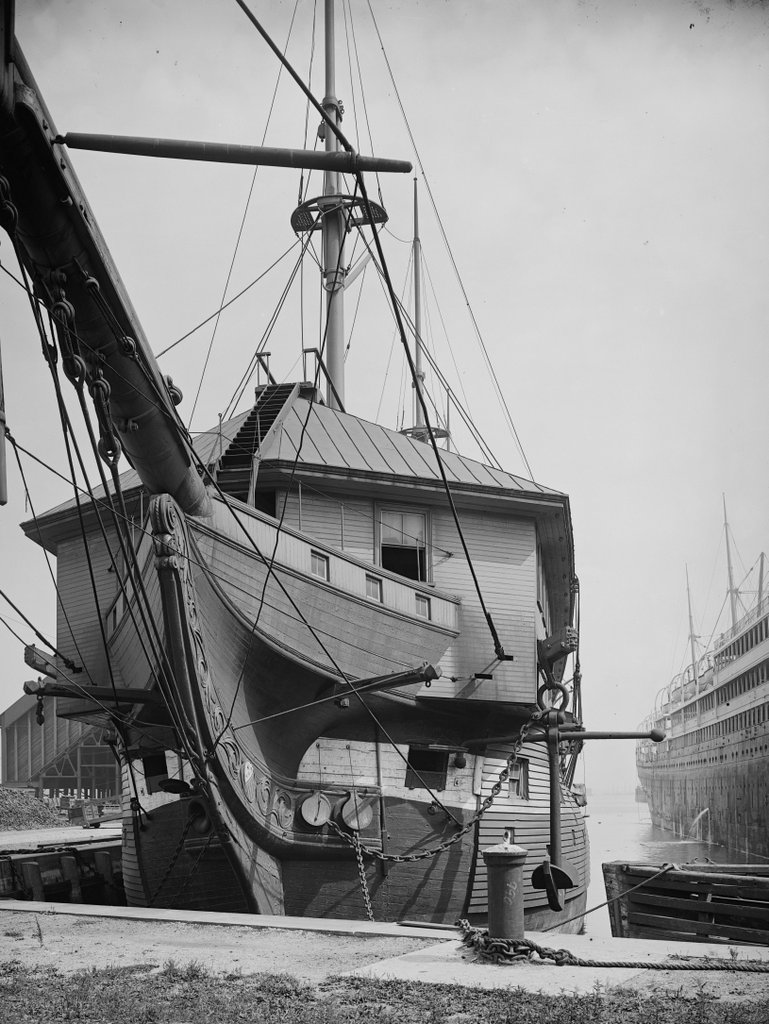
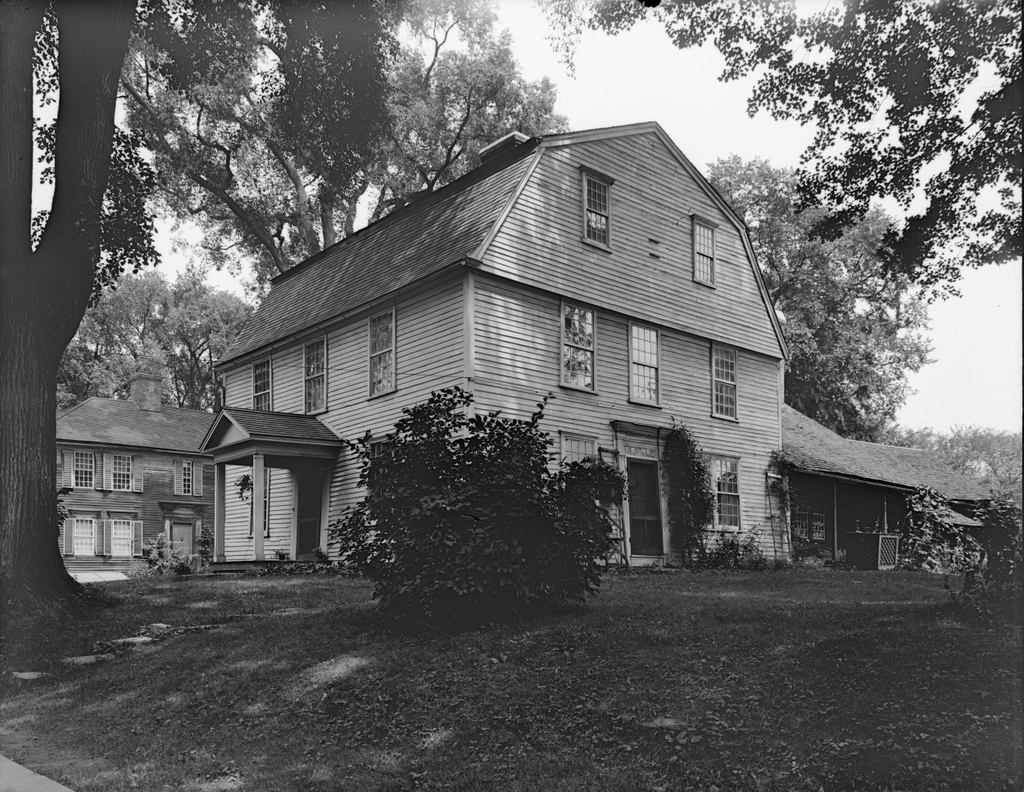
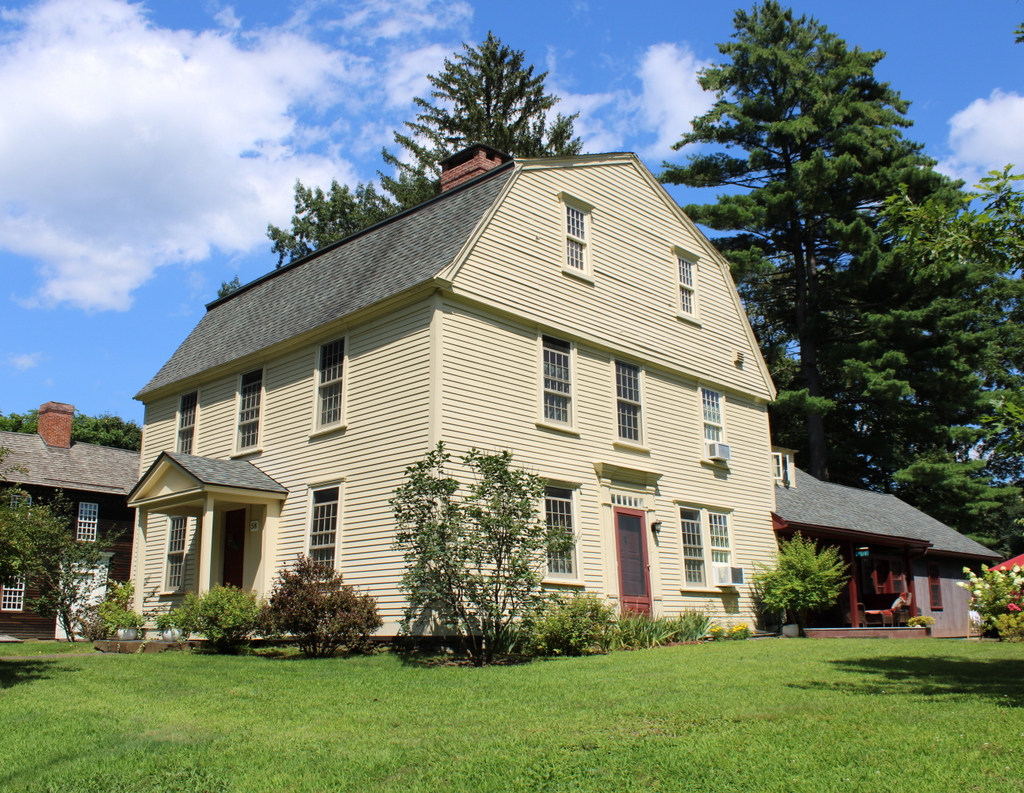
The house at the corner of Longmeadow and Emerson Streets in Longmeadow, Massachusetts, on September 12, 1917. Image courtesy of the Longmeadow Historical Society, Paesiello Emerson Collection.
