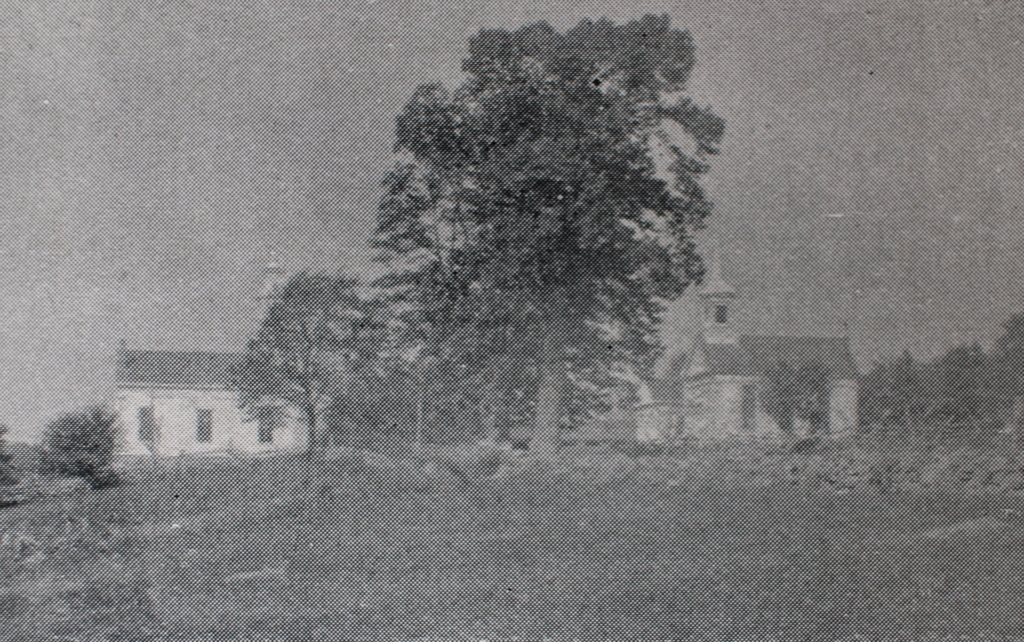
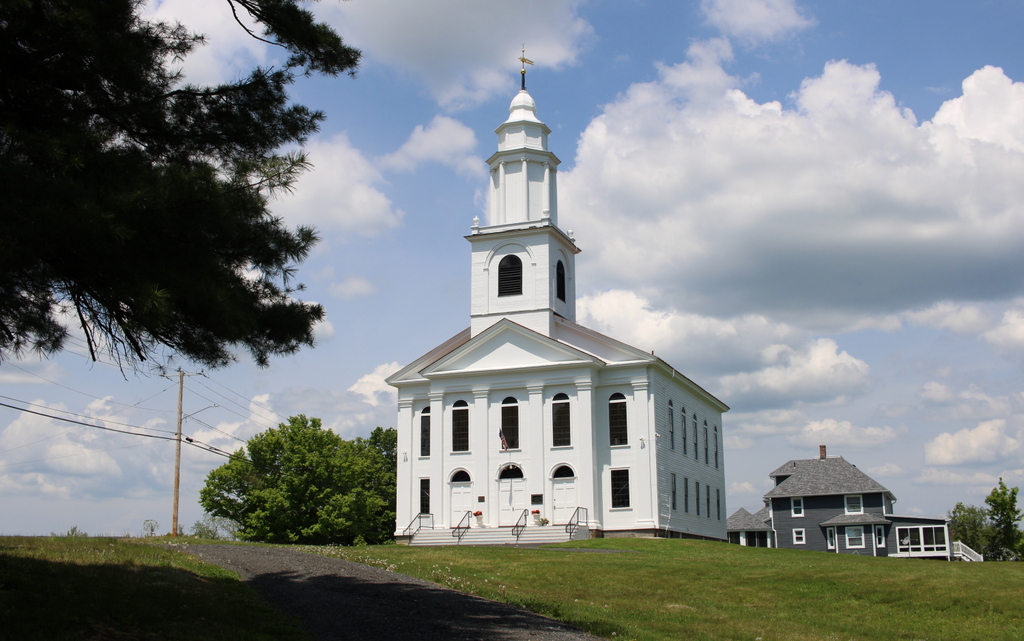
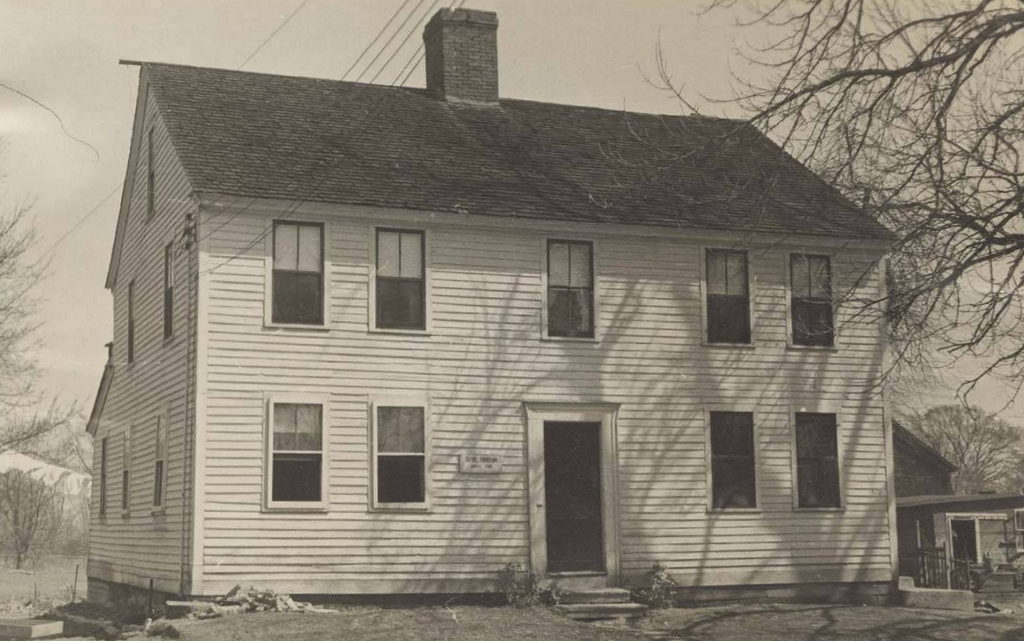
