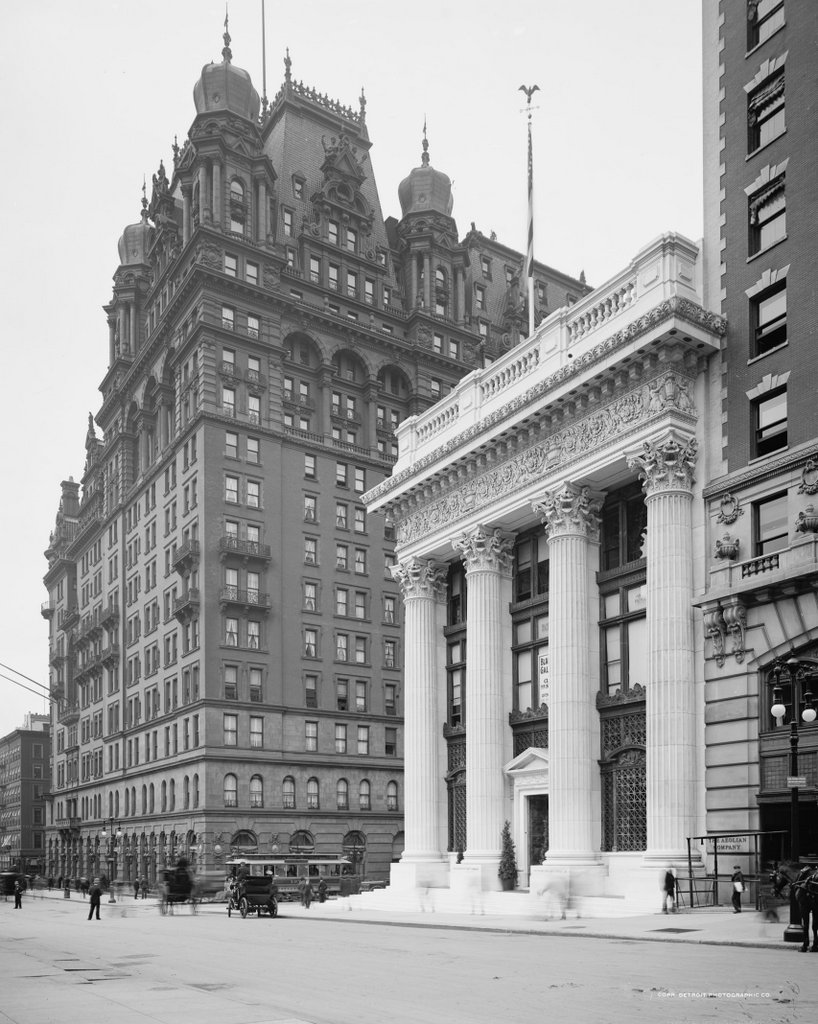
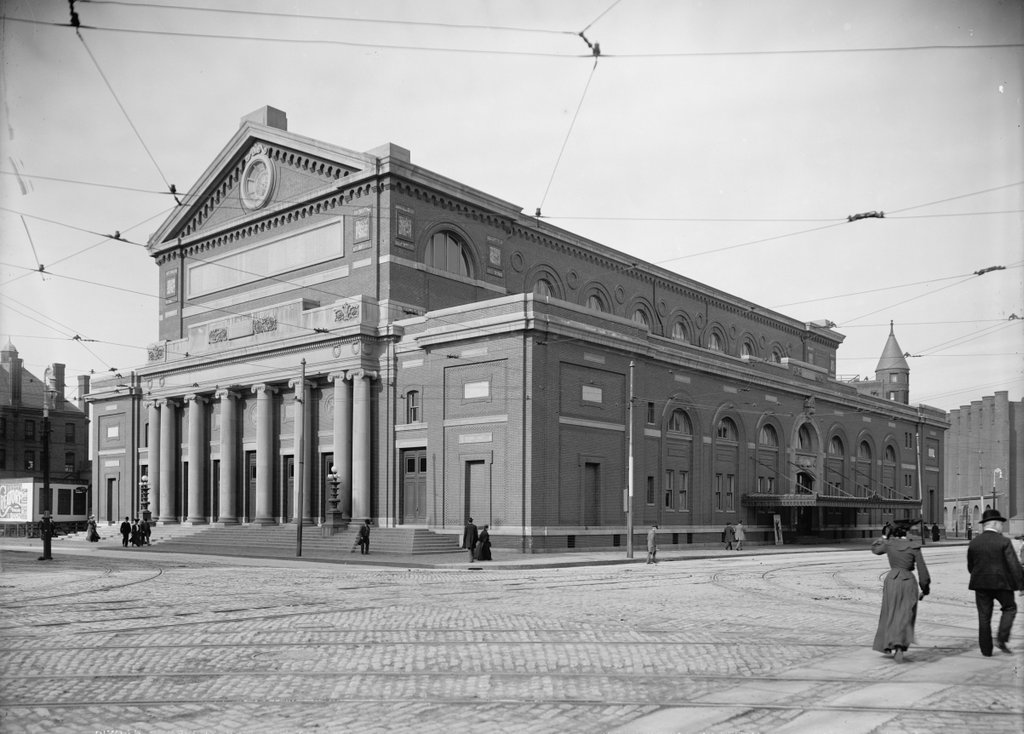
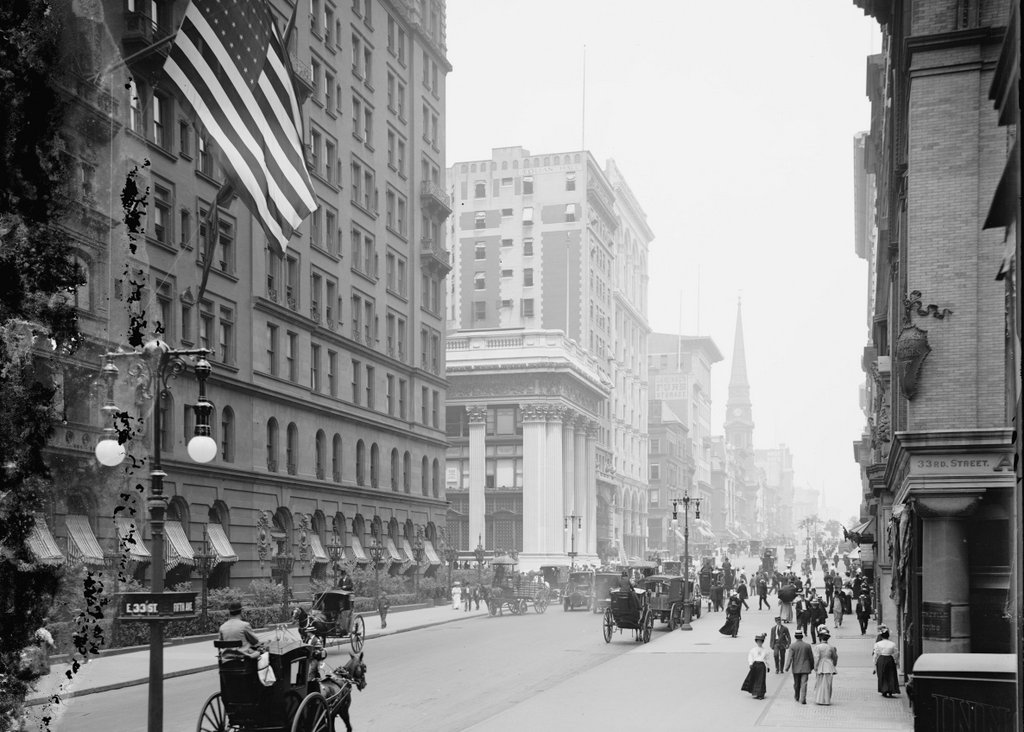
Looking north on Fifth Avenue from 33rd Street, around 1905-1920. Image courtesy of the Library of Congress, Detroit Publishing Company Collection.

