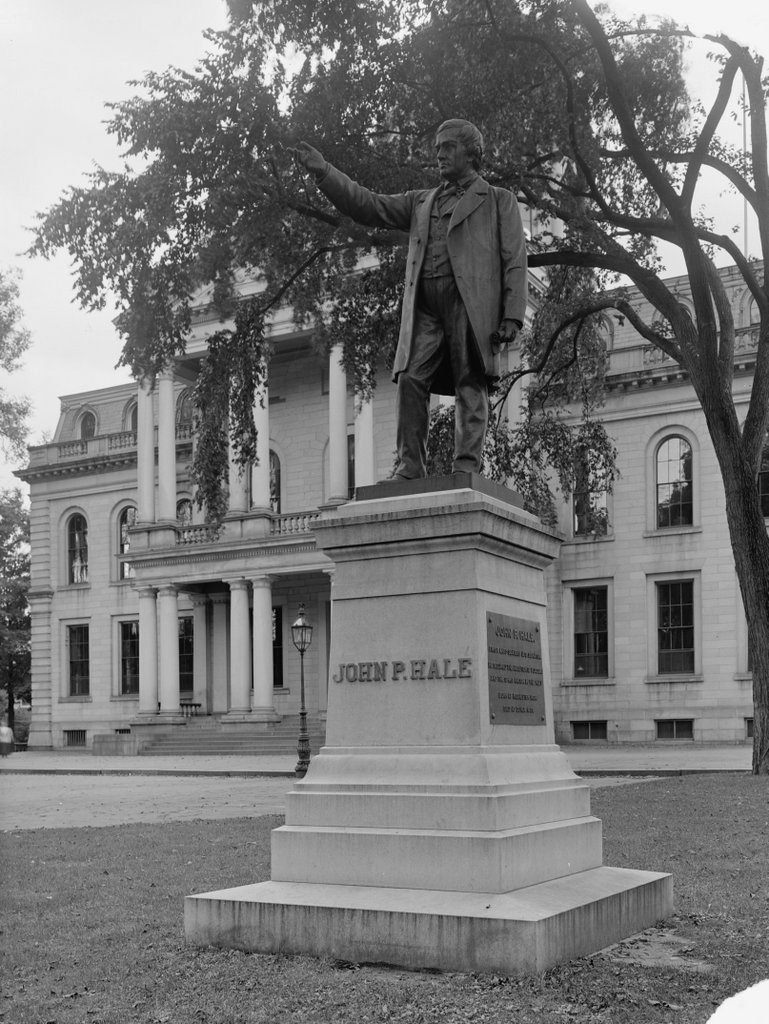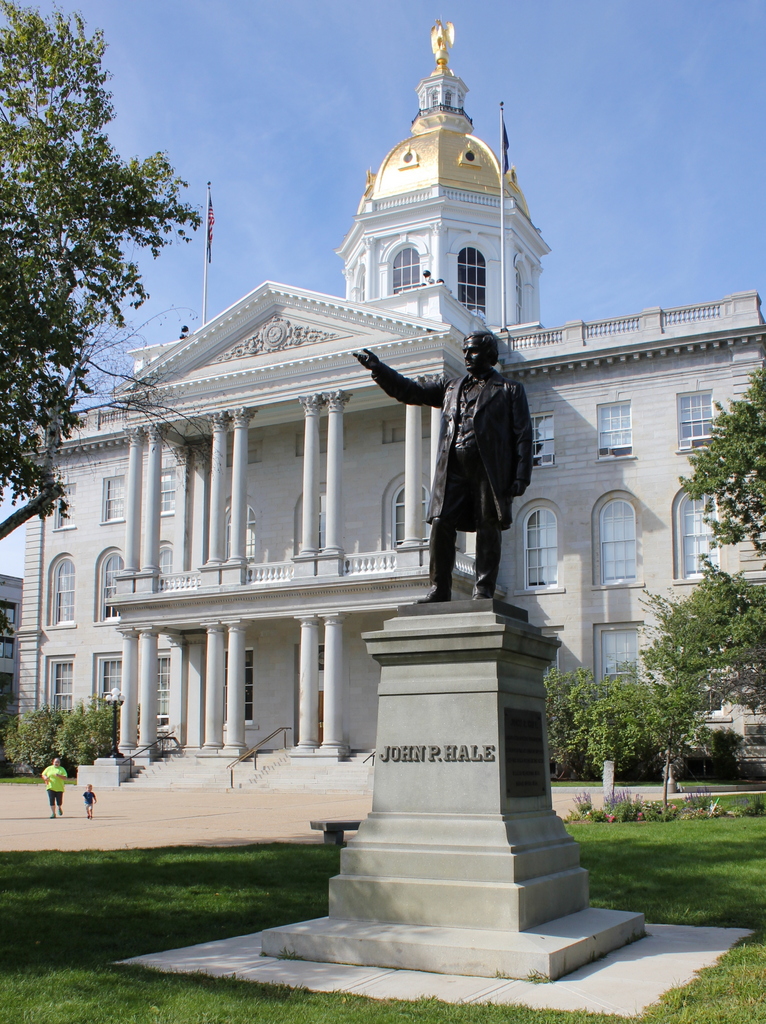The Mount Pleasant mansion in Fairmount Park, around 1900. Image courtesy of the Library of Congress, Detroit Publishing Company Collection.

