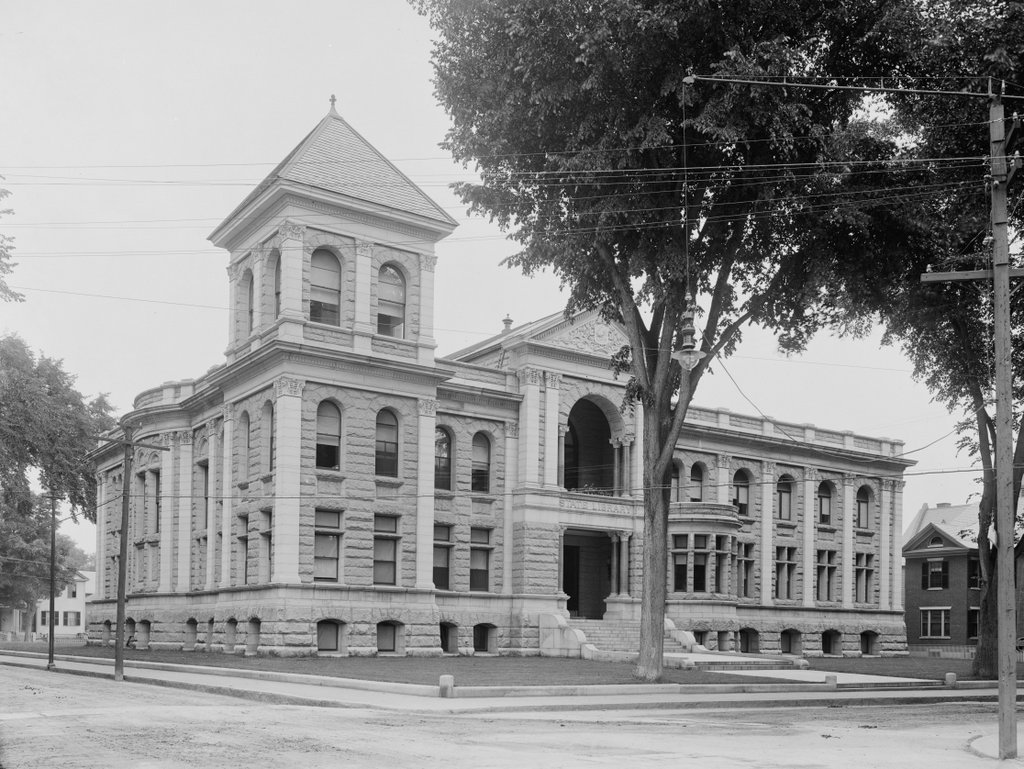
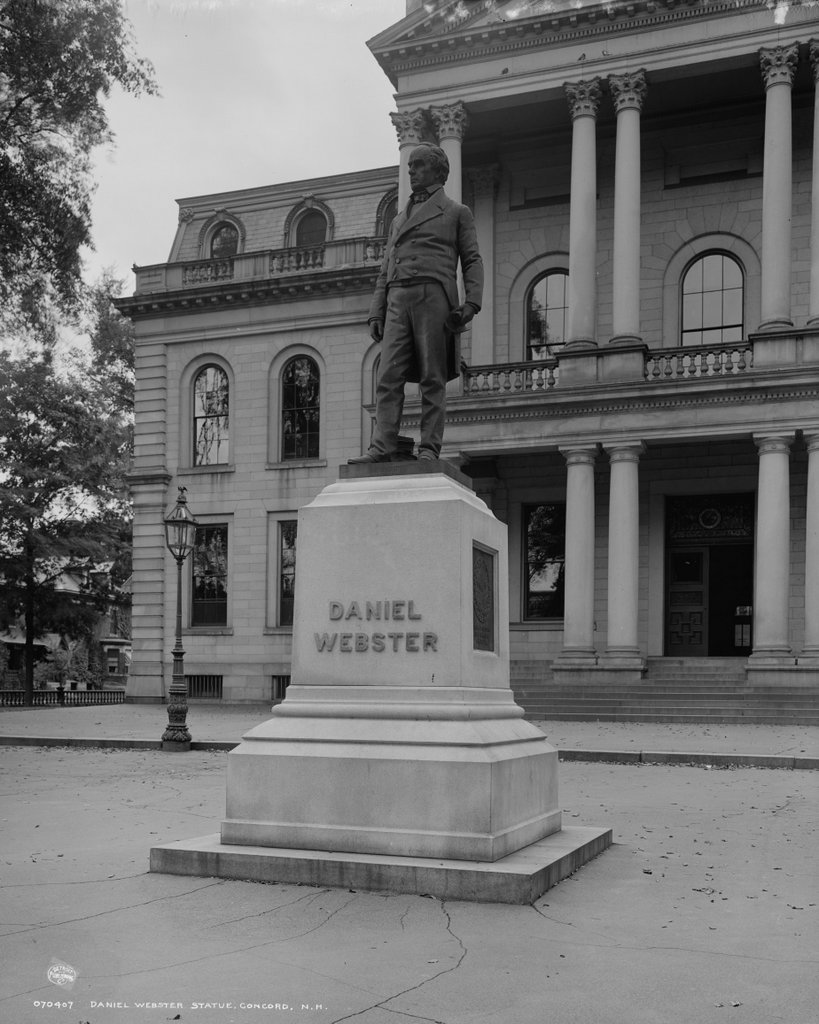
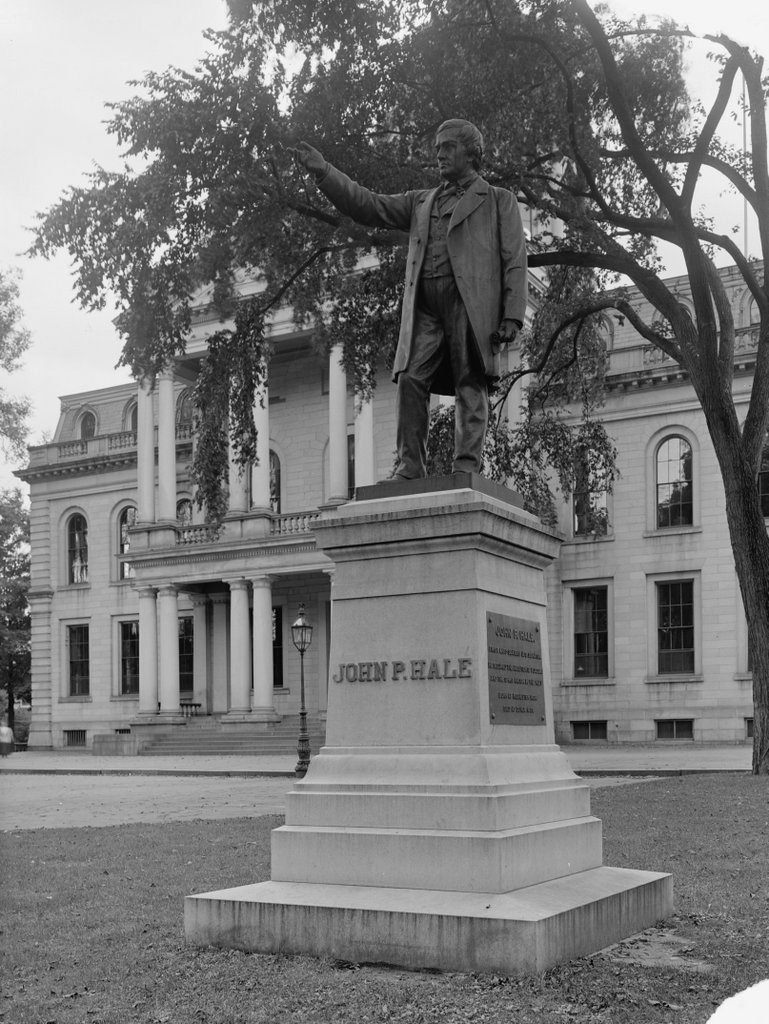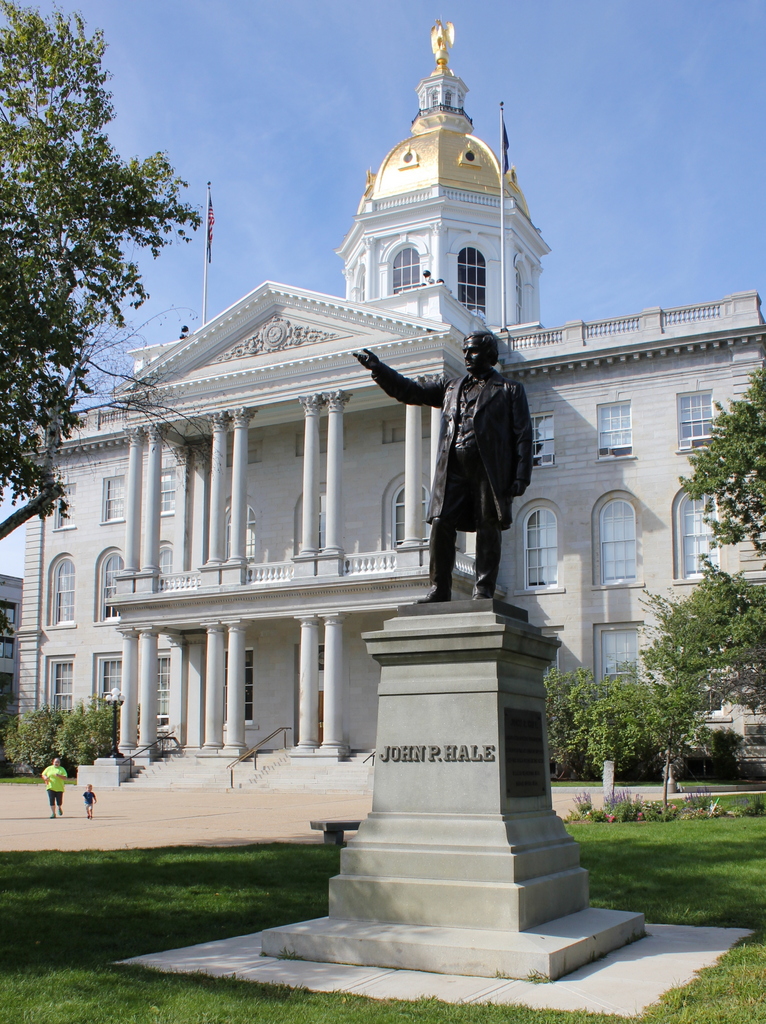The John P. Hale statue on the grounds of the New Hampshire State House in Concord, around 1900-1909. Image courtesy of the Library of Congress, Detroit Publishing Company Collection.
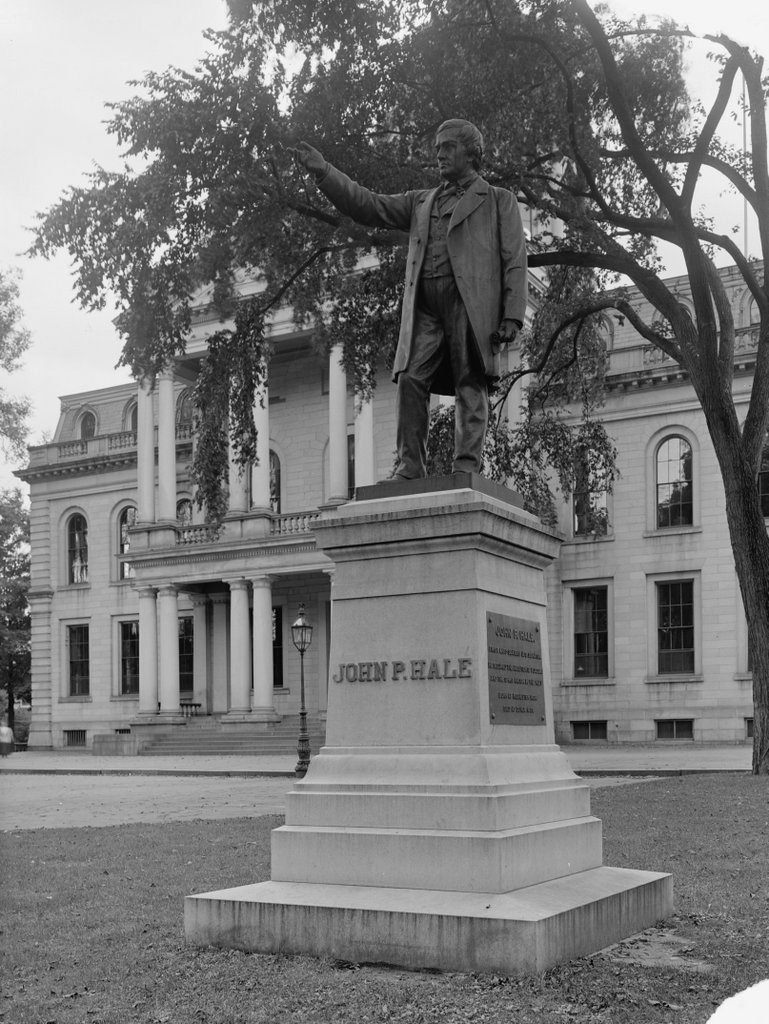
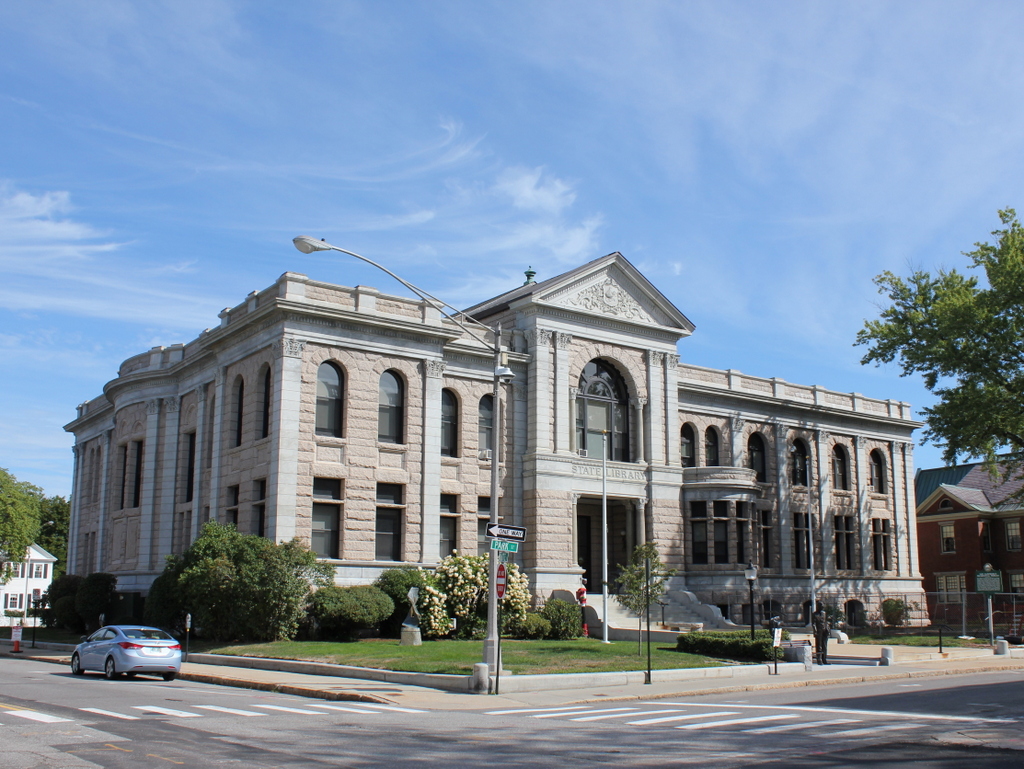
The statue in 2019:
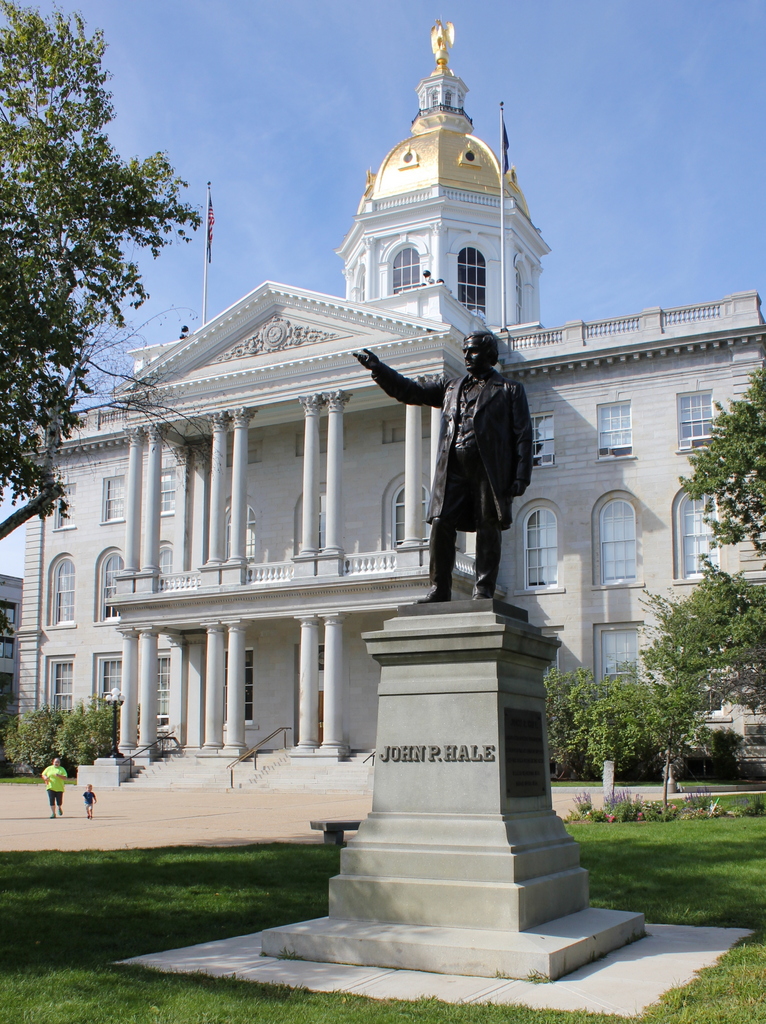
This statue of Senator John P. Hale is one of several on the grounds of the New Hampshire State House that honor famous New Hampshire residents. Although not as nationally-prominent as some of the others, such as Franklin