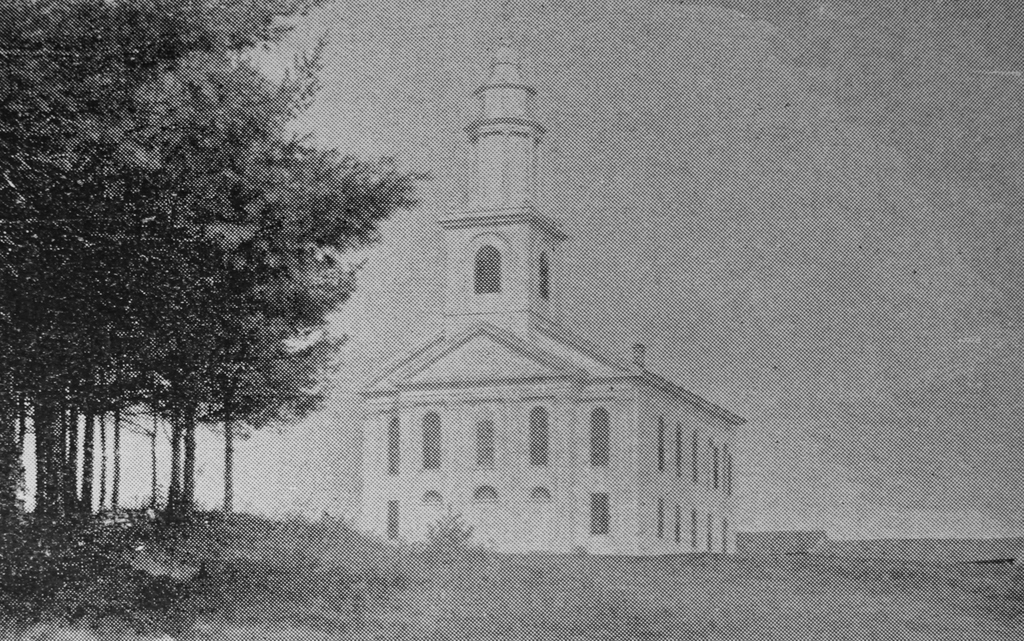The town center on Main Road in Montgomery, Massachusetts, around 1892. Image from Picturesque Hampden (1892).
