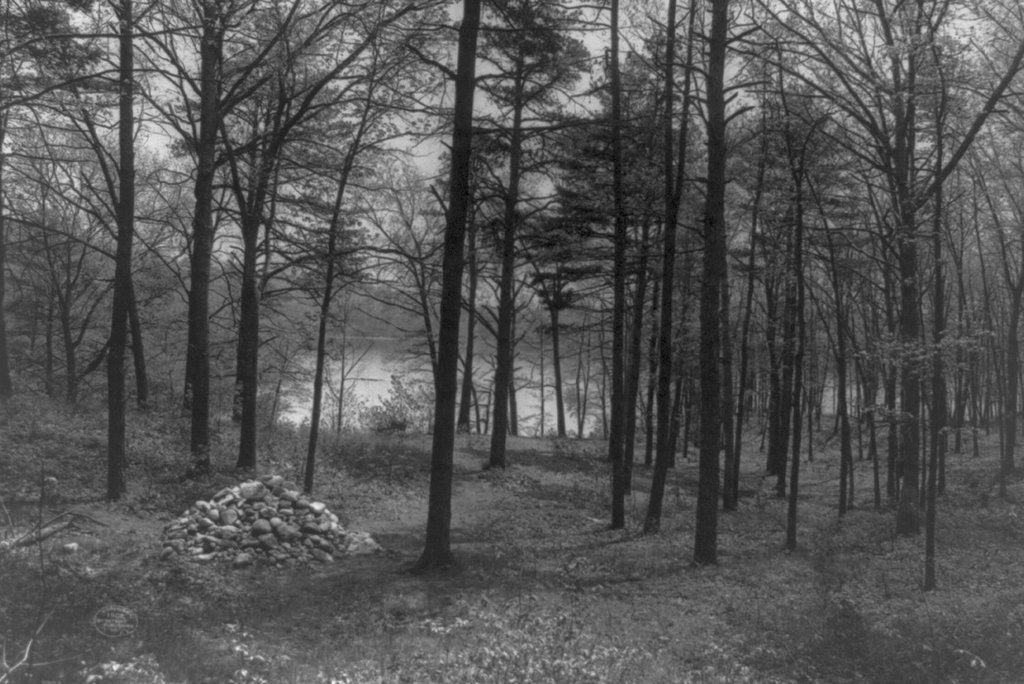
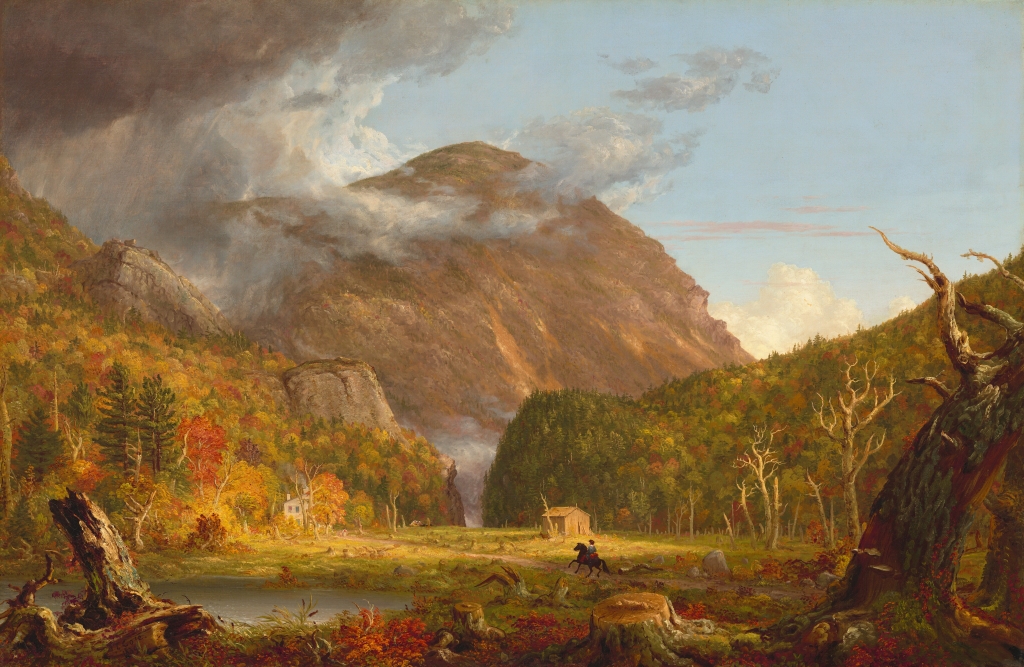
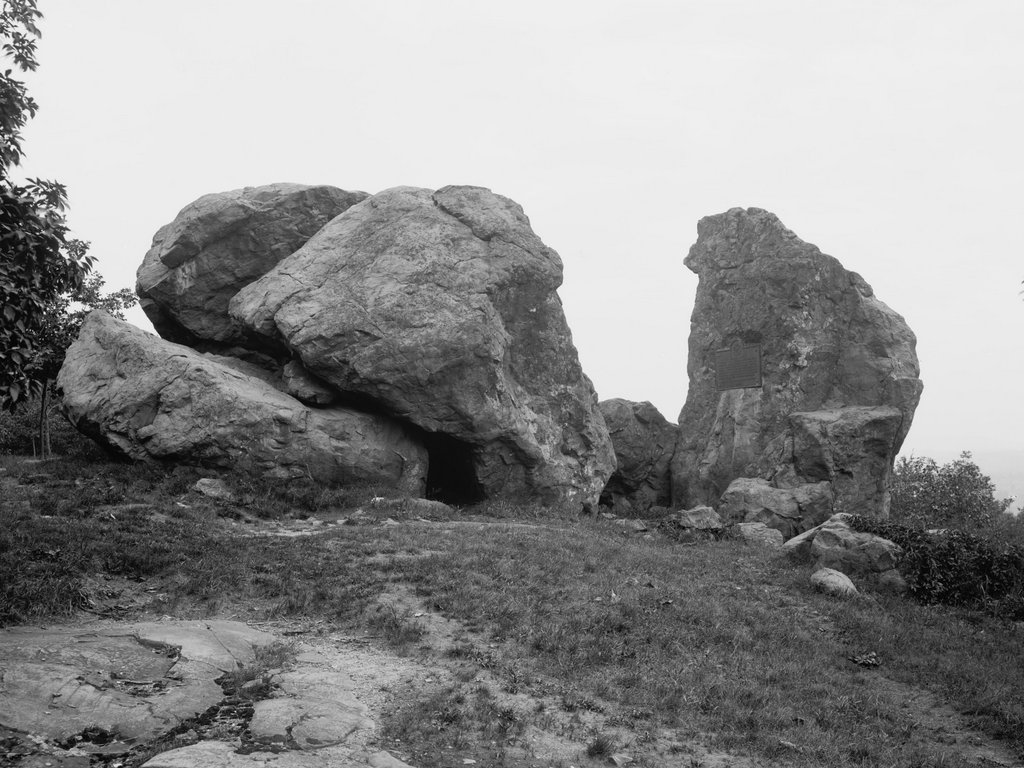
The Judges Cave on West Rock in New Haven, around 1901. Image courtesy of the Library of Congress, Detroit Publishing Company Collection.

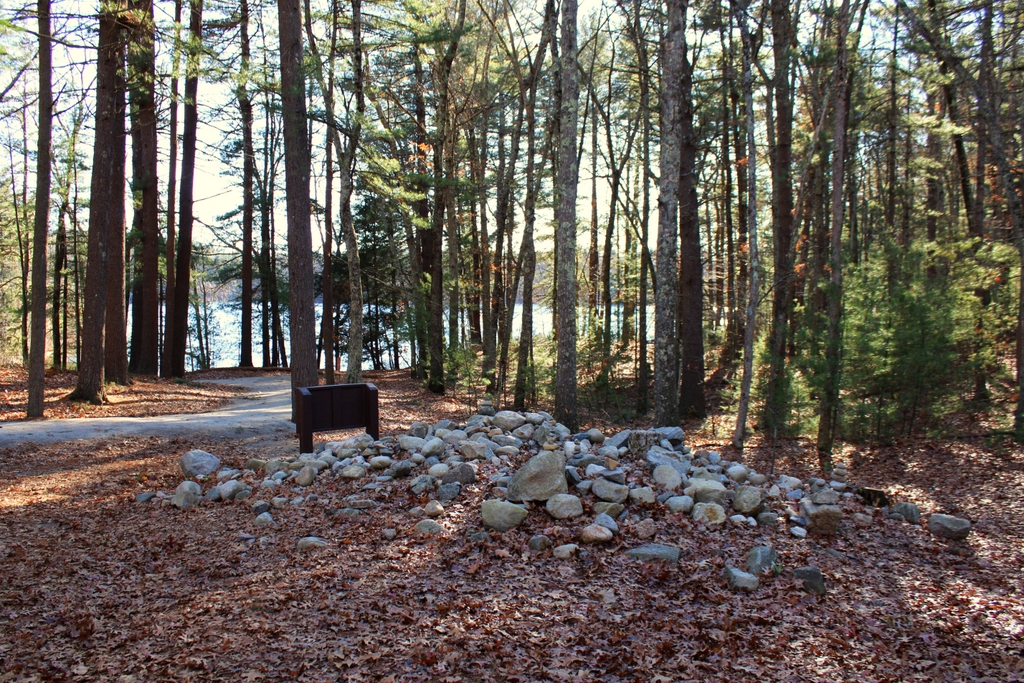
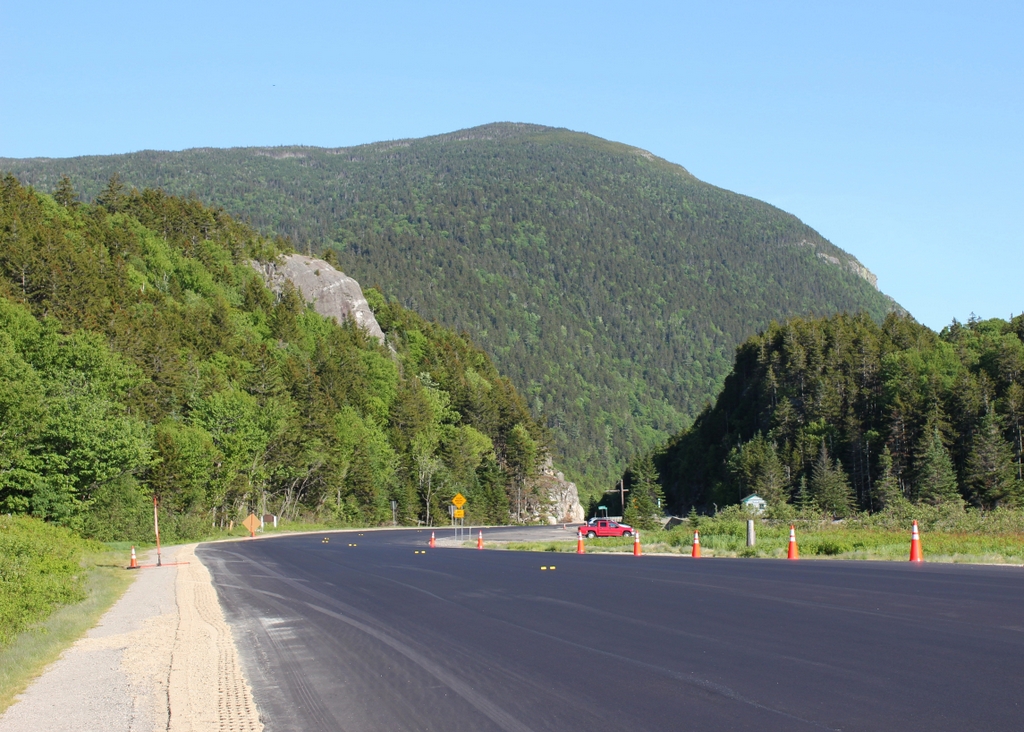
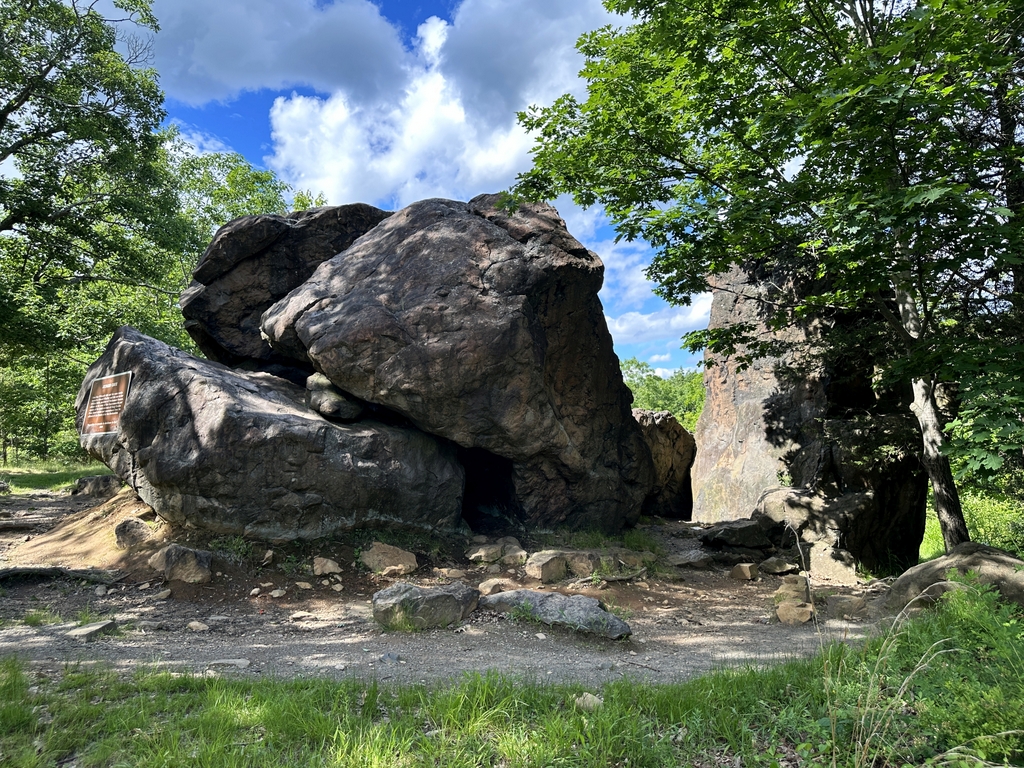
The scene in 2024:

The immediate origins of the American Revolution can be traced back to the 1760s, when colonists began protesting taxes that were being levied on the colonies in the aftermath of the French and Indian War. However, this was hardly the first time that the colonies had defied the British crown. A century earlier, following the English Civil War and the eventual restoration of the monarchy, the colony of New Haven protected several regicides who had signed the death warrant of Charles I in 1649. This ultimately