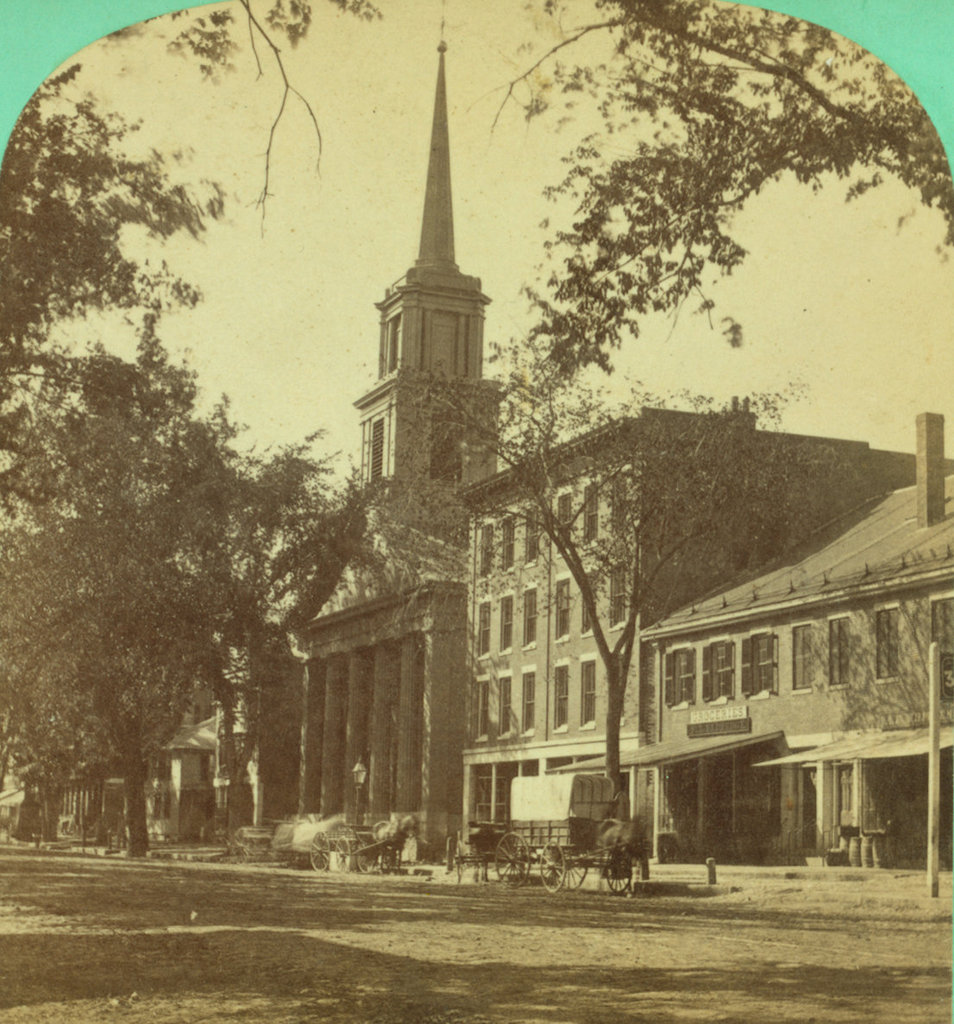
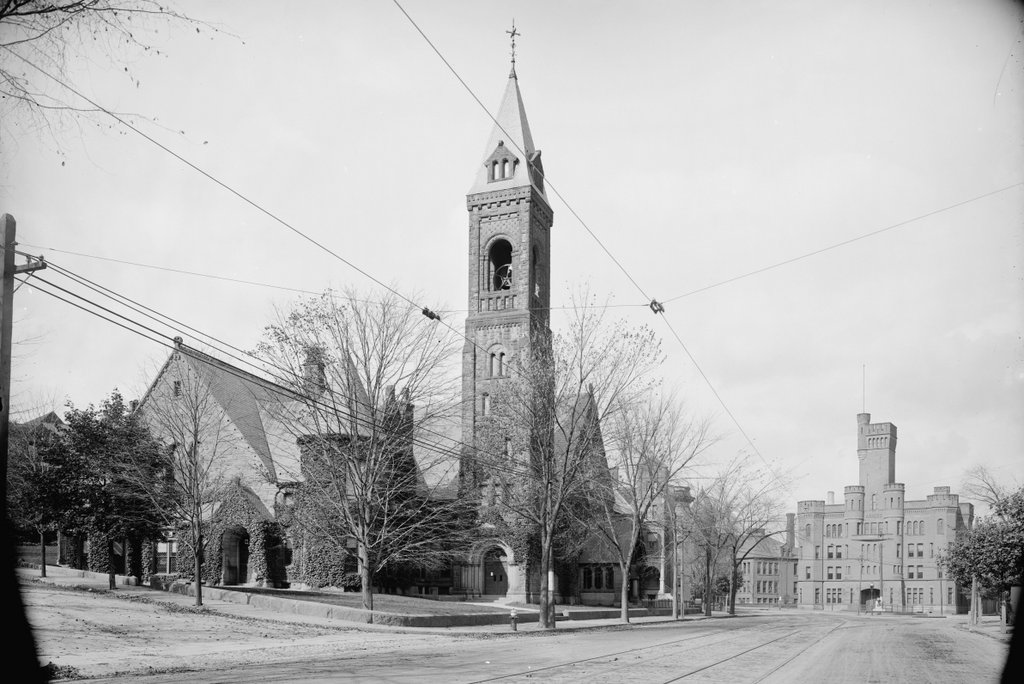
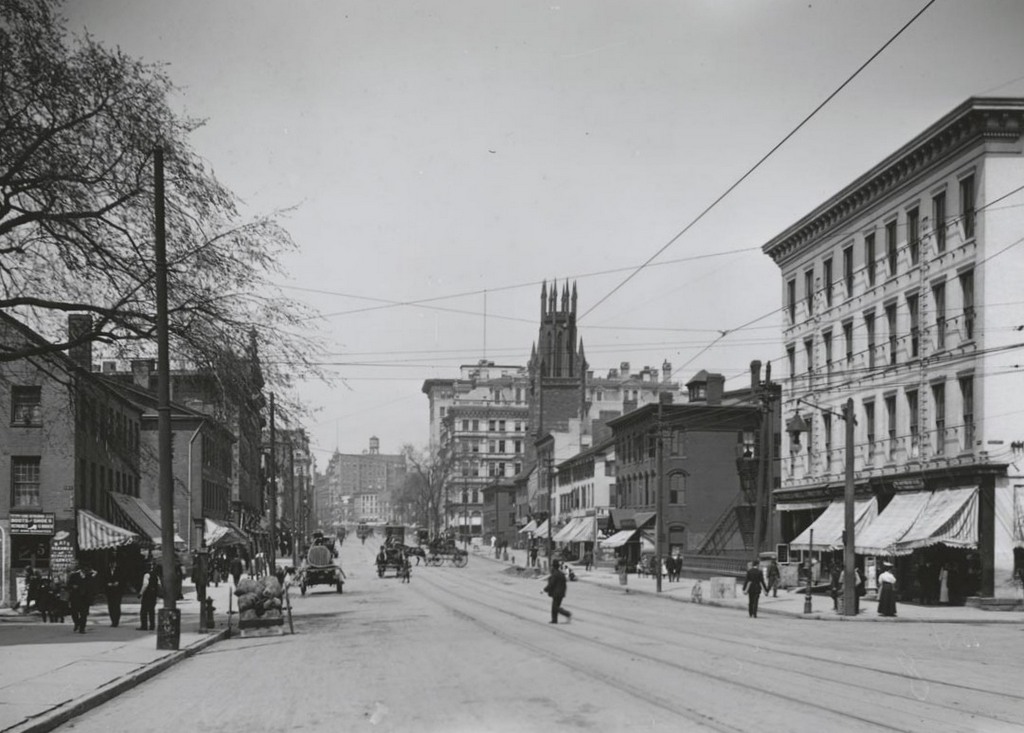
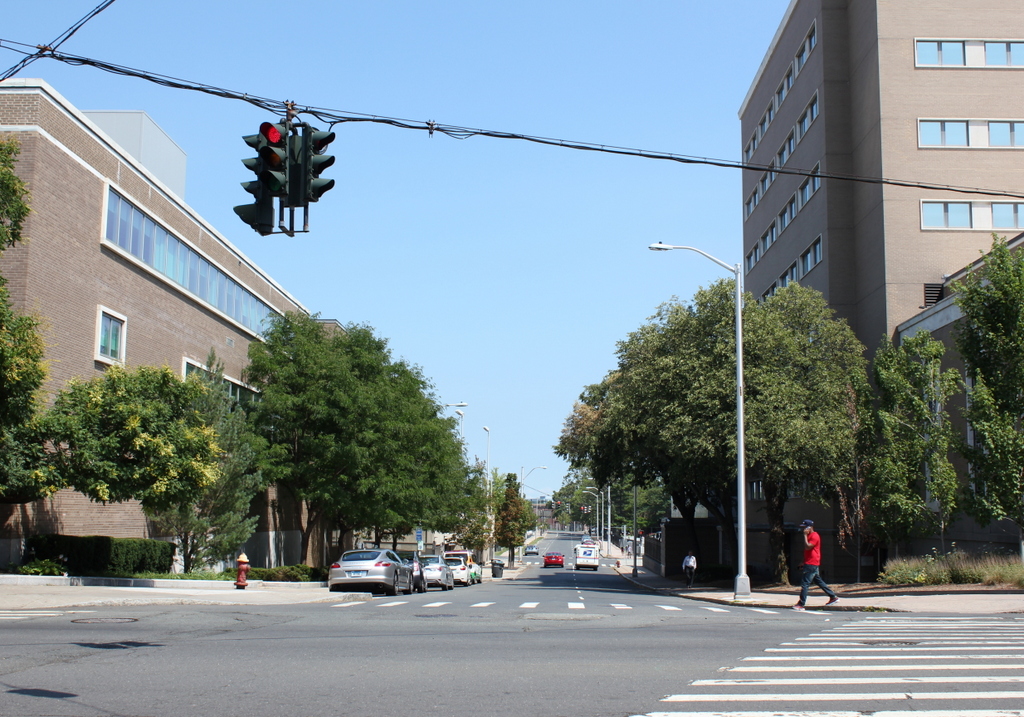
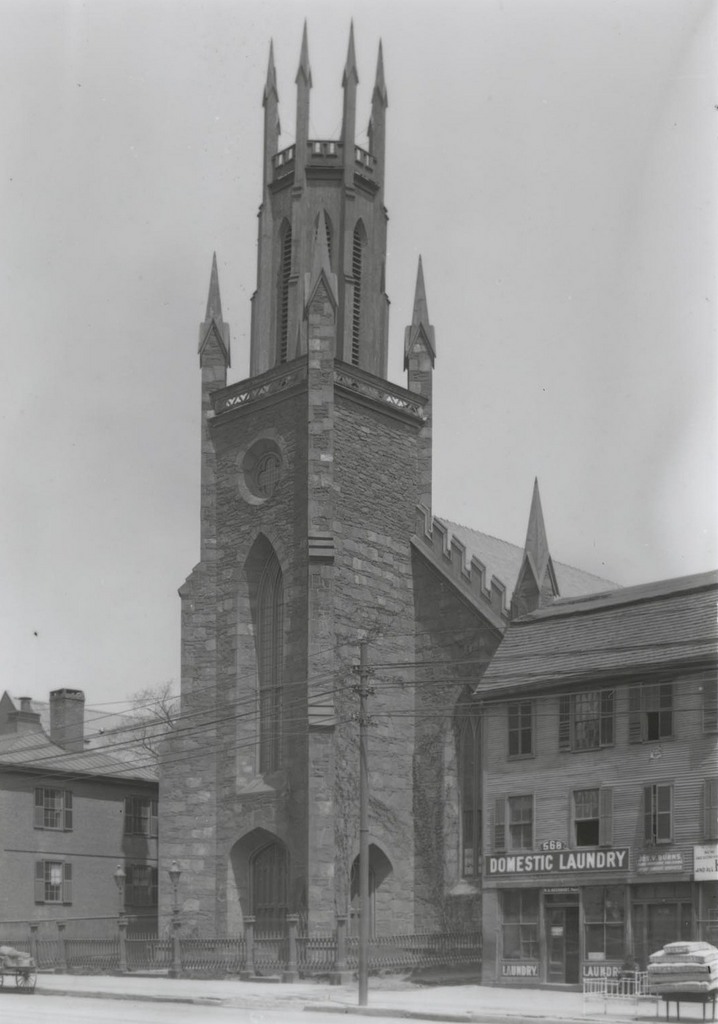Looking south along Main Street from near School Street in Worcester, with a view of the Calvinist Church building, sometime between 1865 and 1885. Image courtesy of the New York Public Library.