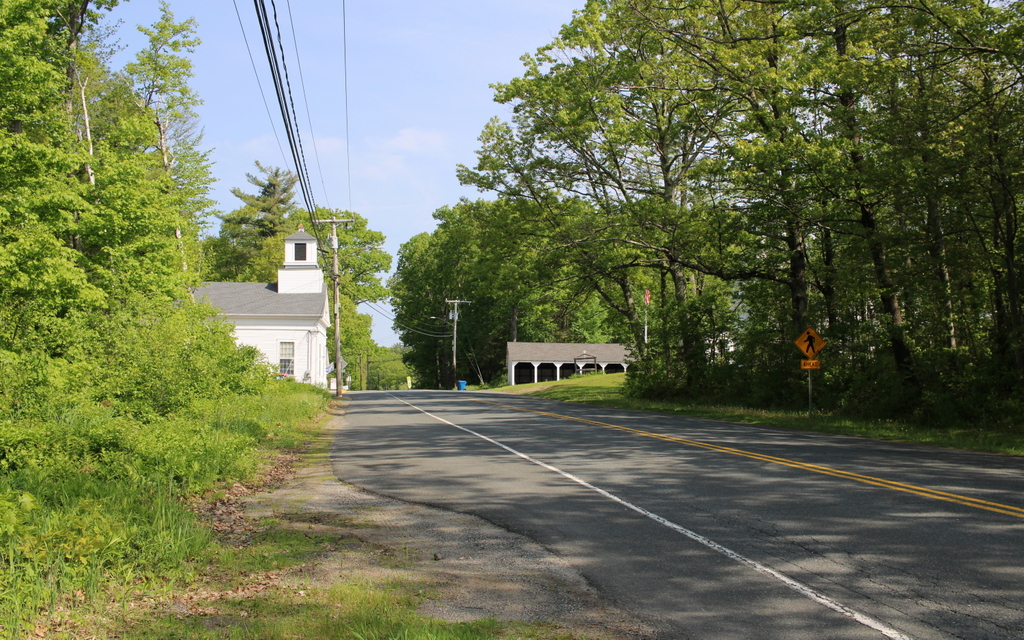
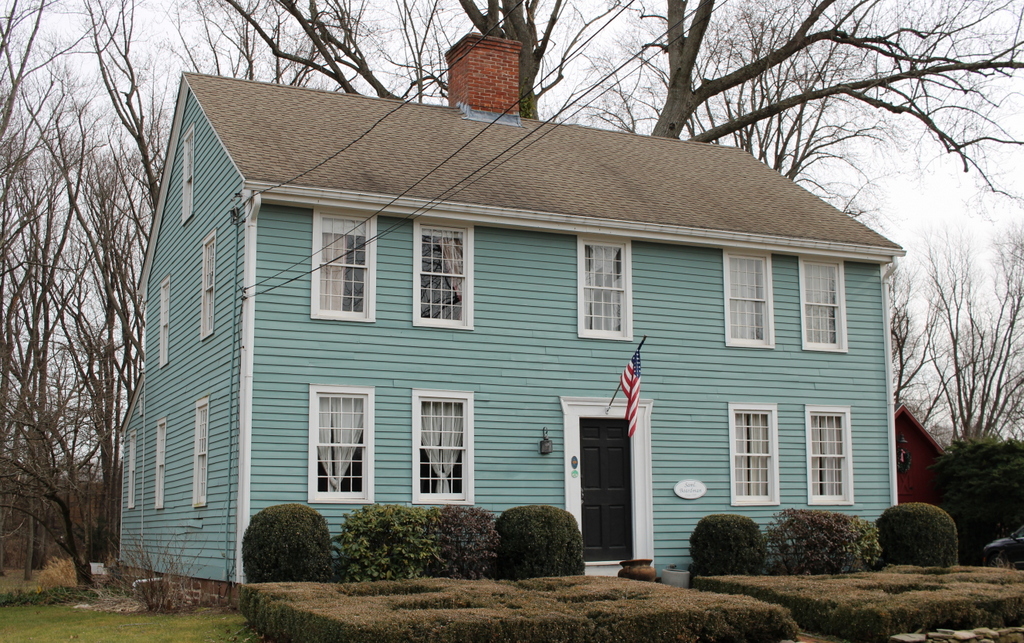
The scene in 2024:
Throughout its history, Montgomery has been one of the smallest towns in Hampden County, with a population that has never even reached 900 at any point. It is nestled in the hills to the northwest of Westfield, and it was first settled b European colonists around the 1760s, before becoming an incorporated town in 1780. Its population fluctuated during the 19th century, reaching as high as 740 by 1840, before plummeting to 393 a decade later. It steadily diminished in population over the next century, reaching as low as 141 in 1930 before seeing steady population growth during the second half of the 20th century. Nonetheless, the town remains small and rural, as shown in these two photos.
