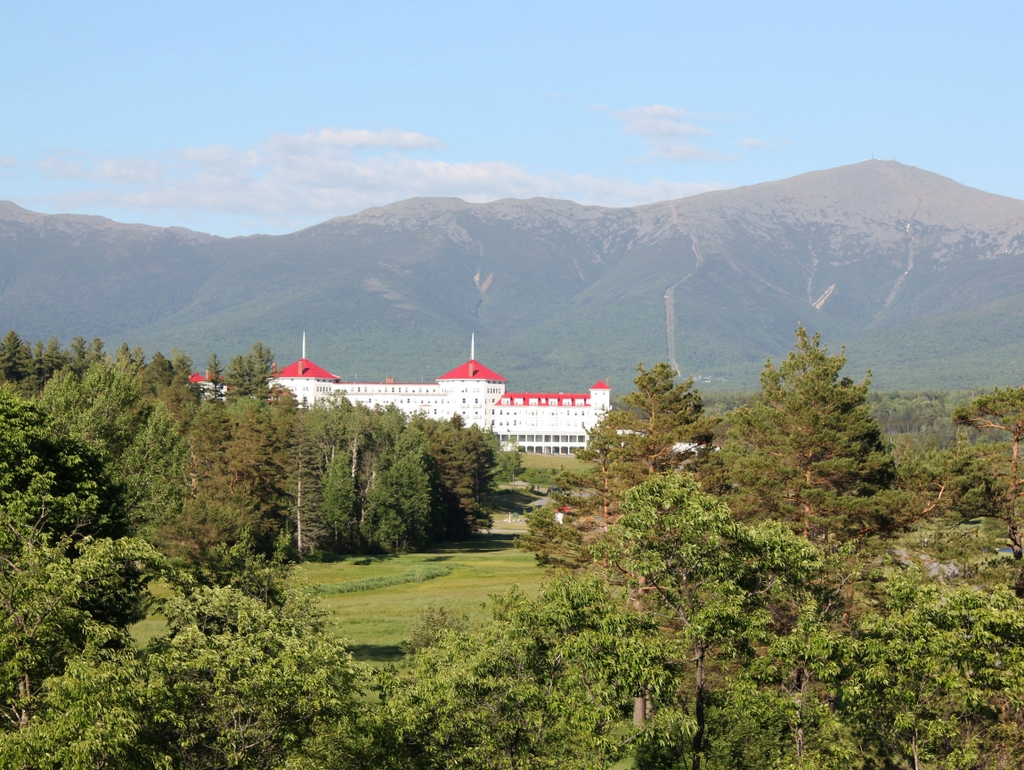
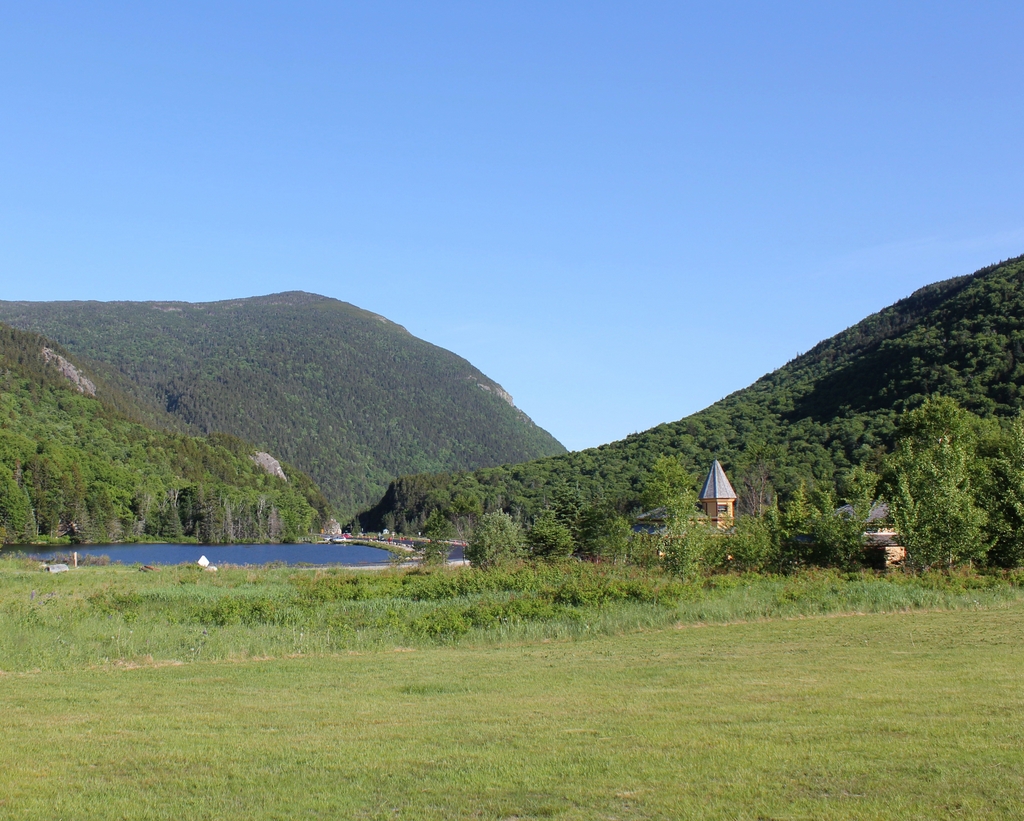
The scene in 2018:

The first photo shows the Crawford House, one of the many large hotels that were built in the White Mountains during the second half of the 19th century. It stood just to the north of the gates of Crawford Notch, one of the most important mountain passes in the region. The location of the hotel was near the high point of the notch, at the divide that separates the watersheds of the Ammonoosuc and Saco Rivers. In the foreground of this scene is Saco Lake, which forms the headwaters of the Saco River. From here, the river flows southeast through Crawford Notch before emptying into the Atlantic Ocean just south of Portland, Maine. Less than a half mile to the north of here, on the other side of the hotel, is Ammonoosuc Lake, which ultimately drains into the Connecticut River and then to Long Island Sound.
This site was an ideal location for a hotel. At the time, this road was the only east-west route through the mountains, and this area to the north of Crawford Notch was relatively broad and flat, unlike the long, narrow valley to the south of here. The first hotel in this immediate vicinity was the Notch House, which was built in 1828 by Ethan Allen Crawford. He was the son of Abel Crawford, the first white settler to live near the notch, and his family operated several taverns in the area. Ethan’s brother Thomas became the manager here at the Notch House, and he ran it until 1852, two years before it was destroyed by a fire.
The Notch House was located near the spot where these two photos were taken, but around 1850 Thomas Crawford began construction of a new hotel nearby, on the site of the hotel in the first photo. However, he ran into financial problems before it was completed, and he had to sell the property in the early 1850s. The new owner finished the hotel, which became known as the Crawford House, but, like the Notch House, it fell victim to fire, burning on April 30, 1859.
Such fires were not uncommon in large resort hotels of this period, which were generally made almost entirely of wood and lacked effective fire suppression systems. Despite this setback, though, the hotel was quickly rebuilt. The work began on May 10, 1859 and it was completed in just two months, with the hotel holding a celebratory dinner here on July 13. This new Crawford House, which was still standing when the first photo was taken, was three stories high and originally measured about 200 feet in length, with two wings that extended back about the same distance. Overall, it was much larger than the old building on the site, and a July 1859 article in the Boston Evening Transcript declared it to be the largest hotel in the state.
