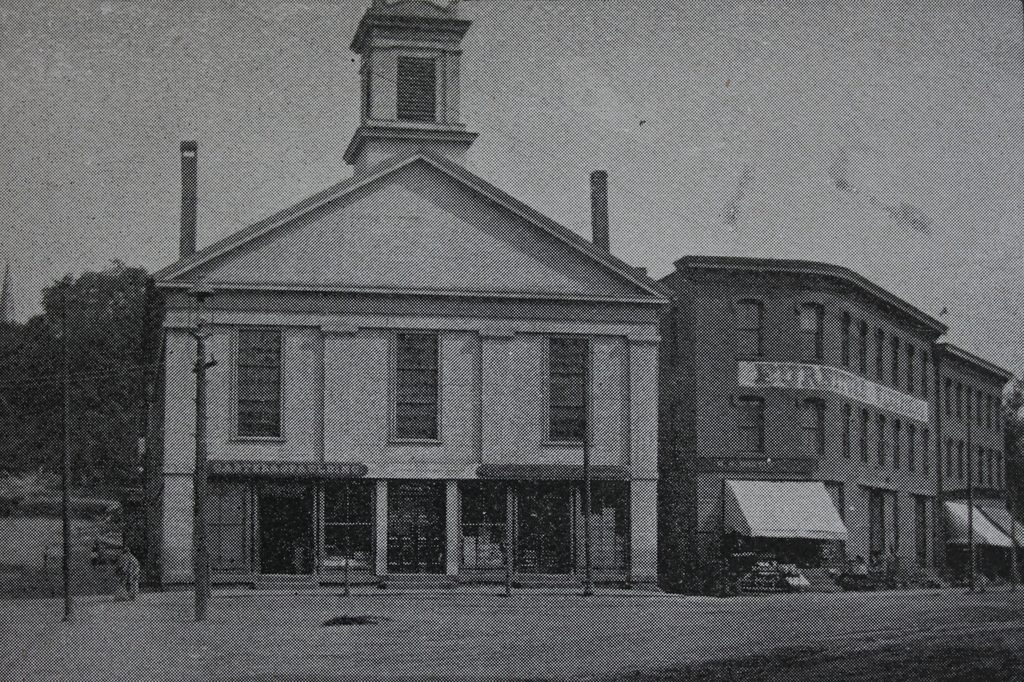
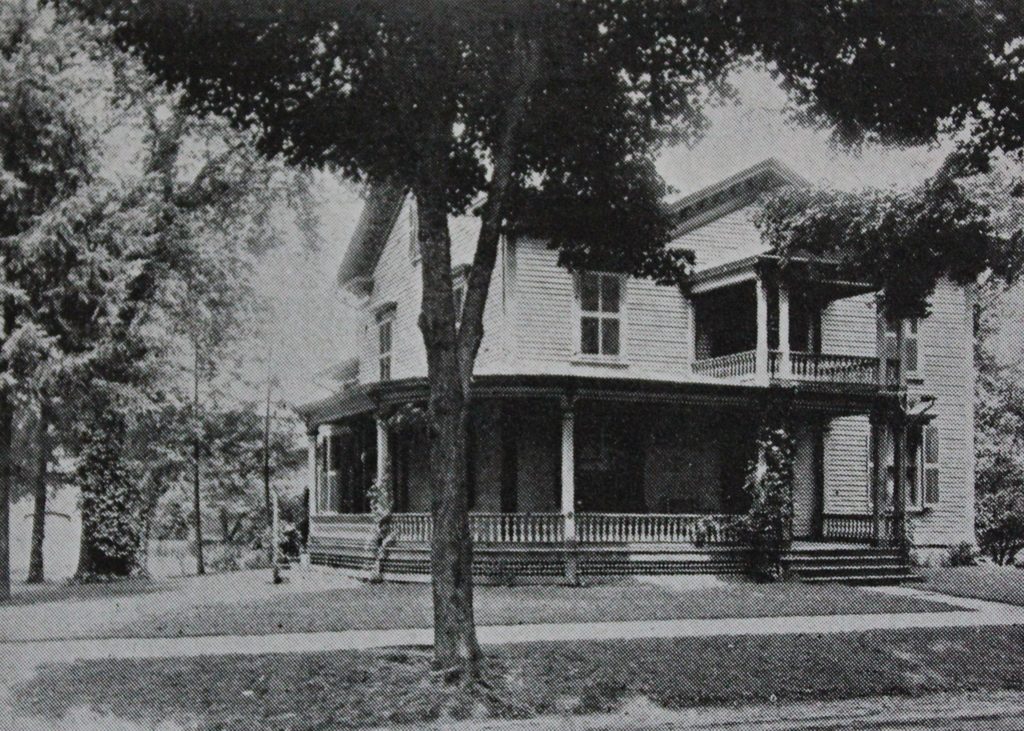
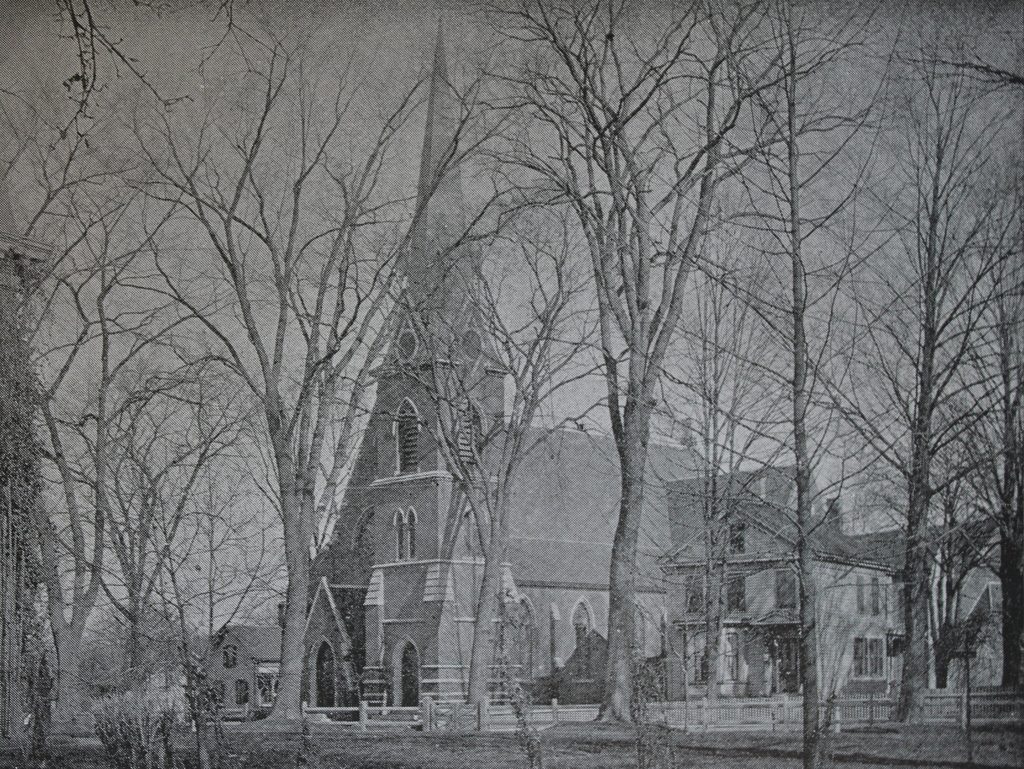The Grape Street School at the corner of Grape and Elm Streets in Chicopee, around 1892. Image from Picturesque Hampden (1892).