helped lead to the downfall of the colony and its merger with Connecticut in 1664, but none of the regicides were ever captured, and the incident has lived on in New England lore.
John Dixwell, William Goffe, and Edward Whalley were three military officers who had fought on the side of Parliament during the English Civil War in the 1640s. Following the defeat of the Royalists, King Charles I was captured put on trial for treason, and was found guilty of being a “tyrant, traitor, murderer and public enemy.” These three men were among the 59 commissioners who signed his death warrant, and he was subsequently beheaded on January 30, 1649.
This led to a decade-long interregnum, during which time Puritan leader Oliver Cromwell took on the title of Lord Protector of the Commonwealth of England. However, this government collapsed soon after Cromwell’s death in 1558, and in 1660 Charles II, the son of Charles I, returned from exile became king. That same year, Parliament passed the Indemnity and Oblivion Act, which pardoned most of the people who took part in the war but specifically excluded the 59 regicides and other high-ranking leaders who were connected to the trial and execution of Charles I. Over the next few years, royal officials tracked down many of these people, who were then imprisoned or executed. Even those who were already dead could not escape punishment; the bodies of Cromwell and several other dead regicides were exhumed from their graves, publicly executed, and then beheaded.
In the meantime, Dixwell, Goffe, and Whalley fled to the New World, to seek shelter among the Puritans. The exact date and location of Dixwell’s arrival is unknown, but he was presumed dead by the British and was not actively pursued by royal authorities. As for Goffe and Whalley, they arrived in Boston in July 1660, and they lived openly in Cambridge, before news of the Indemnity and Oblivion Act reached the colony in the fall. Over the next few months, the colonial leaders debated what to do about the two men. Although many were sympathetic to them and their cause, they feared the consequences to the colony if they continued to shelter them. So, on February 26, 1661 Goffe and Whalley left Cambridge for New Haven, where they arrived on March 7.
Here in New Haven, the men initially lived with the Reverend John Davenport. However, within a few months they were again in danger. News of their formal arrest warrant, dated March 5, reached New Haven around the end of April. This was soon followed by the arrival of royal officials in nearby Guilford, where they met with Governor William Leete. He managed to delay them in Guilford for several days, allowing Goffe and Whalley to quite literally take to the hills in order to escape arrest.