Another New England newspaper, the Independent Democrat of Concord, New Hampshire, published a letter around the same time that the hotel opened. The letter described a journey through the White Mountains, and it paid particular attention to the new Crawford House. The writer commented on how quickly the hotel was built, and also provided a glowing description of its interior, writing:
It is not too much to say that the “New Crawford house” is an advance upon any other at the Mountains. Its dining hall is of magnificent proportions, measuring 85 feet by 40, and 14 feet high. The principal parlor is 60 feet by 40. The general reception room is large and airy; while the sleeping rooms, of which there are some 120, are large, high, and thoroughly ventilated, leaving nothing, in these respects, to be desired. Then, the whole house is to be furnished in the most elegant and substantial style, and the whole is to be lighted with gas.
Guests at the Crawford House could enjoy a variety of outdoor activities. There were short hikes to places such as Ripley Falls, Arethusa Falls, and the summit of nearby Mount Willard, and for the more ambitious there was the Crawford Path, which led 8.5 miles to the summit of Mount Washington. This trail, which began here at the Crawford House, was created by Abel and Ethan Crawford in 1819, and it was eventually incorporated into the Appalachian Trail, making it probably the oldest active hiking trail in the country today. Guests could hike these trails on their own, but the hotel also had ponies that they could ride, along with experienced guides to accompany them.
In 1870, the Crawford House was purchased by brothers Asa T. and Oscar F. Barron. At the time, they also operated the nearby Twin Mountain House and Fabyan House, and their hotel empire would subsequently include the Mount Pleasant House and the Summit House, which was located at the top of Mount Washington. Oscar died here at the Crawford House in 1879, and Asa died eight years later, but the Barron family would continue to run these hotels for many years.
For the first two decades of its existence, the Crawford House was not directly served by railroads, but in 1875 the Portland & Ogdensburg Railroad opened through Crawford Notch, making the hotel far more accessible to visitors. At the time, it was the only hotel in the vicinity of the notch, and it received a glowing review in the 1887 Chisholm’s White-Mountain Guide-Book, which included the following description:
[T]his is a good hotel of the first class, 1,900 feet above the sea, with broad and almost interminable piazzas, cool and airy halls, post-office, telegraph-office, livery-stable, bowling-alley, gaslights; environs which the landscape-gardener has justly approved; and a dining-room where even Epicurus or Uncle Sam Ward need not famish….
Near the front of the house is the pretty little Saco Lake, the cradle of the Saco River, and so far widened and deepened by art as to give a reason for being for the boats which float on its crystal tide. The rugged forest between the lake and the overhanging mountain has been combed and brushed and perfumed, and otherwise adorned for a summer pleasaunce, so that it has won the happily suggestive name of Idlewild.
In 1888, not long after this description was published, the rail line through the notch was acquired by the Maine Central Railroad. Three years later, the railroad built a new station here at the Crawford House, which is visible on the left side of this scene. It was built of wood, and it featured an ornate Queen Anne-style design, complete with a small tower on one corner of the building. Most hotel guests and other visitors to Crawford Notch would have arrived here by way of the station, and the building also served as the local freight house and post office.
By the time the first photo was taken at the turn of the 20th century, the Crawford House was owned by the firm of Barron, Merrill, & Barron. This partnership was comprised of Asa Barron’s sons, Oscar G. and William A. Barron, along with Cardenio H. Merrill, and the trio also ran the other Barron hotels here in the White Mountains. Merrill died a few years later in 1908 at the age of 68, and Oscar in 1913 at 62, but William continued to operate the hotel until 1947, when he retired and sold the property. He died in 1964 at the age of 96, only a week after the death of his son, William A. Barron Jr., who had served as a brigadier general in the Army during World War II and as chairman of the board of Gillette after the war.
The Crawford House outlasted most of the other 19th century grand hotels in the White Mountains, but it ultimately closed in 1975, nearly 120 years after the building was constructed. It was destroyed by a fire two years later, on November 20, 1977, and the property was subsequently acquired by the Appalachian Mountain Club, which constructed the Highland Center on the site. This building, which serves as a lodge and an educational center, stands in the center of the 2018 photo. Today, the only surviving building from the first photo is the railroad station on the left. It was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1982, and it remains in use as a railroad station, serving as the northern terminus for most tourist excursion trains on the Conway Scenic Railroad.