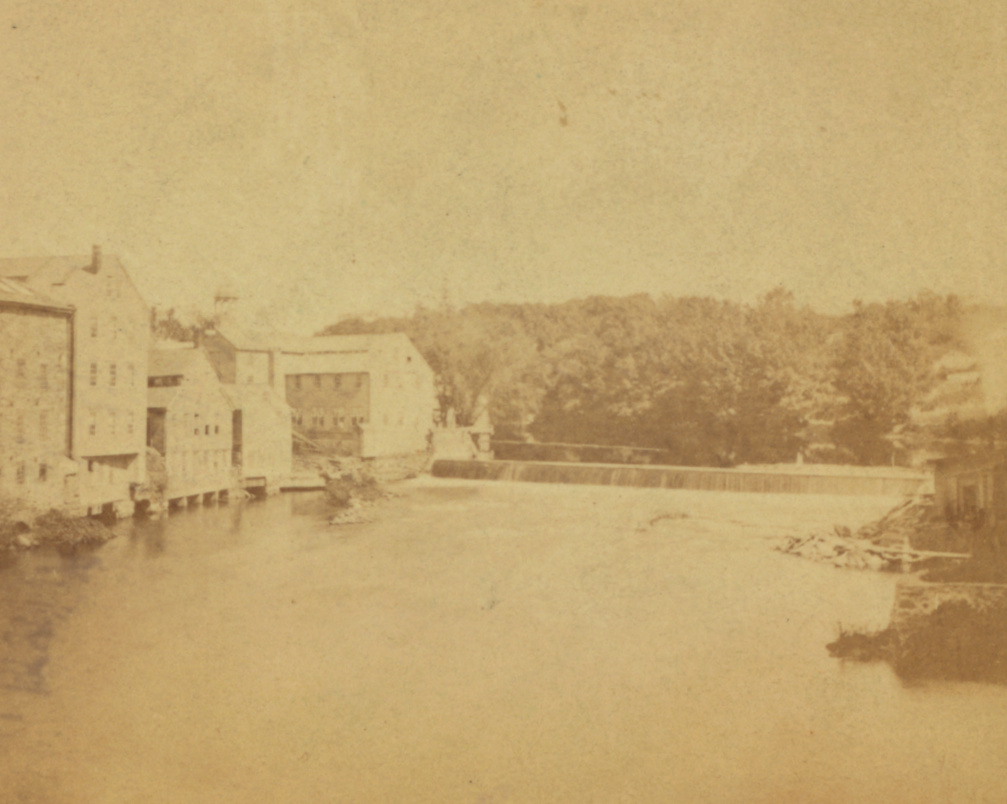
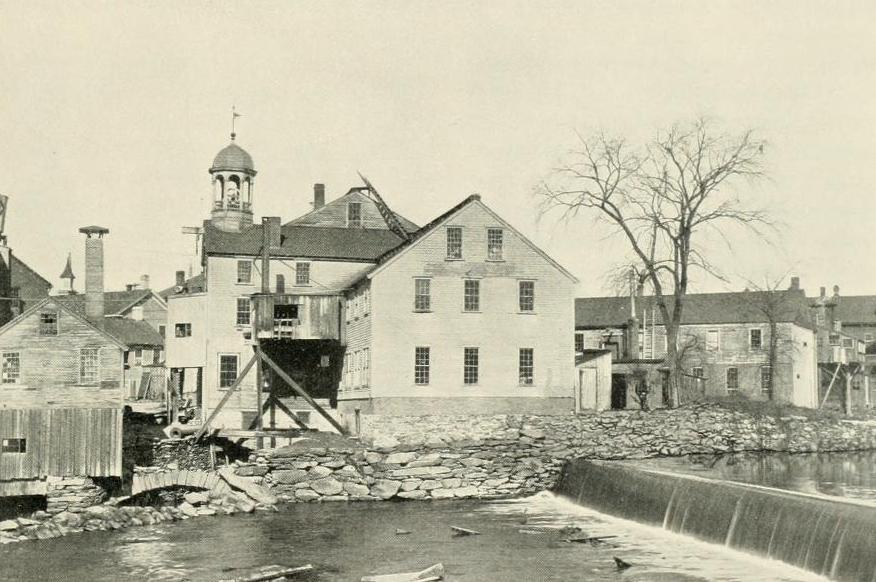
A view of Slater Mill on the Blackstone River in Pawtucket, around 1897. Image from An Illustrated History of Pawtucket, Central Falls, and Vicinity (1897).