Goffe and Whalley spent several nights in temporary lodgings, aided by local farmers, before they were brought here to this rock formation on May 15. Although commonly referred to as Judges Cave, it is a cave in only the most generous sense of the word. In reality, it is a pile of boulders that, in a few areas, overhang enough to provide minimal shelter from the elements. It is located high atop West Rock, a traprock ridge located about three miles northwest of the center of New Haven. At the time, this was a remote, sparsely-settled area, and they were able to live here for nearly a month without being detected.
Throughout this month, Goffe and Whalley received food every day from Richard Sperry, a local farmer who lived about a mile from here. They spent several nights at a nearby house during periods of inclement weather, but otherwise they lived here on the hill, which they named Providence Hill. In the meantime, royal officials were diligently searching for them in New Haven, offering generous rewards for their capture while also threatening Reverend Davenport for having aided them. The two regicides considered turning themselves in, in order to spare the colony any further trouble, but Governor Leete convinced them to remain in hiding. Within a few years, though, New Haven’s aid to the regicides would be a contributing factor in the demise of the colony, which was absorbed by the neighboring Connecticut colony in 1664.
According to legend, it was ultimately not royal officials who drove Goffe and Whalley from this cave, but rather a mountain lion that made an appearance at the entrance to the cave and frightened the two men. They left here on June 11, and lived at two other locations in the vicinity of West Rock for the next few months before finding more permanent lodgings at a house in Milford. They remained at this house for the next two or three years, before eventually moving to Hadley, Massachusetts, where they spent the rest of their lives in safety.
Because of the obvious need for secrecy in the movements of the regicides, there are few contemporary sources to corroborate these events. Perhaps the only primary source document was a diary that Goffe kept from 1660 to 1667, which he wrote in an easily-decipherable shorthand. This diary is now lost to history, but in the mid-1700s it was owned by Thomas Hutchinson, the royal lieutenant governor and later governor of the Province of Massachusetts Bay.
Aside from his role in colonial government, Hutchinson was also a historian, and in 1764 he published The History of the Colony of Massachusetts Bay. This book included an account of the regicides, which was based largely on Goffe’s journal. However, as a loyalist in the years leading up to the American Revolution, Hutchinson took a dim view of the regicides, and this bias is evident in much of his narrative. For example, he emphasizes the role that colonial officials had in trying to apprehend them, in an effort to portray the majority of 17th century New Englanders as having been loyal to the crown
Regardless of the biases, and the fact that it was written a century after the events happened, Hutchinson’s book provides the earliest significant account of the regicides and their flight through New England. The section relevant to their time here at Judges Cave, which is part of a lengthy footnote, reads as follows:
About that time, news came to Boston that ten of the judges were executed, and the governor received a royal mandate, dated March 5, 1660, to cause Whaley and Goffe to be secured. This greatly alarmed the country, and there is no doubt that the court were now in earnest in their endeavours to apprehend them; and to avoid all suspicion, they gave commission and instruction to two young merchants from England, Thomas Kellond and Thomas Kirk, zealous royalists, to go through the colonies, as far as Manhados, in search of them. They had friends who informed them what was doing, and they removed from Mr. Davenport’s to the house of one Jones, where they lay hid until the 11th of May, and then removed to a mill, and from thence, on the 13th, into the woods, where they met Jones and two of his companions, Sperry and Burril, who first conducted them to a place called hatchet-harbor, where they lay two nights, until a cave or hole in the side of a hill was prepared to conceal them. This hill they called Providence hill; and there they continued, from the 15th of May to the 11th of June, sometimes in the cave, and, in very tempestuous weather, in a house near to it. During this time, the messengers went through New-Haven to the Dutch settlement, from whence they returned to Boston by water. They made diligent search, and had full proof that the regicides had been seen at Mr. Davenport’s, and offered great rewards to English and Indians who should give information that they might be taken, but, by the fidelity of these three friends, they remained undiscovered.
Goffe’s journal remained in Hutchinson’s possession until 1765, when his house was ransacked by a Patriot mob in protest of the Stamp Act. The journal was either lost or destroyed in the process, making Hutchinson’s book the only surviving description of its contents. However, at least one other prominent historian, future Yale president Ezra Stiles, had the opportunity to examine the journal before its disappearance. He saw it during a 1763 visit to Hutchinson’s house, and he subsequently wrote his own history of the regicides.