The house in 2019:
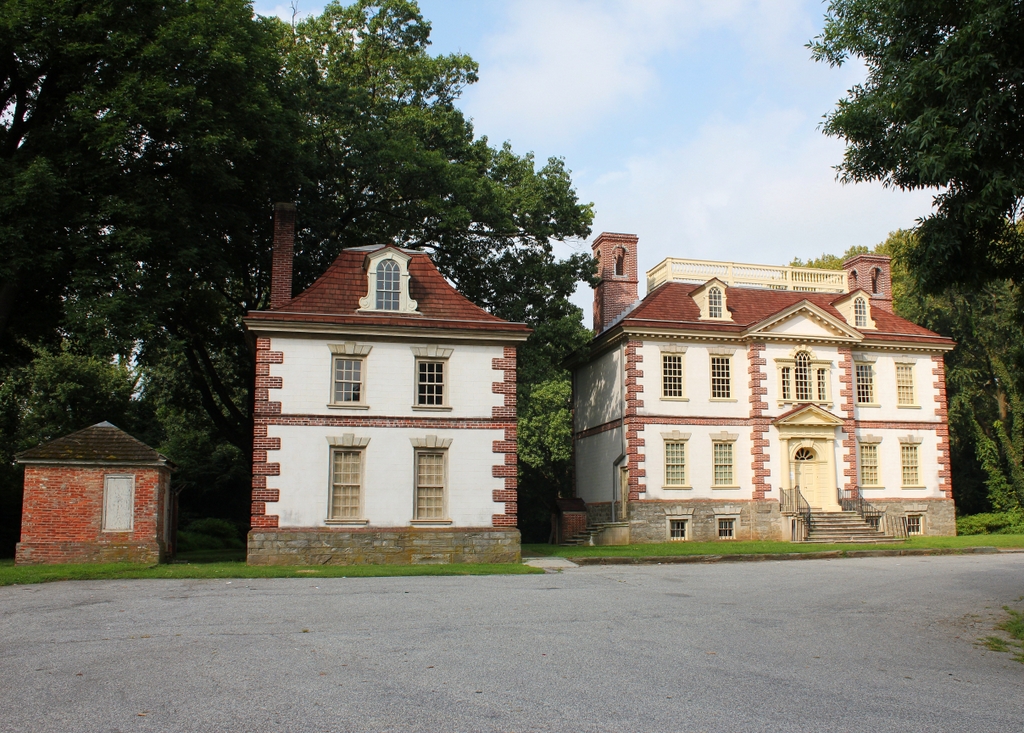

Fairmount Park is located along the banks of the Schuylkill River, several miles to the northwest of downtown Philadelphia. During the colonial era, this area of the city was still sparsely-settled, and the bluffs overlooking the river were desirable locations for the country estates of some of Philadelphia’s affluent families. These mansions were generally used as summer homes, allowing these families to escape the heat and diseases of the densely-populated city center. Most of the homes were built in the 18th or early 19th centuries, and 16 are still standing today as part of Fairmount Park, the largest park in Philadelphia. Of these, perhaps the finest mansion is Mount Pleasant, which was built here in the early 1760s on the east bank of the Schuylkill River.
Mount Pleasant was designed by Thomas Nevell, and it is an excellent example of colonial Georgian-style architecture. As was typical for Georgian houses of the period, its design is symmetrical, and it makes use of decorative elements such as quoins on the corners, a pedimented doorway, a Palladian window, and a hip roof with dormers. The main house is flanked by two smaller buildings with matching exteriors. The one on the north side—which is just out of view on the right side of this scene—was the office, and the one on the south side, in the foreground of these photos, was the summer kitchen.
The original owner of this house was John MacPherson, a sea captain who became wealthy as a privateer during the French and Indian War. In command of the 20-gun ship Britannia, MacPherson captured several dozen French vessels throughout the war, in the process hurting the French war effort while simultaneously enriching himself. His exploits cost him his right arm, which he lost to a French cannonball in the midst of a battle, but upon returning to Philadelphia he used his new wealth to build his country estate here in Philadelphia. He originally named it Clunie, after his family’s ancestral home in Scotland, but subsequently changed it to Mount Pleasant. The size of the property also changed during MacPherson’s ownership; he started with about 31 acres, but the estate eventually grew to 120 acres.