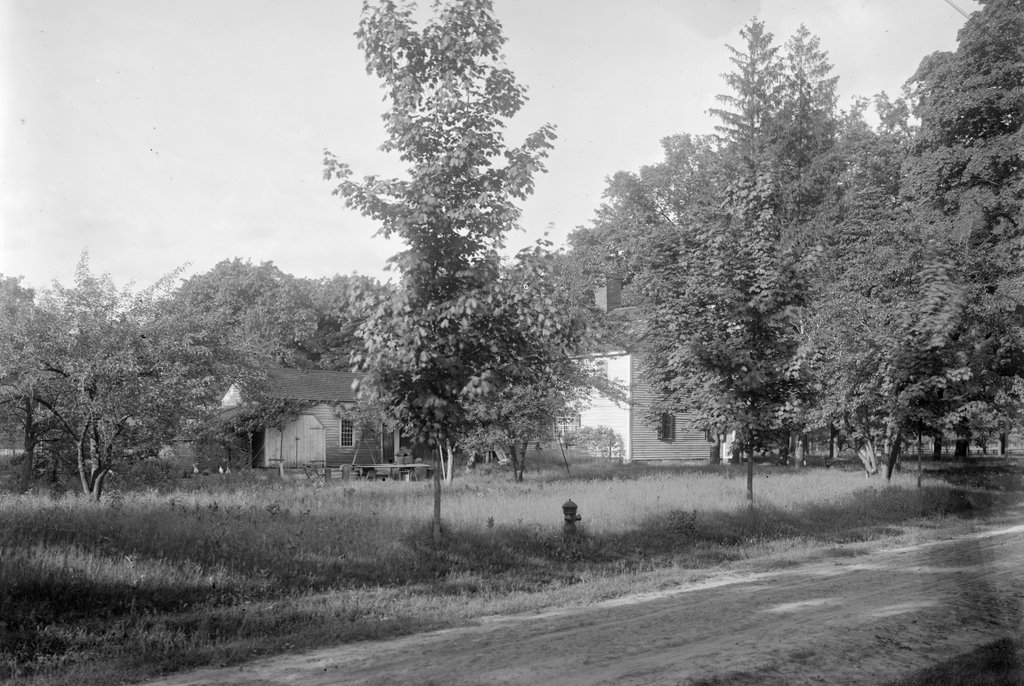

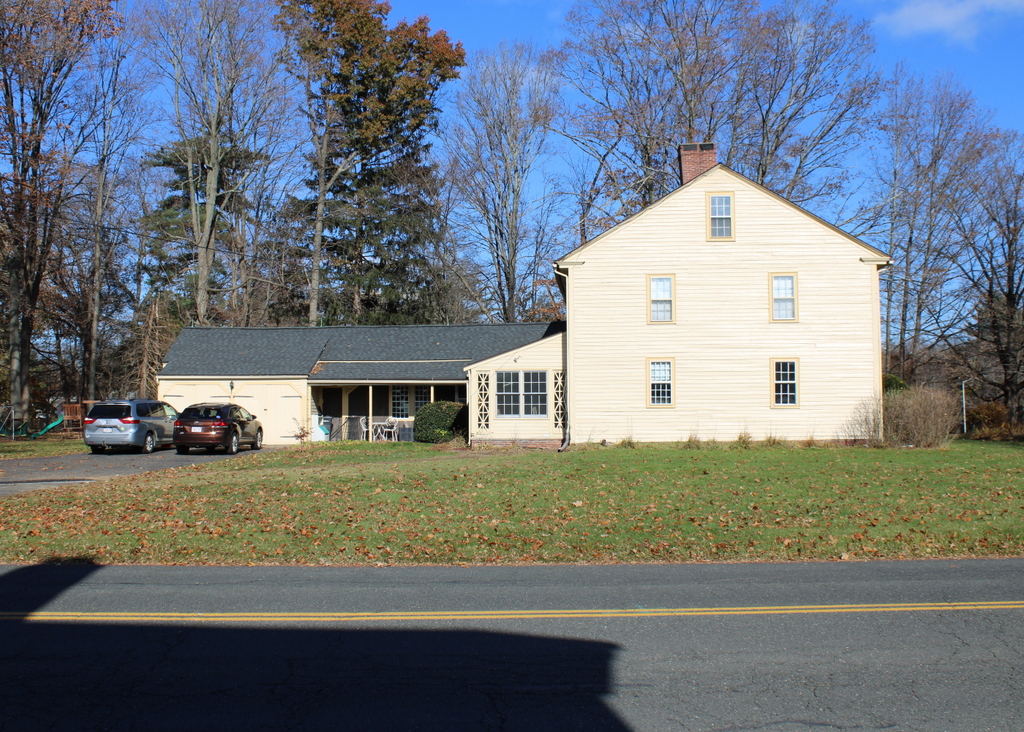
The house in 2023:
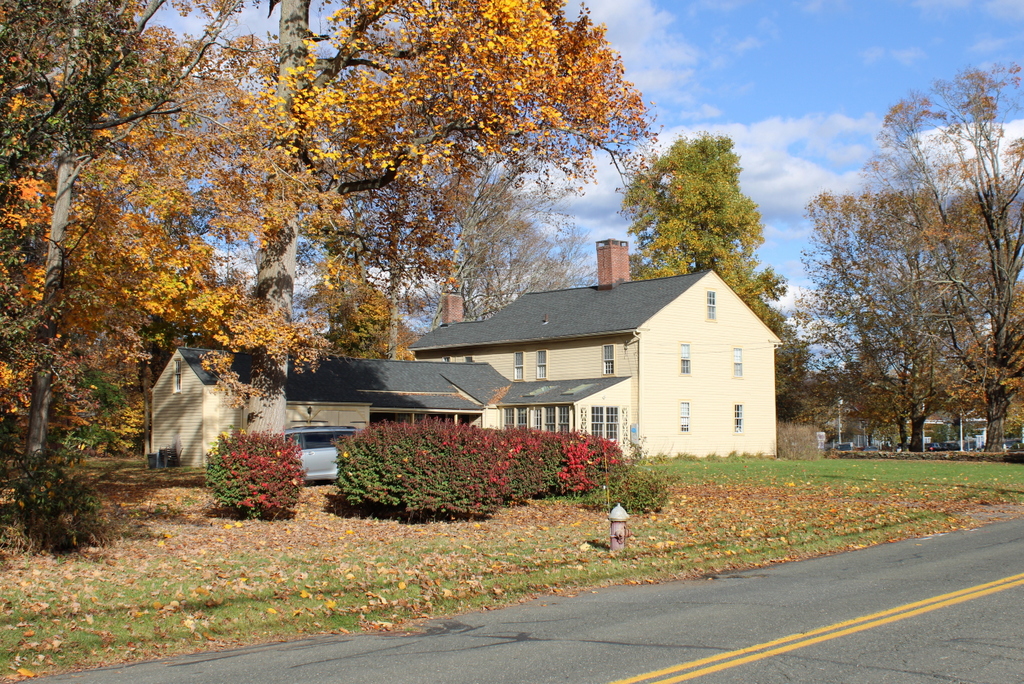

This house has been featured in previous posts, and there are many early 20th century images of it thanks to Paesiello Emerson, an amateur photographer who lived here during that period. As explained in more detail in an earlier post, the house is believed to have been built around 1760 as the home of Josiah and Experience Cooley. An earlier house, belonging to Josiah’s father Eliakim, had stood here on this same spot earlier in the 18th century, and it is possible that the current house may have been built in part on the foundation of Eliakim’s house.
