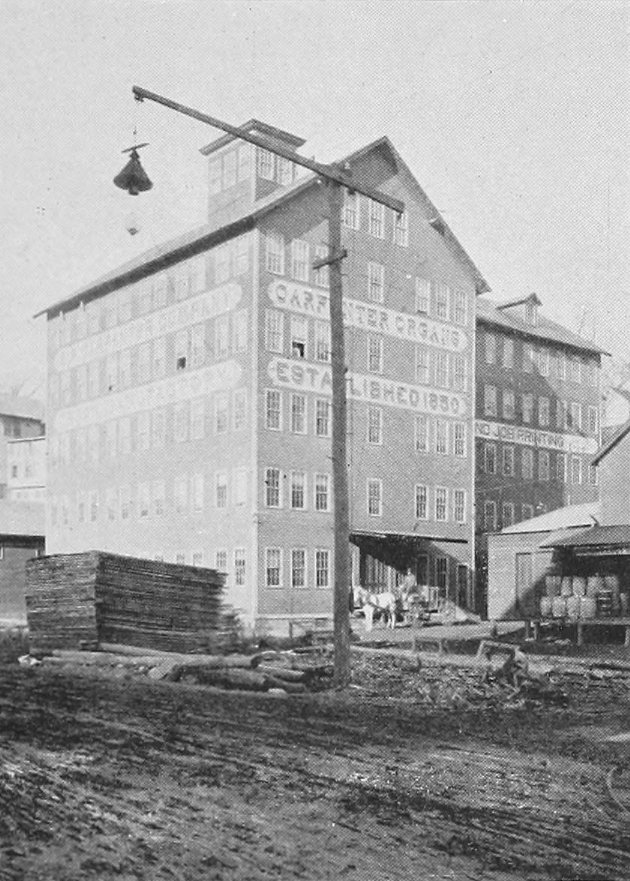
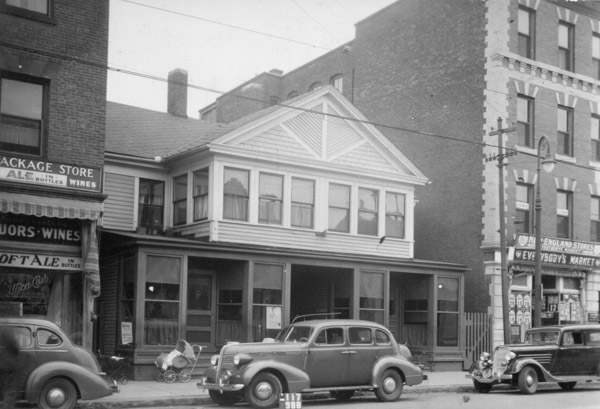
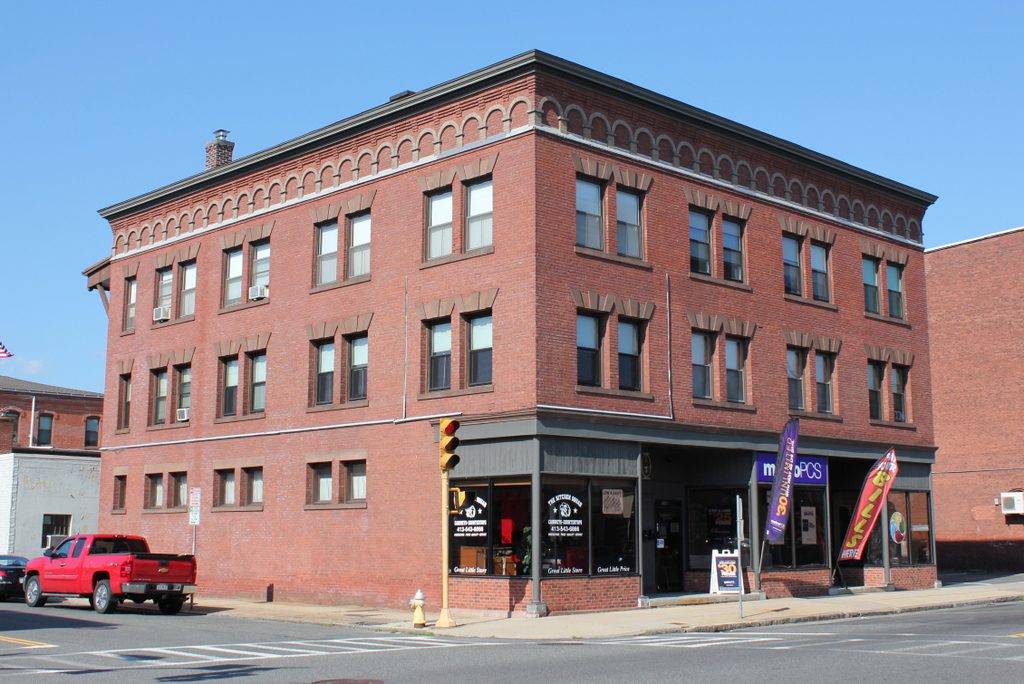
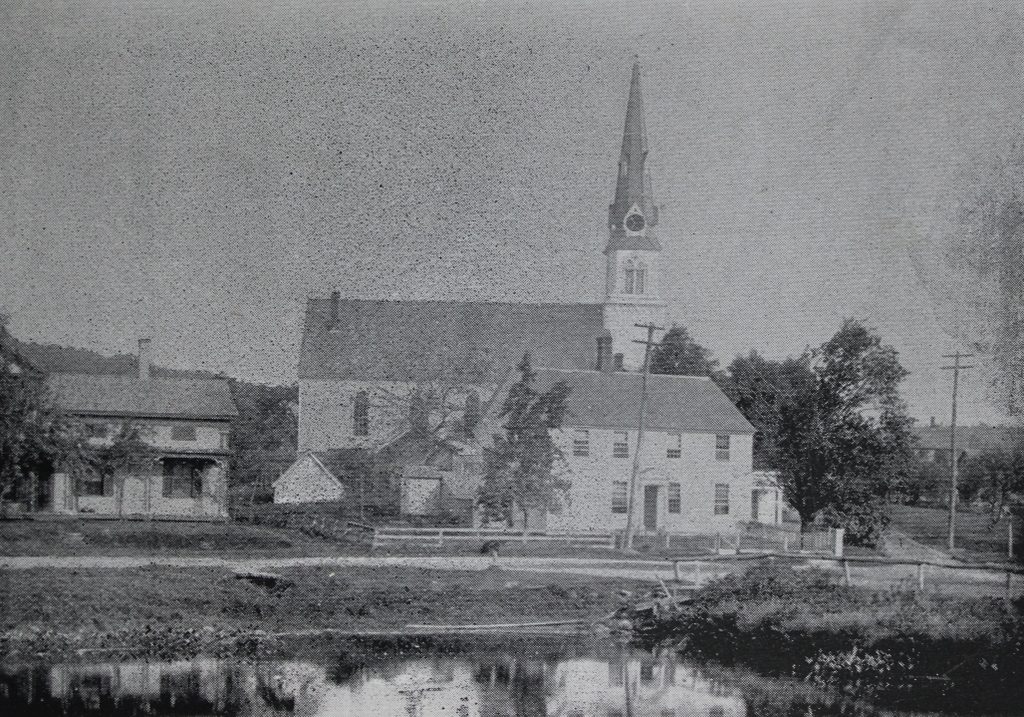The Carpenter Organ Company on Flat Street in Brattleboro, around 1894. Image from Picturesque Brattleboro (1894).
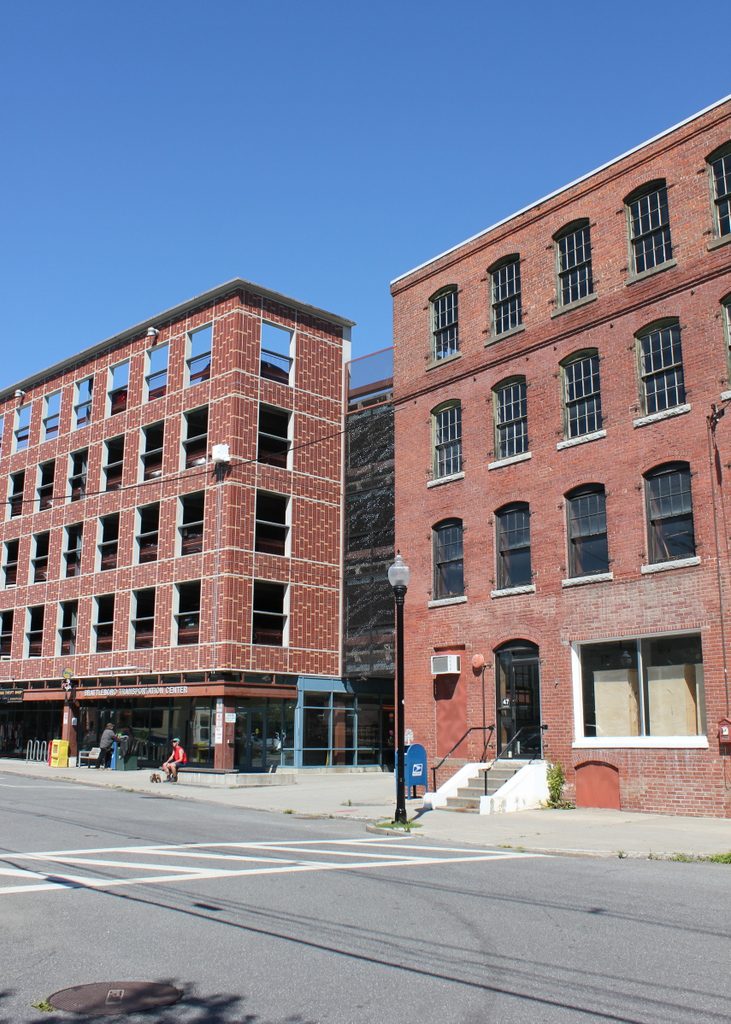
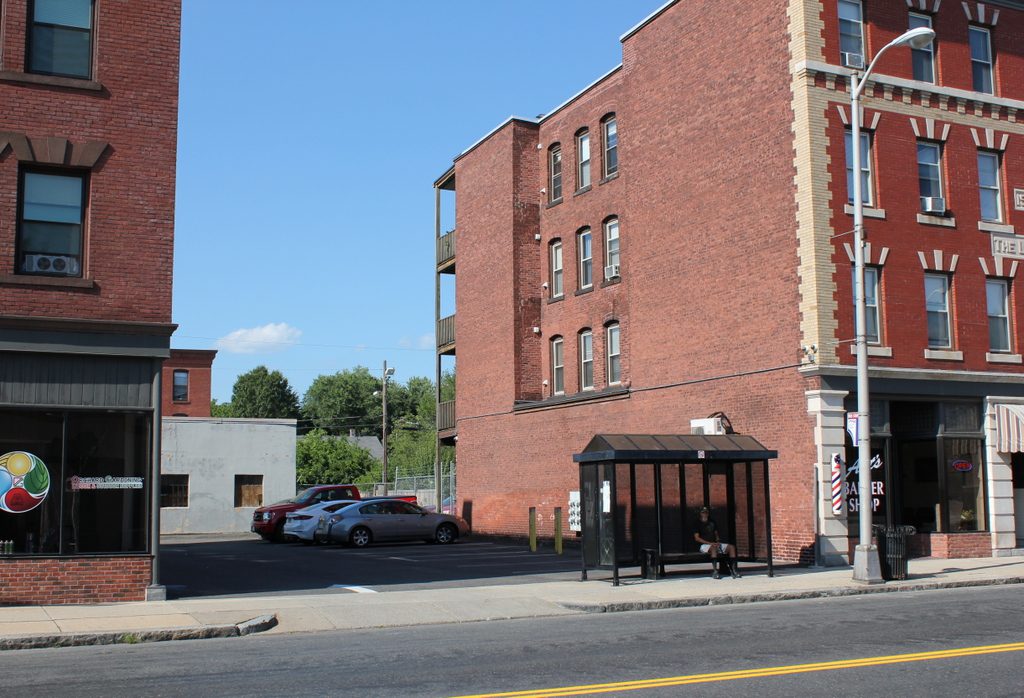
The scene in 2017:
During the second half of the 19th century, Brattleboro became a prosperous mill town, and one of its leading industries was the manufacturing of organs. Also known as pump organs, reed organs, or melodeons, these instruments enjoyed widespread popularity in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, and Brattleboro had several companies that produced them. The largest of these was Estey Organ, which was once the largest organ manufacturer in the country, but Estey also had several competitors, including the Carpenter Organ Company, which was located here in this factory on Flat Street.