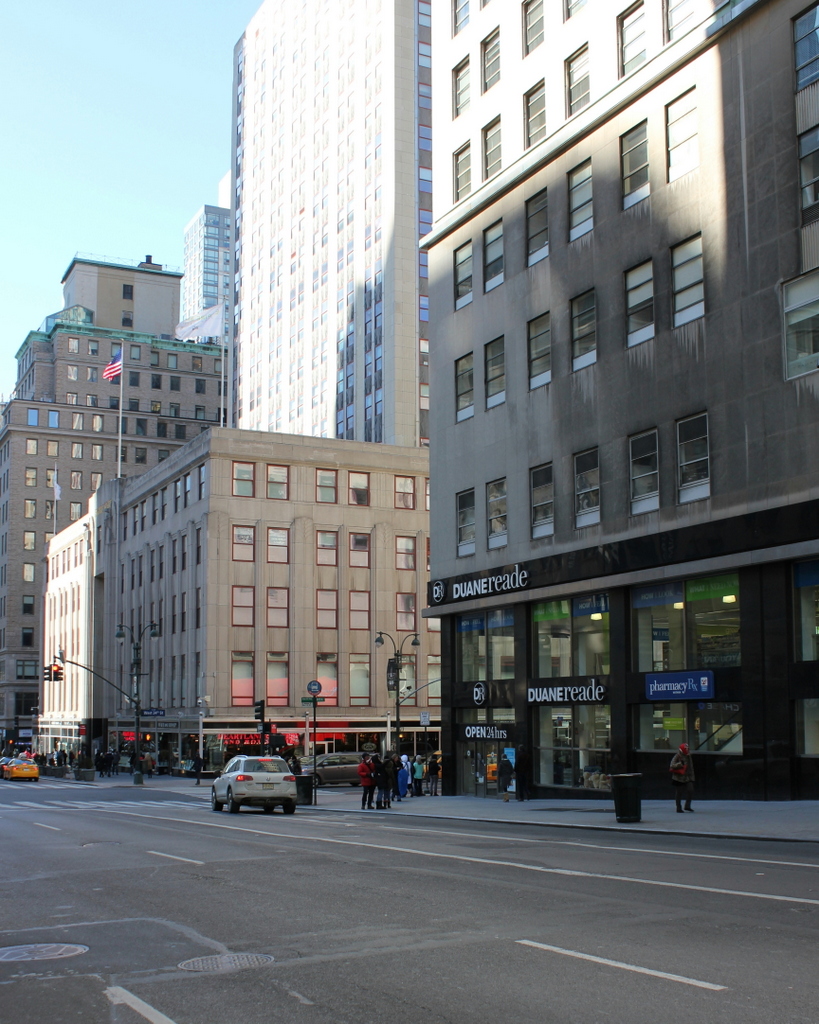
Fifth Avenue in 2016:
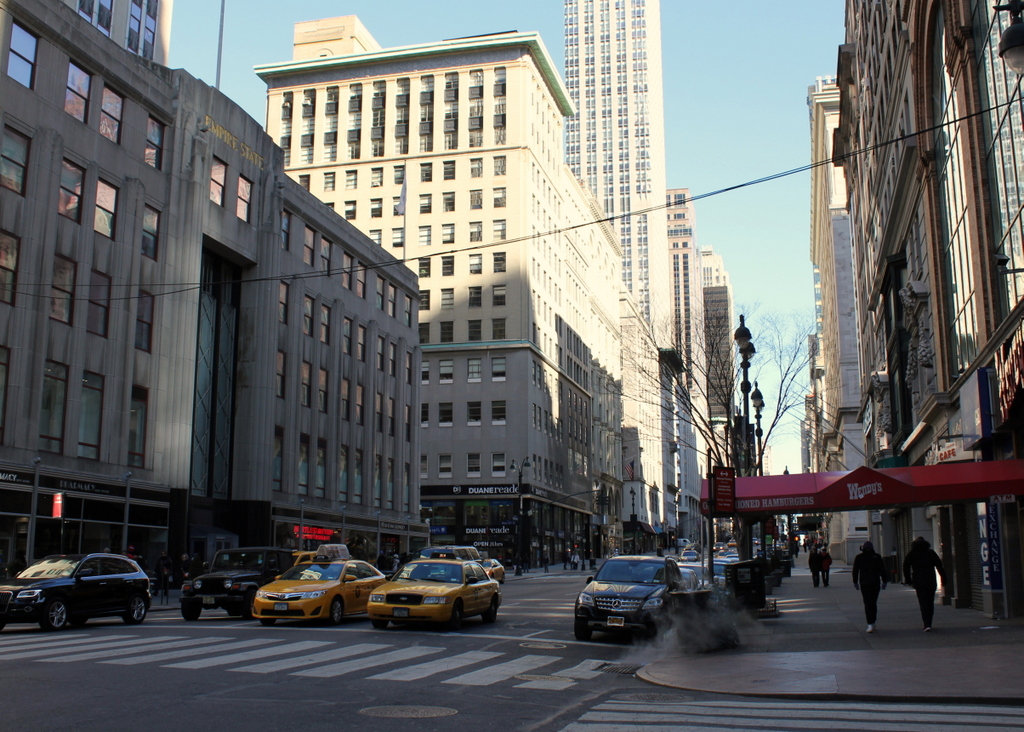

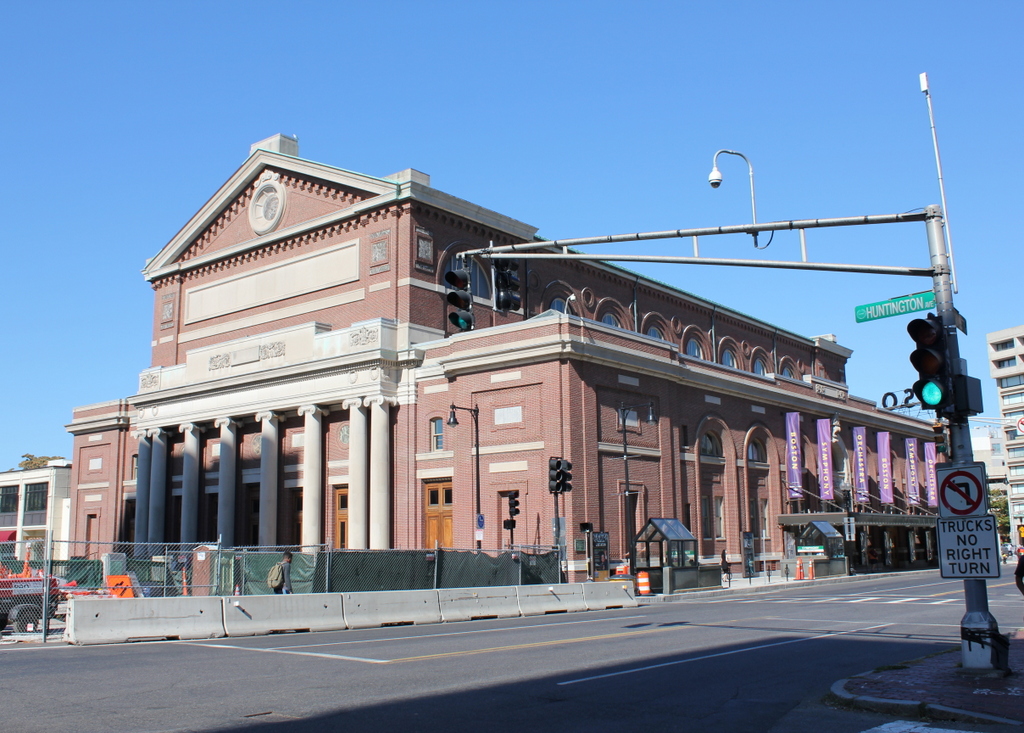
Notice the extremely wide sidewalks in the first photo. Fifth Avenue was originally designed to have a 40-foot roadway with 30-foot sidewalks on either side, but this changed in 1908, shortly after the first photo was taken. To accommodate the growing automobile traffic on the street, it was widened to 55 feet, and the wide sidewalks were trimmed down. Despite over a century of change, though, there are a remarkable number of buildings that have survived from the first photo, especially on the left side. When the first photo was taken, this section of Fifth Avenue had just recently become a major commercial area, and as a result most of the buildings were new at the time.
Perhaps most surprising from the first photo is that the Knickerbocker Trust Company Building – the short building with columns in the center of the photo – is technically still standing, although it has long since been altered way beyond recognition. It was built in 1904 at the corner of Fifth Avenue and 34th Street as the headquarters of one of the nation’s largest banks, but soon after the bank inadvertently played a major role in causing the Panic of 1907. This banking crisis occurred around the time that the first photo was taken, after the Knickerbocker president, Charles T. Barney, attempted to corner the market in copper using the bank’s money. The plan failed, and in the days before FDIC-insured deposits, account holders rushed to the bank to withdraw their money as other banks announced that they would no longer accept checks from Knickerbocker accounts. Ultimately, the bank survived, although Barney was forced to resign and he committed suicide soon after. As for the building, it was significantly changed in 1921 with the addition of ten stories on top of it, and in 1958 the facade was altered to its current appearance, removing any exterior elements from the original structure.
Despite the number of surviving buildings from the first photo, there are several notable ones that have since been demolished. In the distance, at the corner of 37th Street, is the steeple of Brick Presbyterian Church, which was built in 1858 when this area was still largely residential, and it stood there until 1937. Probably the most famous building from the first photo, though, is the Waldorf-Astoria Hotel, on the left side in between 33rd and 34th Streets. This massive hotel is only partially visible in this view, and it stood here until 1929, when it was demolished to build the Empire State Building, which now stands on the site.