Pierce and Daniel Webster, Hale was an important politician in the years immediately before and after the Civil War. He served for 16 years in the Senate, where he was a staunch opponent of slavery, and he later served as the U. S. Minister to Spain from 1865 to 1869.
Ironically, despite being a political ally of Abraham Lincoln, Hale inadvertently almost became the father-in-law of John Wilkes Booth. His daughter, Lucy Lambert Hale, was a leading socialite in Washington D.C., and she had many suitors, including Robert Todd Lincoln, whom Senator Hale hoped she would marry. Instead, though, she became secretly engaged to Booth, who was a successful actor at the time. They never married, and Booth was killed less than two weeks after he assassinated Lincoln, but Lucy’s photo was found on his body after he was killed.
Lucy Lambert Hale ultimately married William E. Chandler, a New Hampshire attorney and newspaper publisher who subsequently represented the state in the Senate from 1887 to 1901. During this time, he lobbied for a statue here on the State House grounds to honor his father-in-law, who had died in 1873. Chandler paid for the statue, and the state agreed to accept it and place it here in front of the northeast corner of the State House. The statue was designed by German sculptor Ferdinand von Miller, and it was cast in his foundry in Munich, the same place where the nearby Daniel Webster statue was cast several years earlier.
Hale’s statue was unveiled on August 3, 1892, in a ceremony that included addresses by William Chandler and Governor Hiram A. Tuttle. Other dignitaries included four former governors, along with members of the Hale and Chandler families, including John Hale’s widow and his daughter Lucy. The keynote speaker was Colonel Daniel Hall, a Civil War veteran from Hale’s hometown of Dover. His speech included an outline of the history of slavery in America and Hale’s opposition to it, noting that Hale had, early in his political career, “found his conscience and his whole better nature insurgent against the slave system.” These abolitionist sentiments are also expressed on the plaque at the base of the monument, which includes the claim that he was the “first anti-slavery U. S. Senator.”
The first photo was taken about a decade or so after the statue’s installation, and it has remained here ever since. Not much else has changed in this scene, with the exception of some alterations to the State House in the background. The building was renovated in 1909-1910 with a large addition to the rear, along with a third floor in place of the 1860s mansard roof. Otherwise, though, the State House looks much the same as it did when the first photo was taken more than a century ago, and it remains in use as one of the oldest state capitol buildings in the United States.