The scene in 2021:
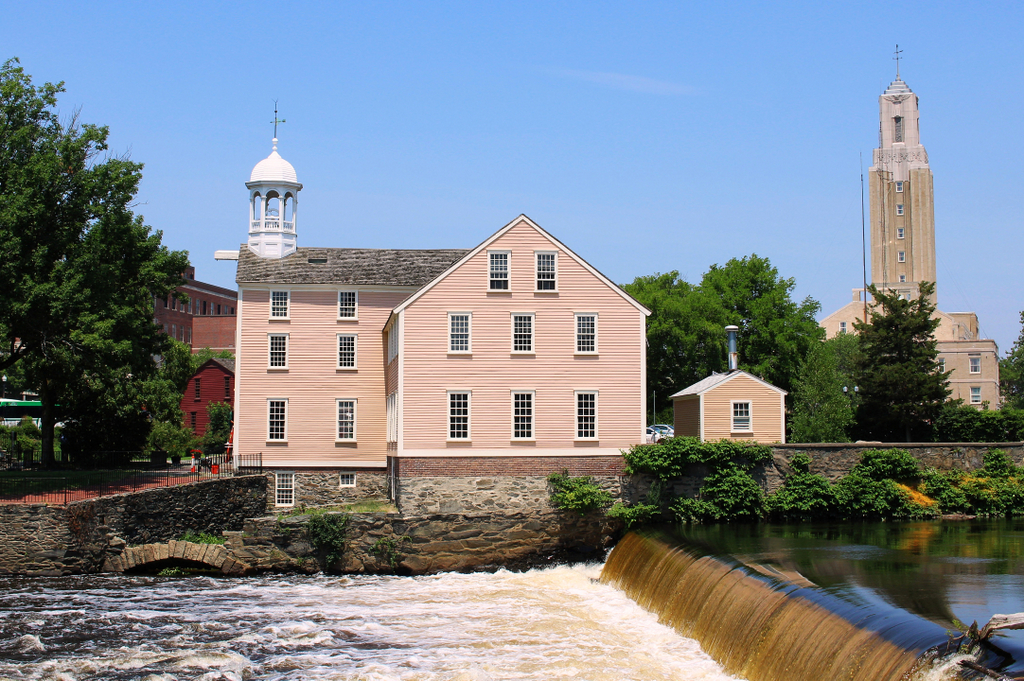

This mill, located on the west side of the Blackstone River in Pawtucket, is an important landmark in the early history of the Industrial Revolution in America. The building has undergone many changes and expansions over the years, but the oldest portion—located in the central part of the building—was completed in 1793 by Samuel Slater, a British emigrant who is credited with bringing the Industrial Revolution to the United States.
The Industrial Revolution had started during the second half of the 18th century in Britain, where a series of inventors had developed ways of harnessing water power to spin thread and weave textiles. However, Britain closely guarded the details of these processes, in order to prevent foreign competition. This was also the case for the American colonies, where Britain discouraged manufacturing in order ensure that colonists purchased manufactured goods from the home country.
After gaining independence, the United States still found itself largely dependent upon British manufacturers, but many American entrepreneurs were interested in bringing these industrial innovations across the Atlantic. This was particularly true here in New England, where the region’s many fast-flowing rivers made it an ideal place for water-powered industry.
Among these early industrialists was Moses Brown, a member of a prominent family in Providence. His family had become wealthy during the colonial era as merchants and slave traders. In particular, his brother John was a notorious slave trader who continued the practice even after the federal government prohibited American ships from being used in the international slave trade. By contrast, Moses became a staunch abolitionist. He freed his own slaves, converted to Quakerism, and spoke out against both slavery and the slave trade. And, while his brother was still bringing enslaved people to America, Moses was looking to apply the new British textile manufacturing processes here in Rhode Island.
To accomplish this, in 1789 Moses established the firm of Almy & Brown, which was comprised of William Almy and Brown’s cousin, Smith Brown. Their goal was to make yarn, but they had poor-quality machinery and only limited knowledge about the manufacturing process, so it became clear that they needed someone who was familiar with the British system.