The Carpenter Organ Company had originally been established in Worcester, Massachusetts by Edwin P. Carpenter, a second-generation organ maker whose father, Edwin B. Carpenter, had been one of the early partners in the Estey company. The elder Carpenter later relocated to Illinois, but his son subsequently returned to New England, producing organs in Worcester until 1884, when he moved the company to Brattleboro. The first photo, taken about a decade later, shows the company’s factory on Flat Street. This six-story building had once been home to Brattleboro Melodeon Company, which had been established in 1867, and the building was likely constructed around the same time.
The first photo comes from the 1894 book Picturesque Brattleboro, which declared that “The Company makes nothing but absolutely high grade goods, and its reputation is such the world over. In England, Germany, Russia, Holland, Denmark, Switzerland, Australia and South Africa its agents are the leading music houses who handle the Carpenter Organ for their best trade, using other makes to supply the demand for cheaper goods.” The article also cited recent recognition given to the company, including awards at the 1890 Edinburgh Exhibition and the 1893 World’s Columbian Exposition in Chicago.
The Carpenter Organ Company continued to produce organs here until it closed around 1917. By this point, musical tastes had changed, and demand for portable, in-home organs was not as high as it had been during the Victorian era. Its greatest competitor, Estey Organ, did manage to survive well into the 20th century, before finally closing in 1961. Most of the Estey buildings are still standing, and have been preserved as a museum, but the Carpenter Organ factory here on Flat Street is long gone. The site of the building is now a parking garage, although the garage’s brick facade helps to give it the appearance of a 19th century factory building.