These two photos show the view of the back of the house from the southwest, on what is now Emerson Road. From this angle, the house would have looked very different when it was initially constructed. It was built as a saltbox, with a second floor on the front part of the house and a long sloping roof here on the back of the house. However, when Josiah and Experience’s granddaughter Lucy Colton inherited the house in the late 1820s, she modernized and expanded the house.
Some of this work included raising the roof to create a full second story, along with additions on the north and west sides of the house. The two-story northern addition, which is visible in the distance on the far side of the house, included living space for Lucy’s son Luther Woolworth Colton and his newlywed wife Abigail. The western addition, shown on the left side of these photos, was one story in height, and it appears to have been used for storage and workshop space, rather than as living space
Aside from these structural changes, Lucy also made some interior and exterior design changes, in keeping with early 19th century trends. On the exterior, this included removing the original 12-over-12 windows from the front of the house and replacing them with new 6-over-6 windows. However, rather than discarding the old windows, they were installed here on the back part of the house and in the back addition, likely because they would not be as visible from the street.
The house would remain in the Cooley-Colton family for several more decades, but in 1869 Lucy’s son Josiah Cooley Colton sold the house and 20 acres of land to Bradford W. Palmer for $4,500. The Palmer family, however, would only stay here for a few years before selling it to William G. Emerson, a carpenter who was originally from eastern Massachusetts. His family included his wife Lovina and their children William, Annie, and Henry. The elder William died in 1887, Lovina died in 1897, and at some point the younger William moved into a house of his own in Longmeadow, but Annie and Henry would live here for their entire lives.
Neither Annie nor Henry ever married, but in 1907 they were joined here by their older half brother Paesiello Emerson. He was a widower in his mid-70s, and he had worked for much of his life as a boot maker. However, when he was in his 70s he took up photography as a hobby. He tended to prefer photographing landscapes and old buildings, and he captured several thousand images, including many here in Longmeadow. He continued his photography into his 90s, creating a valuable photographic archive of the town’s early 20th century development.
Paesiello Emerson died here in the house in 1927 at the age of 95. At some point in the 1920s, William Emerson also returned to live here, and he died in the house in 1930 at the age of 81. The two younger siblings, Annie and Henry, remained here until their deaths in 1941 and 1943, at the age of 81 and 77 respectively. Henry was a farmer who grew raspberries and asparagus here, along with raising poultry. Annie was a teacher, but she was also the town historian. She conducted extensive research on the historic homes in Longmeadow, including her own, and much of the information about this house is based on her notes.
The house was sold by the Emerson heirs after Henry’s death in 1943, and subsequent owners did some restoration work as well as modernization of the house. Here on the back part of the house, this included adding an enclosed porch to the back of the house and adding an open porch to the back addition. The garage was also extended outward by a few feet to accommodate cars, and a second garage door was added. Other changes, which are hard to notice from this particular angle, included removing the “coffin door” from the south side of the house, and adding another second-story window to the back of the house. The latter was evidently done in the late 1940s, when two new bathrooms were installed in the back part of the second floor.
Overall, though, the appearance of the house is not drastically different from its appearance in 1917 when Paesiello Emerson took the top photo. Aside from the porches and the small addition to the garage, the overall form of the house has not changed. It retains its chimneys, including the large central chimney, and most of the windows appear to either be original or, in the case of the 6-over-6 windows, date to the late 1820s renovation. Many of the 12-over-12 windows can still be found in the back part of the house, and are likely the same ones that had once been installed on the front part of the house in the mid-1700s.