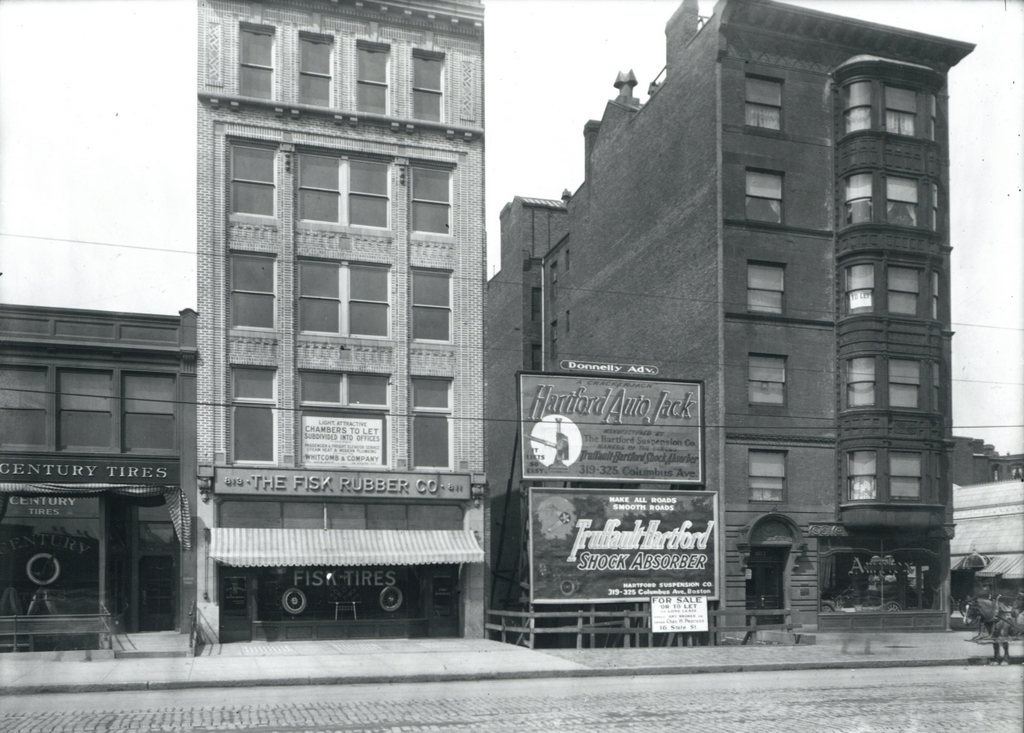
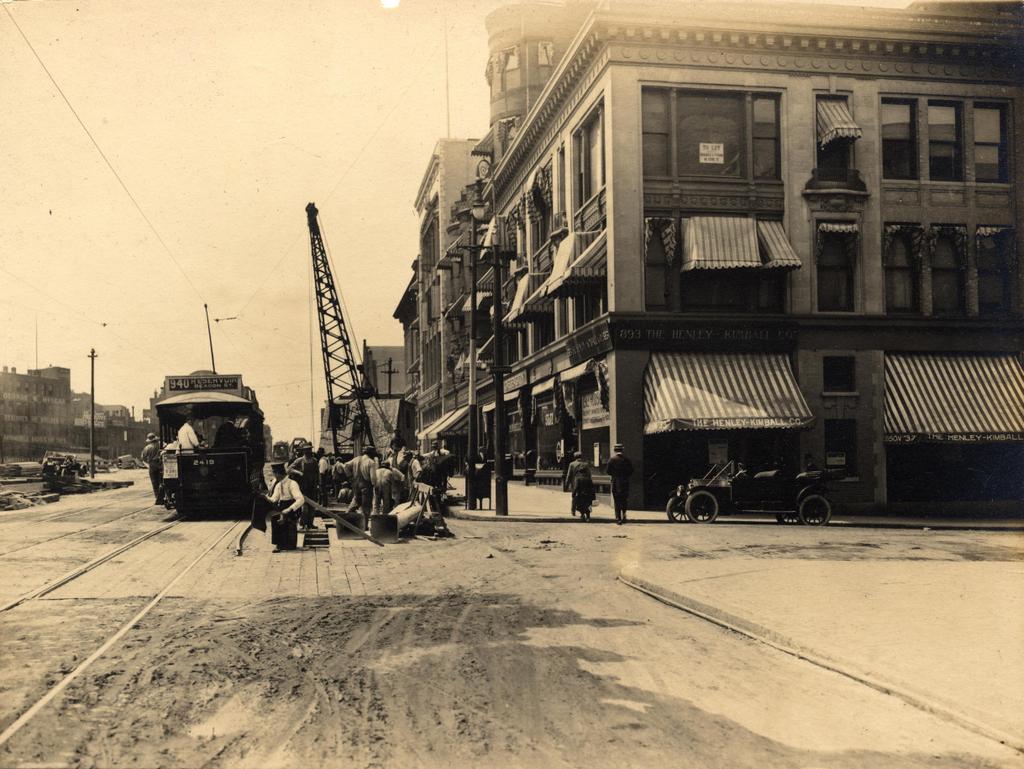
Several buildings on the north side of Boylston Street just west of Fairfield Street, on April 5, 1912.
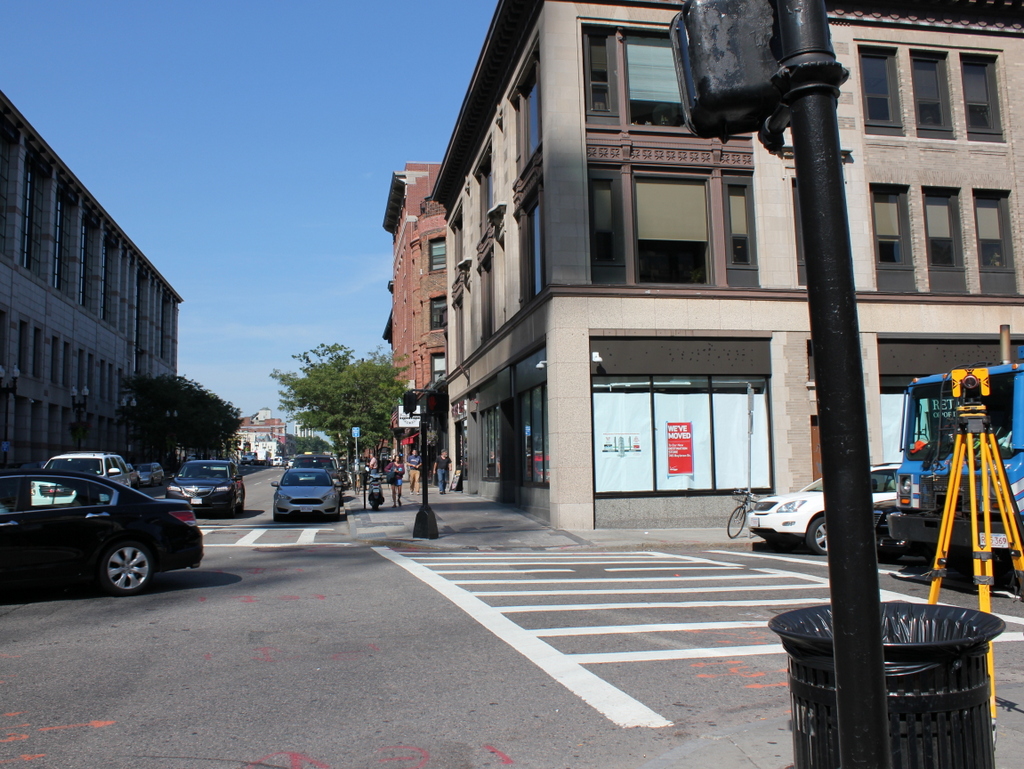
The scene in 2015:
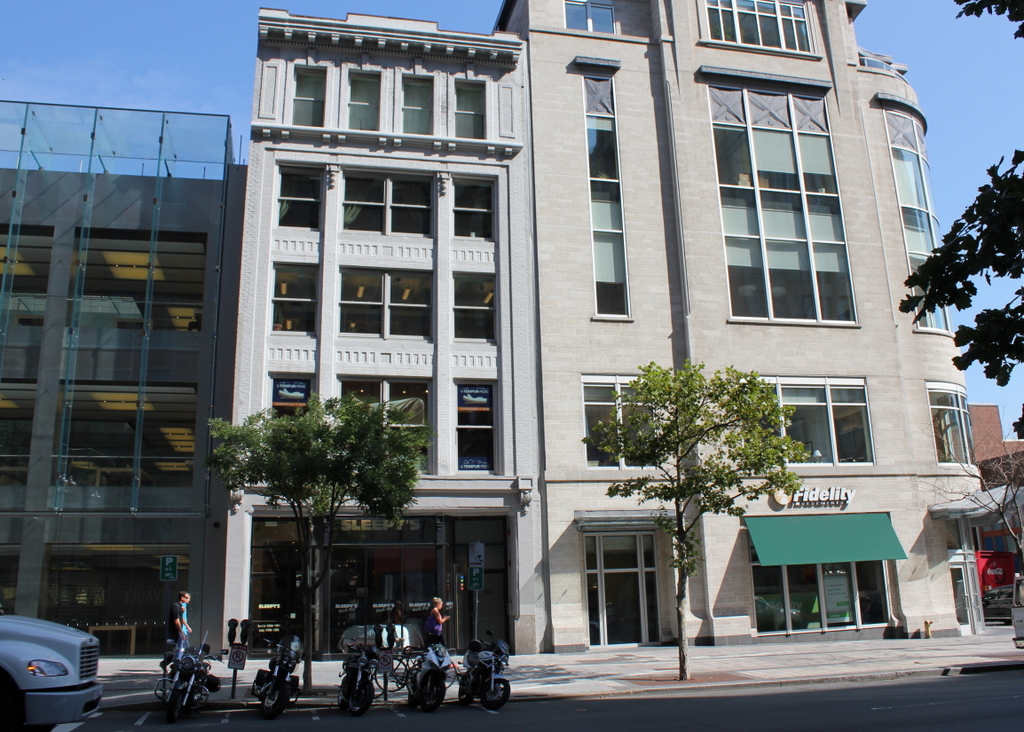

A few important things were happening in early April, 1912, when the first photo was taken. In England, workers had just put the finishing touches on the Titanic, and the ship’s first (and only) departure was less than a week away. Much closer to this scene, workers were putting the finishing touches on a far less auspicious, but as it turned out much longer-lived structure, Fenway Park. Here along Boylston Street, engineers were preparing to begin work on a subway tunnel that would run from the Public Garden to Kenmore Square. This photo, one of many taken in the spring of 1912, was likely part of the preliminary surveys of the street.
When the first photo was taken, cars were just beginning to see widespread use, and there were many businesses along Boylston Street that catered to these new motorists. Both of the buildings on the left housed tire companies: Century Tires on the far left and The Fisk Rubber Company in the five-story white building. Fisk, which was headquartered in Chicopee, Massachusetts, was one of the country’s leading tire companies in the early 20th century. To the right of that building, the 1912 photo shows billboards for auto jacks and shock absorbers, and the building at the corner of Fairfield Street appears to have had a car dealership in the ground-floor storefront, although I can’t read the name.
Today, only the former Fisk building still stands. It was built in 1910, but appears to have still needed tenants by 1912, as the first photo shows a large “Chambers to Let” sign in the window. It is now home to a Sleepy’s store, but aside from that the exterior has not changed much in over a century. The Century Tires building is gone, though, and an Apple Store now occupies its spot. On the far right, the building at the corner was probably the oldest one in the first photo, but it was gone by 1960, when a gas station was built there.