As it turned out, that person was 21-year-old Samuel Slater, who arrived in New York from England on November 18, 1789. He had been an apprentice at a textile mill in England, where he became familiar with the machinery that had been developed by inventor Richard Arkwright. In addition, he learned about the management side of the textile industry. So, by the time his apprenticeship term had ended, he not only knew how to build and maintain the machinery itself, but also how to operate a profitable factory.
However, by this point Richard Arkwright’s patents had expired, and Slater apparently believed that Britain would become too oversaturated with textile businesses. America, on the other hand, seemed to offer more potential for an aspiring young industrialist, and he knew that there were plenty of American entrepreneurs who were looking for someone with his knowledge and experience. With this in mind, he left England in September 1789, just two months after the end of his apprenticeship. Because of strict British laws against exporting machinery plans or drawings, Slater did not carry any with him, and he is said to have disguised himself as a farm laborer.
Upon arriving in New York, he soon heard of Moses Brown’s efforts to produce yarn, so he wrote to him on December 2, offering his services. Brown responded eight days later, and in his letter he explained the problem that his company faced:
We are destitute of a person acquainted with water-frame spinning; . . . As the frame we have is the first attempt of the kind that has been made in America, it is too imperfect to afford much encouragement;
He then went on to make his offer to Slater:
[W]e hardly know what to say to thee, but if thou thought thou couldst perfect and conduct them to profit, if thou wilt come and do it, thou shalt have all the profits made of them over and above the interest of the money they cost, and the wear and tear of them. We will find stock and be repaid in yarn, as we may agree, for six months. And this we do for the information thou can give, if fully acquainted with the business. After this, if we find the business profitable, we can enlarge it, or before, if sufficient proof of it be had on trial, and can make any further agreement that may appear best or agreeable on all sides.
These terms were acceptable to Slater, who traveled to Pawtucket in January 1790. However, once he arrived, he saw for himself the poor quality of the machinery, which was evidently worse than he had anticipated. Moses Brown would later tell Slater’s biographer, George S. White, that,
When Samuel saw the old machines, he felt down-hearted, with disappointment—and shook his head, and said ‘these will not do; they are good for nothing in their present condition, nor can they be made to answer.’
Slater then spent the next few months working on the machinery, with assistance from local craftsmen such as Sylvanus Brown and Slater’s future father-in-law, Oziel Wilkinson. They succeeded in constructing a water-powered spinning machine, and in April, Slater became a partner in the newly-established firm of Almy, Brown & Slater. A year later, Slater married Oziel Wilkinson’s daughter Hannah. She would go on to become an inventor in her own right, and in 1793 she became the first American woman to receive a patent when she developed a new way of making cotton sewing thread.
In the meantime, Slater’s machinery worked so well that the production of yarn soon outpaced the firm’s ability to sell it through their existing supply chains. However, once Slater and his partners began expanding into new markets, the original mill was unable to keep up with the increased demand. So, in the fall of 1791 the firm purchased this site here on the west side of the Blackstone River in Pawtucket, in order to construct a new mill. The wood-frame dam, shown here in the foreground of these two photos, was constructed in 1792, and the mill itself opened in 1793.
It was the first large-scale cotton mill in the United States, and it marked the beginning of an industry that would dominate the New England economy for more than a century. This building is still standing, in the center of these two photos, although it has been significantly expanded over the years. The original 1793 portion of the building was two stories high, and measured 40 feet long and 26 feet wide. It was built of wood, with a stone foundation, and it stood directly atop the Great Flume, which was built parallel to the river to provide water power for this mill and others further downstream.
Aside from his knowledge of textile machinery, Slater was also familiar with the management and operation of British mills, and he brought many of these innovations to America. Among these was the idea of continuous production, rather than the earlier practice of only making yarn to fill specific orders. Slater also took advantage of economies of scale, with his mill specializing in a relatively small number of products. More troublingly, though, Slater also copied the British practice of employing child laborers, and his workforce typically consisted of children between the ages of 7 and 12. However, unlike the British system, which tended to exploit orphans and other destitute children, Slater sought to develop factory villages that employed entire families. This approach, which came to be known as the Rhode Island System, involved having children produce yarn at the mill, and then have women weave the yarn into cloth at their homes.
