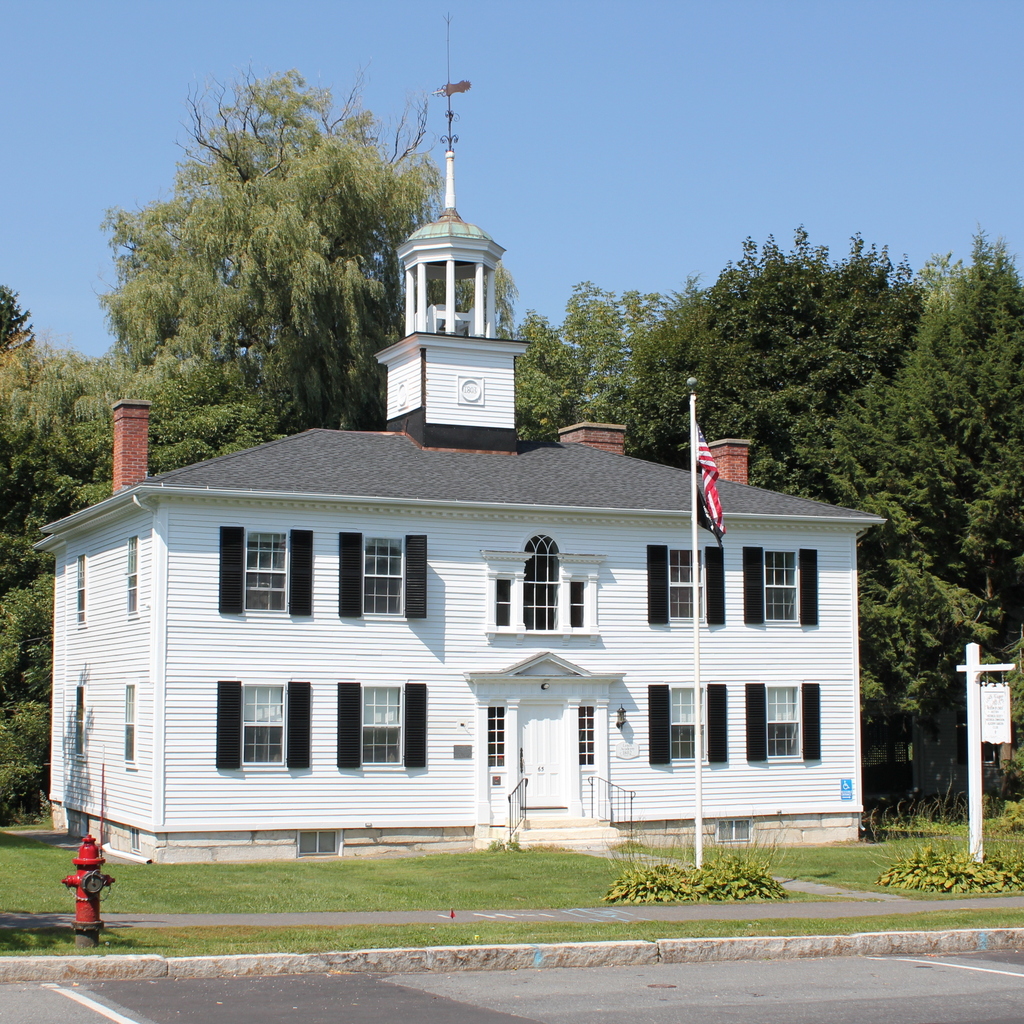
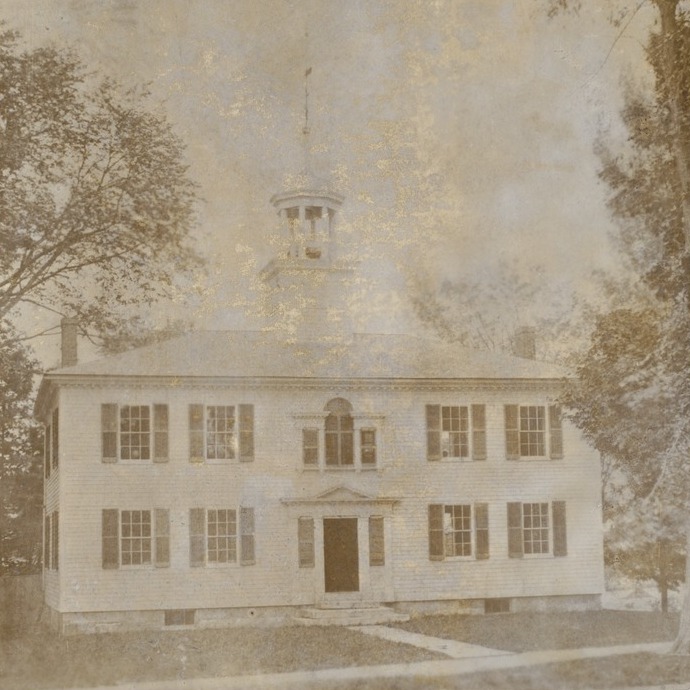
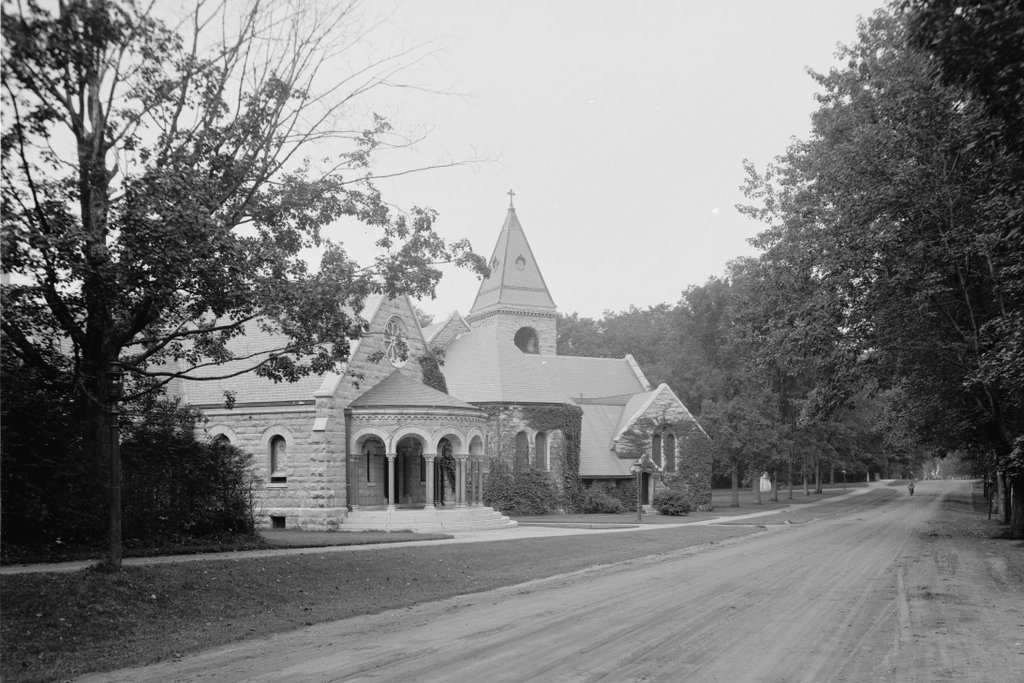
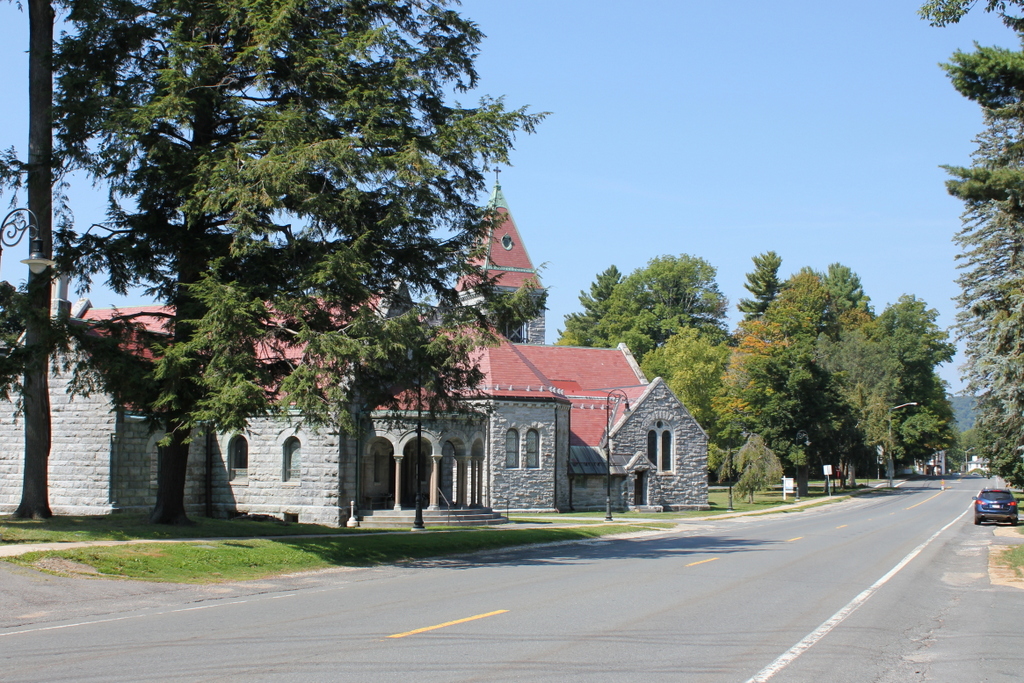
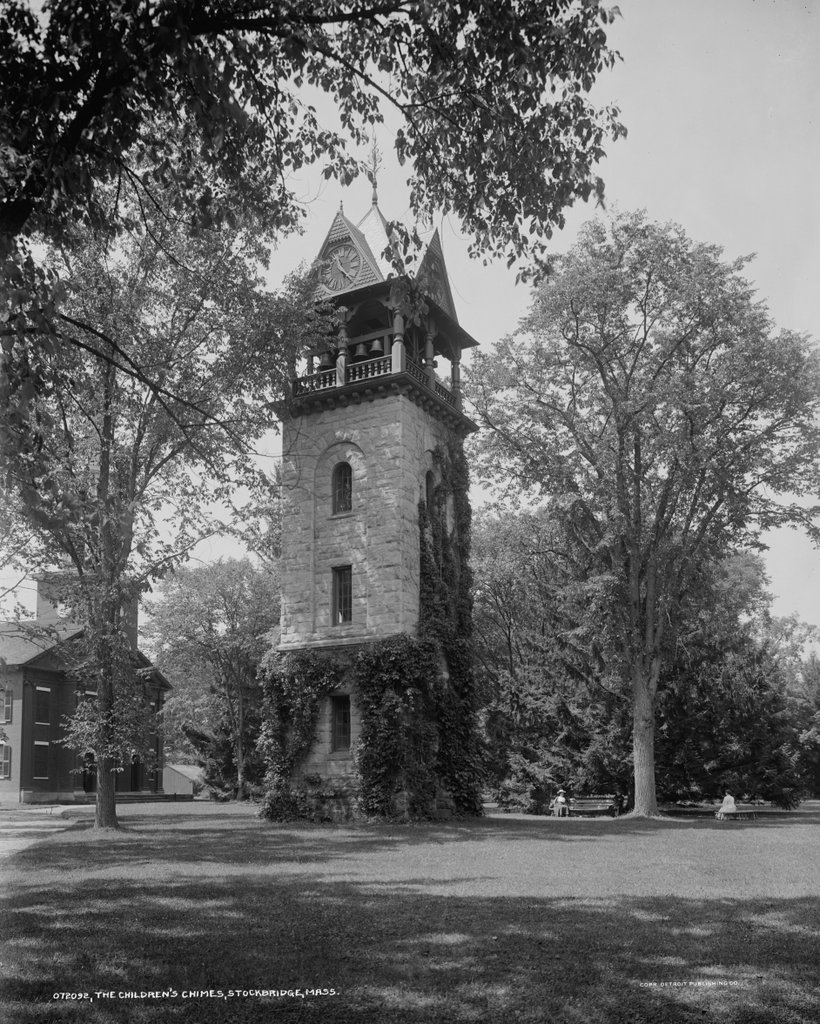
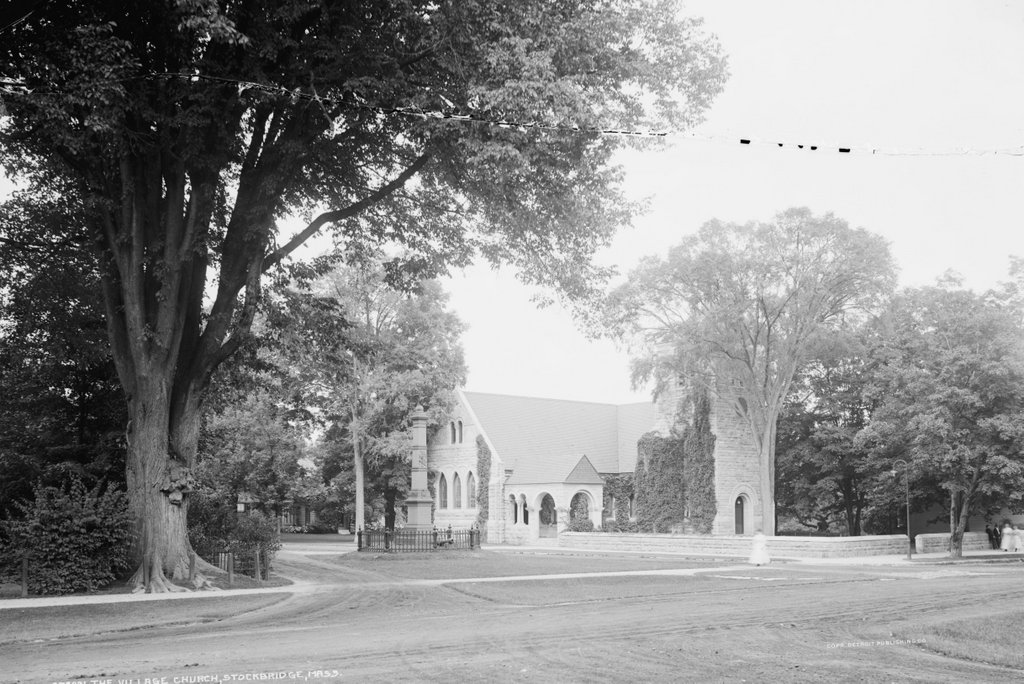The Children’s Chimes Tower in front of the First Congregational Church in Stockbridge, around 1905-1915. Image courtesy of the Library of Congress, Detroit Publishing Company Collection.

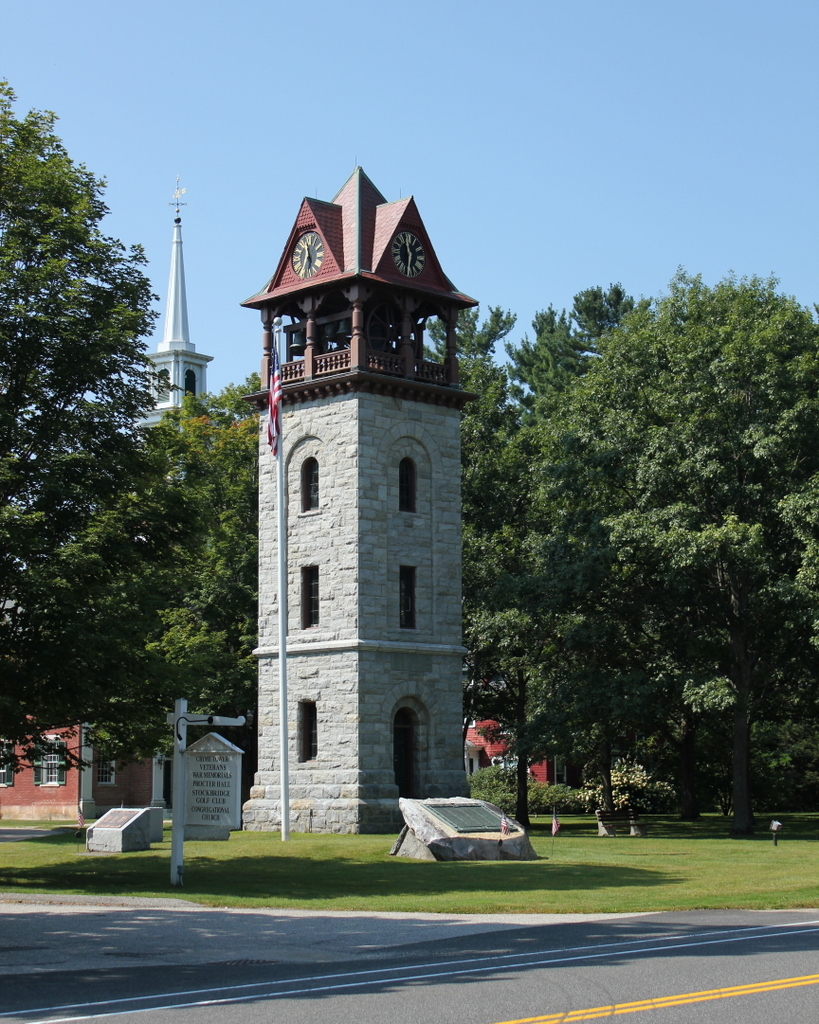
The tower in 2015:

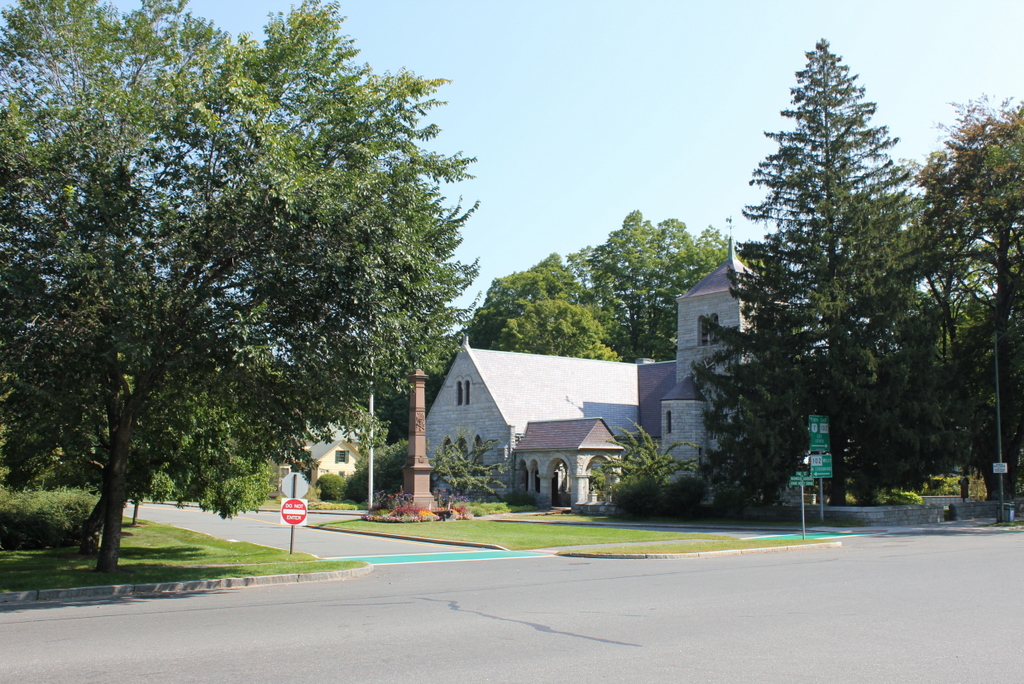
This bell tower was built on the site of the original church in Stockbridge, which stood here from 1739 until 1785. The church was established by John Sergeant, a missionary who moved here to convert the Mahican people to Christianity. He served here until his death in 1749, and he was replaced by Jonathan Edwards, the former Northampton pastor and prominent theologian who helped influence the First Great Awakening. Edwards was here until 1758, when he became the president of the College of New Jersey, now known as Princeton University.
The present church building, visible in the distance to the left in both photos, was built in 1824, during the pastorate of David Dudley Field, who served here from 1819 to 1837. He and his wife Submit raised their nine children here, four of whom became prominent figures in American history. Their oldest, David Dudley Field II, was a lawyer and law reformer who briefly served in the House of Representatives 1877. Stephen Johnson Field was also a lawyer, and he served on the US Supreme Court from 1863 to 1897 for what was at the time a record 34 years. Cyrus West Field chose business over law, and he also enjoyed success; in 1858, he and a group of other investors established the first transatlantic telegraph cable. Henry Martyn Field, the youngest of the nine siblings, followed in his father’s footsteps and became a pastor, but he was also a successful writer, publishing a number of travel books in the second half of the 19th century.
The Children’s Chimes bell tower in front of the church was built in 1878 by David Dudley Field II, in honor of his grandchildren, with the intention that, “It will be a memorial of those who are enshrined in my heart, while the ringing of the chimes at sunset I trust will give pleasure to all whose good fortune is to live in this peaceful valley.” Today, almost 140 years later, it is still rung, according to his wishes, every evening at 5:30 between Memorial Day and Labor Day.