Unlike Hutchinson’s description of the regicides, which fills just seven pages in his massive multi-volume history of the colony, Ezra Stiles published an entire book about their exploits in 1794. Titled A History of Three of the Judges of King Charles I, the book is over 350 pages long, and it relies heavily on oral traditions that were passed down to the descendants of the men involved in helping the regicides. Like Hutchinson’s account, Stiles’s book also has a political slant, although in the opposite direction. Writing just a decade after the American Revolution, in the midst of republican, anti-monarchical sentiment, Stiles viewed the regicides in a positive light, and he even included a chapter in which he justified their actions.
Stiles’s seemingly uncritical use of oral tradition in his book would come under criticism from later scholars, including biographer Edmund S. Morgan. Writing in his 1962 book The Gentle Puritan: A Life of Ezra Stiles, 1727-1795, Morgan asserted that it “represents Stiles at his worst. It is a tedious hodgepodge of fact and fancy, compounded mainly out of dim recollections by old men and women of things their grandfathers had told them fifty years before.” One such recollection, which relates to the Judges Cave, came from an interview with Joseph Sperry, whose grandfather Richard Sperry had aided the regicides in 1661. Stiles provided the following account in his book, including a description of this cave:
In 1785 I visited aged Mr. Joseph Sperry, then living, aged 76, a grandson of the first Richard, a son of Daniel Sperry, who died in 1751, aged 86, from whom Joseph received the whole family tradition. Daniel was the sixth son of Richard, and built a house at the south end of Sperry’s farm, in which Joseph now lives, not a half a mile west from the Cave, which Joseph shewed me. There is a notch in the mountain against Joseph’s house, through which I ascended along a very steep acclivity up to the Cave. From the south end of the mountain for three or four miles northward, there is no possible ascent or descent on the west side, but at this notch, so steep is the precipice of the rock. I found the Cave to be formed, on a base of perhaps forty feet square, by an irregular clump or pile of rocks, or huge broad pillars of stone, fifteen and twenty feet high, standing erect and elevated above the surrounding superficies of the mountain, and enveloped with trees and forest. These rocks coalescing or contiguous at top, furnished hollows or vacuities below, big enough to contain bedding and two or three persons. The apertures being closed with boughs of trees or otherwise, there might be found a well covered and convenient lodgement.
After this description of the cave and its surroundings, he wrote of what he learned from Joseph Sperry:
Here, Mr. Sperry told me, was the first lodgment of the Judges, and it has ever since gone and been known by the name of the Judges’ Cave to this day. Goffe’s Journal says, they entered this Cave the 15th of May, and continued in it till the 11th of June following—Richard Sperry daily supplied them with victuals from his house, about a mile off; sometimes carrying it himself, at other times sending it by one of his boys, tied up in cloth, ordering him to lay it on a certain stump and leave it: and when the boy went for it at night he always found the basons emptied of the provisions, and brought them home. The boy wondered at it, and used to ask his father the design of it, and he saw no body. His father only told him there was some body at work in the woods that wanted it. The sons always remembered it, and often told it to persons now living, and to Mr. Joseph Sperry particularply [sic].
They continued here till 11th of June. Mr. Joseph Sperry told me that the incident which broke them up from this Cave was this, that this mountain being a haunt for wild animals, one night as the Judges lay in bed, a panther, or catamount, putting his head into the door or aperture of the Cave, blazed his eye-balls in such a hideous manner upon them, as greatly affrighted them. One of them was so terrified by this grim and ferocious monster, her eyes and her squawling, that he took to his heels, and fled down the mountain to the Sperry’s house for safety. They thereupon considered this situation too dangerous, and quitted it. All the Sperry families have this tradition.
Aside from the events here in New Haven, the subsequent lives of Goffe and Whalley in Hadley are shrouded in mystery and legend. They lived at the home of the Reverend John Russell, but it appears that most townspeople were unaware of their identities. At some point around 1664, they were reunited with John Dixwell, the third regicide who had fled to New England. He eventually moved to New Haven, where he lived under the name John Davids until his death in 1689. Because the authorities believed that he was dead, he was able to live in relative security, and does not appear to have required the use of this cave or any other improvised shelters.
In the meantime, Edward Whalley died in Hadley around 1675 of natural causes, but Goffe lived long enough to become the subject of perhaps the most memorable regicide legend. According to tradition, at some point in either 1675 or 1676 the town of Hadley was facing an attack by Native Americans during King Philip’s War. The townspeople started panicking, but then an elderly man, identified in the legend as William Goffe, emerged and began to take charge. Some 30 years after he fought the Cavaliers on the battlefields of the English Civil War, he rallied the people and led their defense, and succeeded in saving the town. Then, as suddenly as he had appeared, the “Angel of Hadley” was gone.