By focusing on relatively small-scale industrial production of the yarn, along with having a decentralized weaving process, Slater’s Rhode Island System was in contrast to the subsequent Waltham-Lowell System, which would come to dominate New England textile production during the 19th century. However, despite this comparatively limited scope of manufacturing, Slater’s mill was an important first step in transitioning the new nation into a major industrial center.
Although Slater’s mill here in Pawtucket was a success, he often clashed with the other two partners in the firm, who handled the financial side of the business. After just a few years, he established his own company in partnership with his in-laws. This new mill was constructed in 1799, directly across the Blackstone River from the original mill, near the spot where these two photos were taken. At the time, the river formed the border between Massachusetts and Rhode Island, so the new mill was located in the town of Rehoboth, Massachusetts. Later in the 19th century, though, the state border would shift a few miles to the east, making the east side of the river part of Pawtucket, Rhode Island.
In the meantime, Slater retained his share of the original mill, which underwent several expansions in the early 19th century. The first of these came in 1801, when the building was expanded by 57 feet to the north, more than doubling its length. Then, in the late 1810s it was extended closer to the river, with a 40-foot addition here on the south side, followed by a stair tower and cupola on the west side around 1830.
In addition to this mill, Slater and his family opened a number of other mills in Rhode Island, Massachusetts, and Connecticut. Here in Pawtucket, he continued his partnership with Almy and Brown until 1829, when an economic downturn forced him to sell his share in the original mill, along with several of his other mills, in order to repay his debts. Despite this setback, he was able to recover financially, and upon his death in 1835 he left an estate valued at over $1 million.
Slater’s former firm here in Pawtucket subsequently became Almy & Jenkins, and the old building was later occupied by several other partnerships during the 19th century. The building itself also changed, with the construction of at least three more additions during this time. The surrounding area likewise continued to be transformed, and the waterfront of the Blackstone River became lined with other mills.
Over time, the mill came to be used by a variety of tenants. By the late 19th century, these included a bicycle shop and a manufacturer of jewelers’ tools. Alongside these uses, the building continued to produce cotton until 1895, just over a century after Samuel Slater and his partners launched the American Industrial Revolution here. The first photo was taken around this time, showing the heavily-altered mill surrounded by an assorted mix of smaller industrial buildings along the river. By this point it had become a much-photographed local landmark, but it was still in active commercial use, and it was starting to show its age.
Many of the surrounding buildings were demolished at the turn of the 20th century, but the mill remained standing. It was ultimately acquired by the Old Slater Mill Association in 1923, with the goal of preserving the building and restoring it to its historic appearance. Over the next few years, the later additions to the mill were removed, leaving only the original 1793 section and the early 19th century wings. The resulting structure, which still stands here today, thus approximates how the mill would have looked at the time of Samuel Slater’s death in 1835.
In keeping with early to mid-20th century historic preservation trends, nearly all of the neighboring buildings were subsequently demolished. The intent was to make the mill the centerpiece of a riverfront park, but it also took away the historic character of its surroundings. Not even Samuel Slater’s house was spared in the process, although Oziel Wilkinson’s three-story stone mill was preserved. Built in 1810, it stands just out of view on the left side of the present-day scene. However, this site did have one addition later in the 20th century, when Sylvanus Brown’s house was moved here from its original location about two miles away, to save it from demolition. It was in this house that Samuel Slater spent his first night upon arriving in Pawtucket, and it is visible in the present-day scene, just to the left of the mill.
Overall, despite the many changes here, the mill and dam are still recognizable from the first photo. However, there is nothing else left from the photo; to the left of the mill is the park, and to the right of it is a parking lot. Further in the distance, on the other side of the mill, are still more parking lots, and on the right side of the scene is the tower of Pawtucket City Hall, an Art Deco building that was completed in 1936.
The mill was designated as a National Historic Landmark in 1966, and it is now part of the Blackstone River Valley National Historical Park, which focuses on the industrial history of the Blackstone River. Here in Pawtucket, the park includes the two mills and the Sylvanus Brown house, along with the original dam and associated water structures, including the Great Flume. The Slater Mill is open to the public seasonally from Thursdays through Sundays, and park rangers conduct free guided tours of the building.