This site is usually referred to as the town center, mainly because it is the site of the meeting house and the town hall. However, this was never a true village or population center, as historically the town’s development consisted primarily of farms that were scattered across the landscape. But, because this spot is near the geographic center of the town, it was a logical place to gather for church services and town meetings
The town center consists of three Greek Revival-style buildings, as shown in the top photo. On the right side is the Montgomery Community Church, which appears to have been built in 1848 on the site of an earlier 1797 meeting house. The property had been owned by the town until 1848, when a new town hall was built immediately to the west of it, as shown in the distance to the left of the church in the top photo. The old meeting house was then sold to the town’s Congregational church, which subsequently built the current Greek Revival structure. A year later, in 1849, the town’s Methodist society constructed their own church building across the street, as shown on the left side of the scene.
Despite this late 1840s construction boom here in the town center, the town’s population was by this point on a downward trend. The 1850 census showed 393 inhabitants, and it would continue to decline for many decades afterwards. Both churches struggled to sustain themselves, with the Methodists only holding services in the summer and fall. The Congregational church eventually closed in the late 1860s, and the building was later used by a Second Adventist group.
By the time the top photo was taken around the early 1890s, the town’s population had dropped to under 300 residents. All three of the buildings from the 1840s were still standing here, and they were joined by a carriage shed, which was built around 1890 in the distant center of the scene.
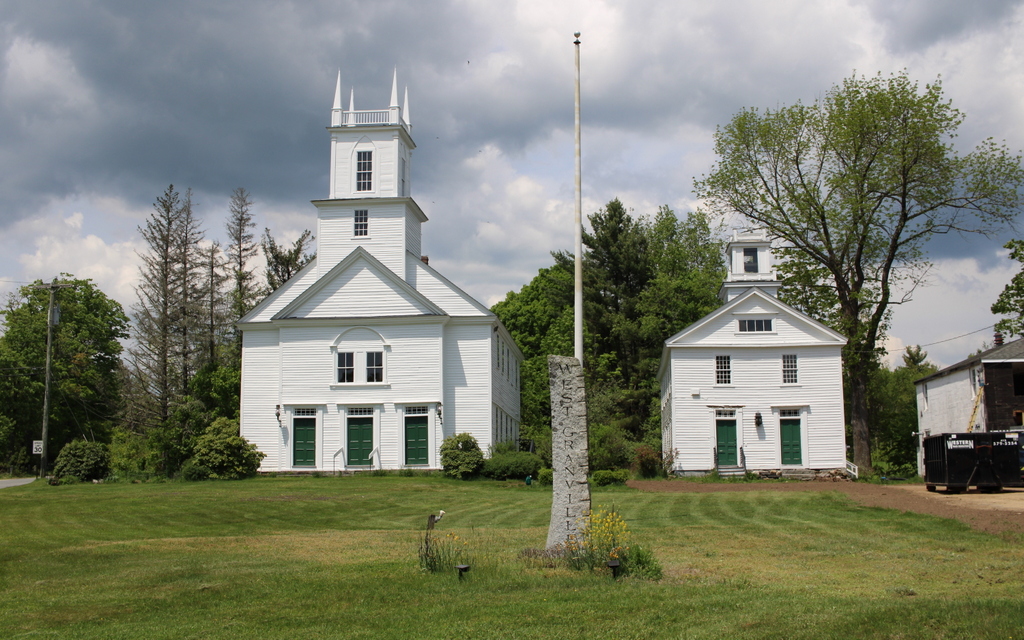
Today, more than 130 years after the top photo was taken, not much has changed in this scene. The landscape is more forested, making it difficult to get the exact same angle as the top photo. The trees also hide the buildings on the right, but they are still standing, although their uses have changed over time. On the left side, the former Methodist church is now the town hall, and it has been expanded to include space for the town offices, library, and senior center. On the right side, the old town hall is now the historical society, and the former congregational church is now the Montgomery Community Church. The late 19th century carriage shed is also still standing, and collectively these buildings stand as a well-preserved example of a rural town center.