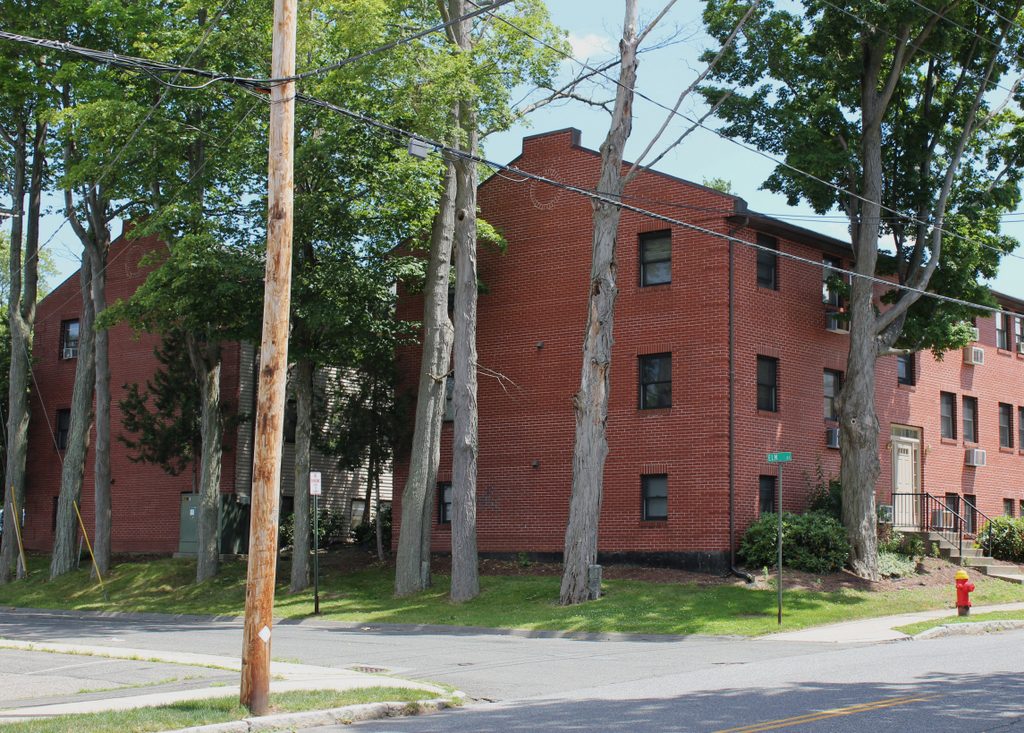
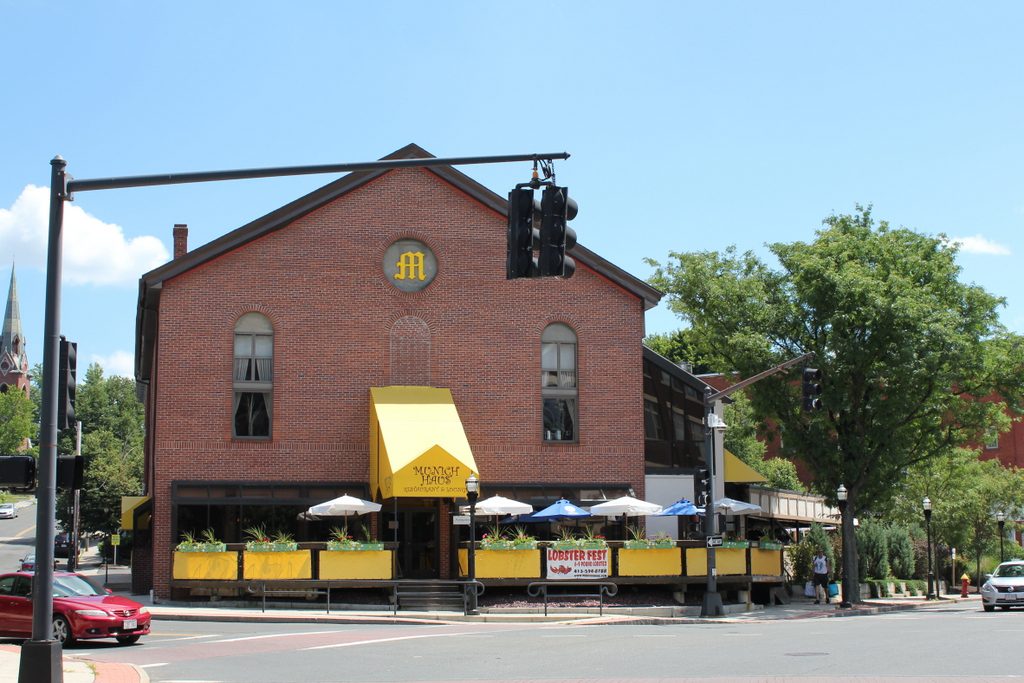
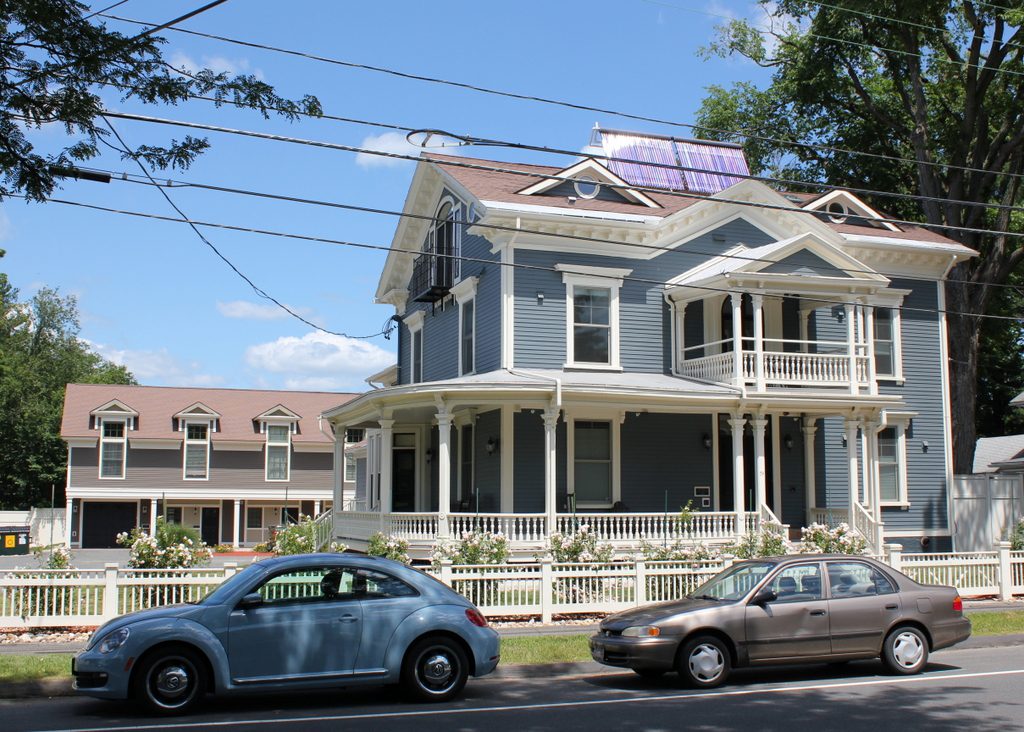
The scene in 2017:
During the mid-19th century, Chicopee developed into an industrial center, with factories in the villages of Chicopee Center and Chicopee Falls. Although situated less than two miles apart along the Chicopee River, these two villages were largely independent of one another, and for many years each had its own high school. The first high school was built in 1825 on Church Street in Chicopee Falls, and was replaced by a new building 20 years later. In the meantime, though, a second high school was opened in Chicopee Center in 1843, in this school building on Grape Street.
The Grape Street School had been completed a year earlier, and housed a primary school in the basement and the high school on the second floor. At the time, there were just two teachers in the high school, including a principal and an assistant. Thaddeus M. Szetela, in his 1948 History of Chicopee book, describes the layout of the high school: “There was one large assembly hall, equipped with desks for pupils, with a raised platform in front for the principal’s desk. There were blackboards and tables in the rear on which were a few reference books and magazines. There were openings off this platform to the north, three recitation rooms, one a library.”
This building continued to be used for Center High School throughout most of the 19th century. During this time, by far the longest-tenured and most prominent of its principals was George D. Robinson, who took the position in the fall of 1856. A native of Lexington, Massachusetts, Robinson was a 22-year-old Harvard graduate when he began working as principal, and remained here at the school until 1865, when he left to study law. He subsequently became a prominent lawyer and politician, serving as a Congressman from 1877 to 1884, and as governor of Massachusetts from 1884 to 1887.
Chicopee continued to have two high schools up until the fall of 1890, when Falls High and Center High were combined here at the school on Grape Street. A year later, a new high school building was built on Front Street, midway between the two villages, but the old Grape Street School continued to be used as a public school. It was subsequently renamed the Robinson School, in honor of its famous principal, and in 1899 a second school building was completed just to the right of it, known as the Valentine School.
The Robinson School remained in use well into the 20th century, but it was ultimately demolished in 1959 and an apartment complex was later built on the site. However, the neighboring Valentine School was used as a school into the 1980s, and it has since been preserved and converted into apartments. It stands just beyond and to the right of the apartment buildings in the 2017 photo, and it is listed on the National Register of Historic Places.