MacPherson was a patriot during the American Revolution, and he even made an ultimately unsuccessful bid to become commander of the newly-established Continental Navy. His two sons, William and John, served in the Continental Army during the war. William resigned his commission as a British lieutenant in order to join the Continental Army, and he eventually became a brevet major and served on the staff of the Marquis de Lafayette. His brother John was also a staff officer during the war, serving as aide-de-camp to General Richard Montgomery, but both he and Montgomery were killed in the Battle of Quebec on December 31, 1775.
In the meantime, the elder John MacPherson interacted with high-ranking members of the Continental Congress, which met in Philadelphia’s Independence Hall throughout the war. On at least one occasion, on September 25, 1775, Massachusetts delegate John Adams visited him here at Mount Pleasant for dinner. The future president subsequently wrote about it in his diary, commenting on the house, his family, and MacPherson’s naval ambitions:
Rode out of town, and dined with Mr. McPherson. He has the most elegant seat in Pennsylvania, a clever Scotch wife, and two pretty daughters. His seat is on the banks of the Schuylkill. He has been nine times wounded in battle; an old sea commander; made a fortune by privateering; an arm twice shot off, shot through the leg, &c. He renews his proposals of taking or burning ships.
Despite living in “the most elegant seat in Pennsylvania,” MacPherson eventually decided to move out of the house and offer it for sale. He had no immediate buyers, but in the meantime he leased the house to Juan de Miralles, Spain’s unofficial envoy to the United States. Although Spain was officially neutral at this point in the war, Miralles established connections with many American leaders in Philadelphia, including by hosting lavish balls here at Mount Pleasant.
Then, in 1779 General Benedict Arnold purchased Mount Pleasant from John MacPherson. At the time, Arnold was still an ostensibly loyal officer in the Continental Army. He had been a hero at the Battle of Saratoga, but in the process he suffered a leg injury. During his recovery he was unable to fight on the front lines, so Washington appointed him military governor of Philadelphia in 1778. However, Arnold’s volatile personality made him ill-suited for a position that required tact and subtlety in dealing with local leaders, and he also faced accusations that he was using his position to enrich himself. It was also during his time in Philadelphia that Arnold met and fell in love with 18-year-old Peggy Shippen, whose wealthy family had Loyalist sympathies. Despite being twice her age and from a very different social background, Arnold began courting her later in 1778, and they were married on April 8, 1779.
At the time, Arnold’s financial situation was somewhat strained, and he was under suspicion for misusing his authority for personal gain. However, he purchased Mount Pleasant as a wedding gift for Peggy, giving the impression that he was wealthier than he really was. In reality, he was hampered by debt, which would only worsen after he and Peggy moved in here and began living a lavish lifestyle. This, combined with Arnold’s belief that patriot leaders were not grateful for his actions and sacrifices that he made on the battlefield, ultimately helped lead him to famously betray the Continental Army in 1780. Peggy likely played a role in this decision as well, as she had Loyalist connections and may have helped initiate contact between Arnold and his British handler, Major John André.
As it turned out, the Arnolds’ stay here at Mount Pleasant was short. His treason was discovered after André was captured on September 23, 1780, and Arnold himself only narrowly escaped capture. Mount Pleasant was subsequently confiscated, and it changed hands several times before being purchased by Peggy’s father, Edward Shippen, in 1784. Despite his Loyalist connections during the war, and the infamy of his son-in-law, Shippen remained a respected member of Philadelphia society, eventually becoming chief justice of the Supreme Court of Pennsylvania. He owned Mount Pleasant until 1792, when he sold it to Jonathan Williams.
Originally from Boston, Williams spent much of the Revolutionary period in France, first as a secretary to his great uncle, Benjamin Franklin, and then as a commercial agent of the United States. He later became an Army officer upon returning to the United States, and he held the position of Chief of Engineers for the Army Corps of Engineers from 1802 to 1803, and 1805 to 1812. During this time, he also became the first superintendent of West Point, serving from 1801 to 1803, and 1805 to 1812. In 1814 Williams was elected to the House of Representatives, but he died just two months into his term in 1815, without ever having attended a session of Congress.
After his death, his son Henry J. Williams inherited Mount Pleasant, and the house remained in the Williams family until 1853. By this point, the banks of the Schuylkill River were no longer as desirable a location for country estates as they had been a century earlier, in part because the city’s growth was encroaching on the area. Starting in the mid-19th century, the city of Philadelphia began purchasing estates along the river, in order to better protect the public water supply. These acquisitions became Fairmount Park, and in 1868 the city purchased Mount Pleasant and added it to the parkland.
The first photo was taken at the turn of the 20th century, and it shows the exterior in a somewhat deteriorated condition, with plenty of peeling paint on both the main house and the kitchen building. However, in 1927 Mount Pleasant was restored by the Philadelphia Museum of Art, which has administered the house ever since. It underwent another major restoration in the early 2000s, and today its exterior looks far better than it did when the first photo was taken 120 years ago. Adams’s description of it as being “the most elegant seat in Pennsylvania” is as true now as it was in 1775, and in 1974 it was designated as a National Historic Landmark because of its historic and architectural significance.