As is the case for nearly all of the regicide-related stories, the first published account of the Angel of Hadley did not appear for nearly a century, until Thomas Hutchinson included it in his book in 1764. He included it at the end of his lengthy footnote on the movements of the regicides, writing:
The town of Hadley was alarmed by the Indians in 1675, in the time of publick worship, and the people were in the utmost confusion. Suddenly, a grave elderly person appeared in the midst of them. In his mien and dress he differed from the rest of the people. He not only encouraged them to defend themselves; but put himself at their head, rallied, instructed and led them on to encounter the enemy, who by this means were repulsed. As suddenly, the deliverer of Hadley disappeared. The people were left in consternation, utterly unable to account for this strange phœnomenon. It is not probable, that they were ever able to explain it. If Goffe had been then discovered, it must have come to the knowledge of those persons, who declare by their letters that they never knew what became of him.
Writing in his book 30 years after Hutchinson, Stiles repeats essentially the same account of the incident, although his wording tends to be more explicitly favorable to Goffe. Rather than describing him as “a grave elderly person,” Stiles writes of “a man of a very venerable aspect.” He copies Hutchinson’s wording by saying “the inhabitants could not account for the phœnomenon,” but then added “but considering that person as an Angel sent of God upon that special occasion for their deliverance; and for some time after said and believed that they had been delivered and saved by an Angel.”
Stiles’s romanticized description helped to solidify the idea of the “Angel of Hadley,” and by the early 19th century the story had become a part of early American folklore. In his 1823 novel Peveril of the Peak, Scottish writer Sir Walter Scott alluded to the incident, and in 1829 James Fenimore Cooper included it in his novel The Wept of Wish-ton-Wish. Nathaniel Hawthorne, who was never one to pass up a good story about the Puritans, also took inspiration from it. As a young man, he visited Judges Cave here in New Haven, and one of his early short stories, “The Gray Champion,” was loosely based on the Angel of Hadley legend. In the story, the title character is a shadowy, mysterious figure who embodies the Puritan ancestors of New England. Instead of defending a town against Native Americans, Hawthorne’s hero challenges the authoritarian rule of Edmund Andros in the 1680s. The Gray Champion disappears once the threat to the colony is over, but over the years he continues to make appearances whenever American liberty is at stake, including nearly a century later on the battlefields at Lexington and Bunker Hill.
Although Hutchinson’s and Stiles’s accounts provided plenty of material for 19th century authors, many historians began calling into question the accuracy of these tales, especially the ones that were handed down to Stiles through multi-generational hearsay. Legends such as the Angel of Hadley might very well have some basis in reality, but at this point it is difficult to sort out fact from fiction, given the inherent secrecy involved in the regicides and their activities here in New England. As for the tradition that the regicides spent a month hiding here in this rock formation, it is impossible to state with certainty that this is true. However, this belief does not seem to have been seriously questioned, and it seems plausible that this was, in fact, their hiding place during the spring of 1661.
The first photo was taken around 1901, showing the south side of the rock formation. By this point, the surrounding land was owned by the city of New Haven as part of West Rock Park. In the early 1890s a road was opened up here to the Judges Cave, and then in 1896 a plaque was installed here on the rocks. This plaque, which is visible here on the right side of the scene, commemorates the role that this site played in sheltering the regicides, and it was presented to the city by the Society of Colonial Wars. The formal dedication occurred on October 14, 1896, and it was attended by dignitaries such as Mayor Frederick B. Farnsworth, state adjutant general Edward E. Bradley, future governor Simeon E. Baldwin, and writer Charles Dudley Warner. Along with providing a short description of the regicides, the plaque features the phrase “opposition to tyrants is obedience to God,” which had apparently been inscribed on the rocks here as early as 1803.
Today, more than a century after the first photo was taken, the Judges Cave still looks essentially the same. It is still preserved as parkland, although it was acquired by the state in 1975, and it is now named West Rock Ridge State Park. The Judges Cave remains an important landmark within the park, and the only real difference between these two photos is the loss of the plaque, which was evidently stolen at some point. Its replacement is a somewhat larger plaque on the left side, although it bears the same inscription as the original one. It includes the same closing line about how “opposition to tyrants is obedience to God,” reflecting the beliefs that had led two Puritans across the Atlantic Ocean and to this secluded cave on the fringes of European settlements in the New World.