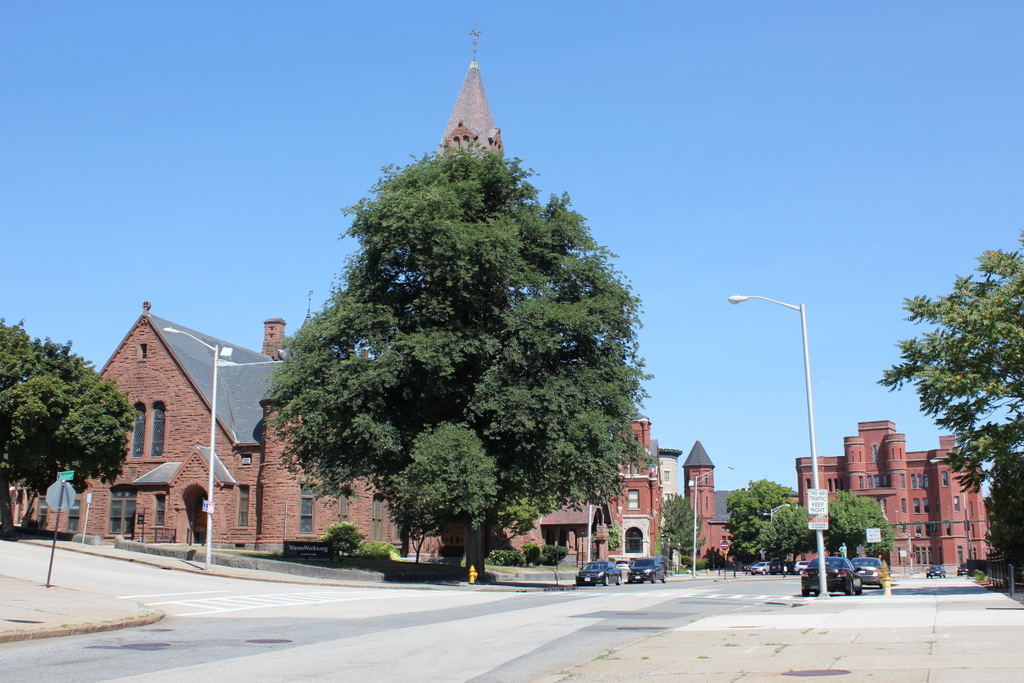
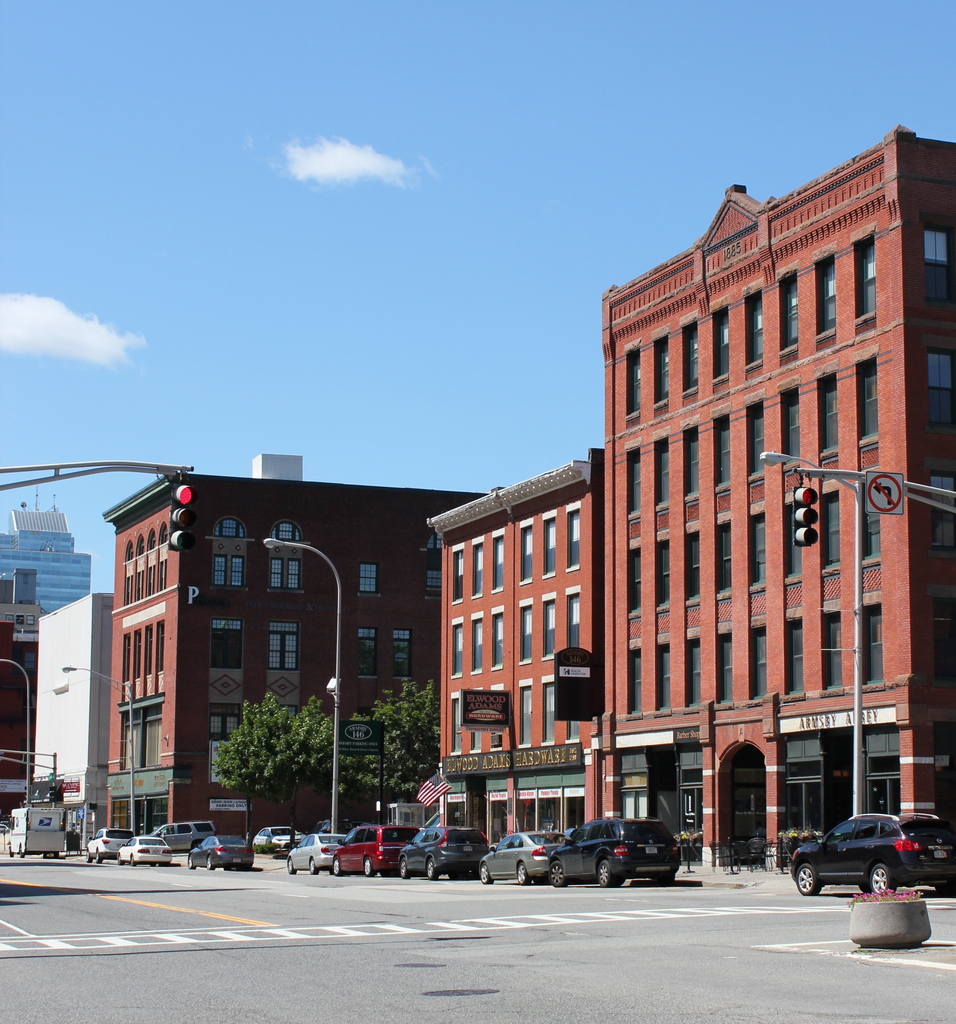
The scene in 2016:

Organized in 1820 after a split with the First Church, the members of the Calvinist Church met in different locations in Worcester until 1825, when this building was completed on Main Street, just North of George Street. It was built on the property of Daniel Waldo, a prominent local merchant who provided the land and paid the $14,000 construction costs. Architecturally, it fit in with the popular Greek Revival design of New England churches at the time, which most prominently included a portico with a triangular pediment, supported by large pillars.
Although located in the northern part of downtown Worcester, as the city grew this area became more commercially developed, as the first photo shows. Because of this, in 1885 the church moved into a new building a few blocks north of here, and the old 1825 building was subsequently demolished.
Today, the only building left from the first photo is the Elwood Adams Block, just to the right of the church. It was built in 1831 as a two and a half story commercial building, similar to the one next to it in the first photo, but in 1865 it was extensively renovated, adding two floors and an Italianate-style facade. At some point after the photo was taken, several other historic buildings were added to this scene. On the far right is the 1885 Armsby Block, and further down Main Street on the left side of the photo is the 1905 Thule Building. Along with the much older Elwood Adams Block, these buildings are all listed on the National Register of Historic Places.