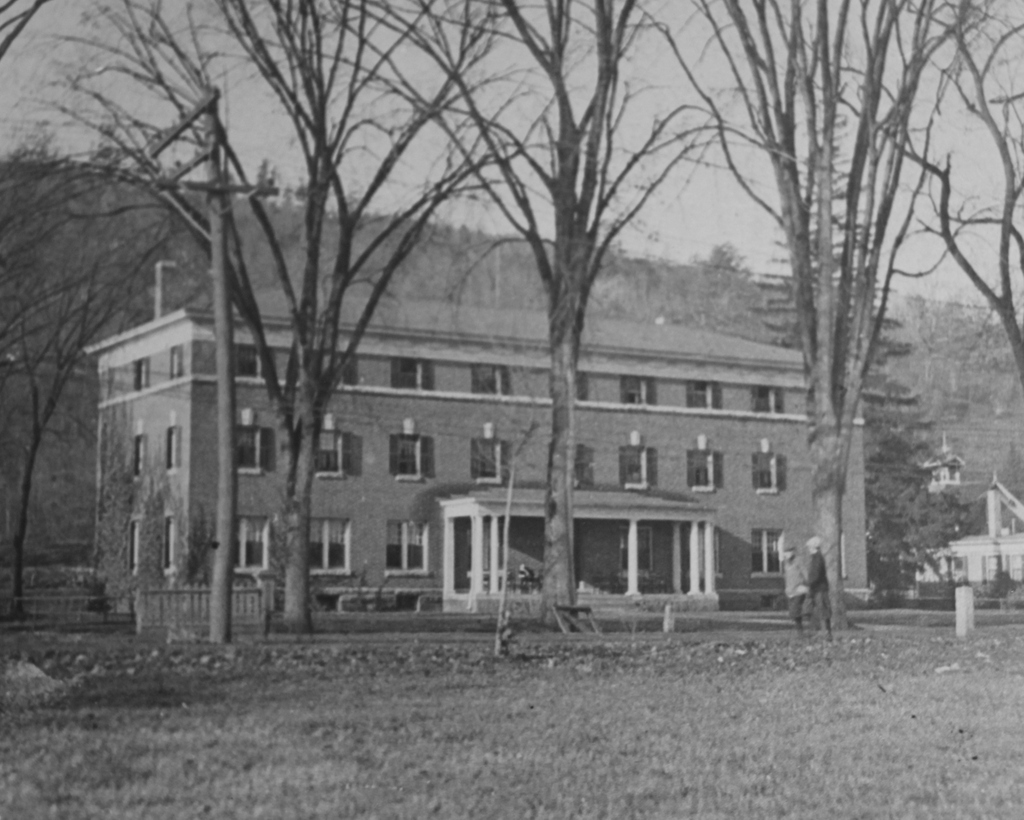
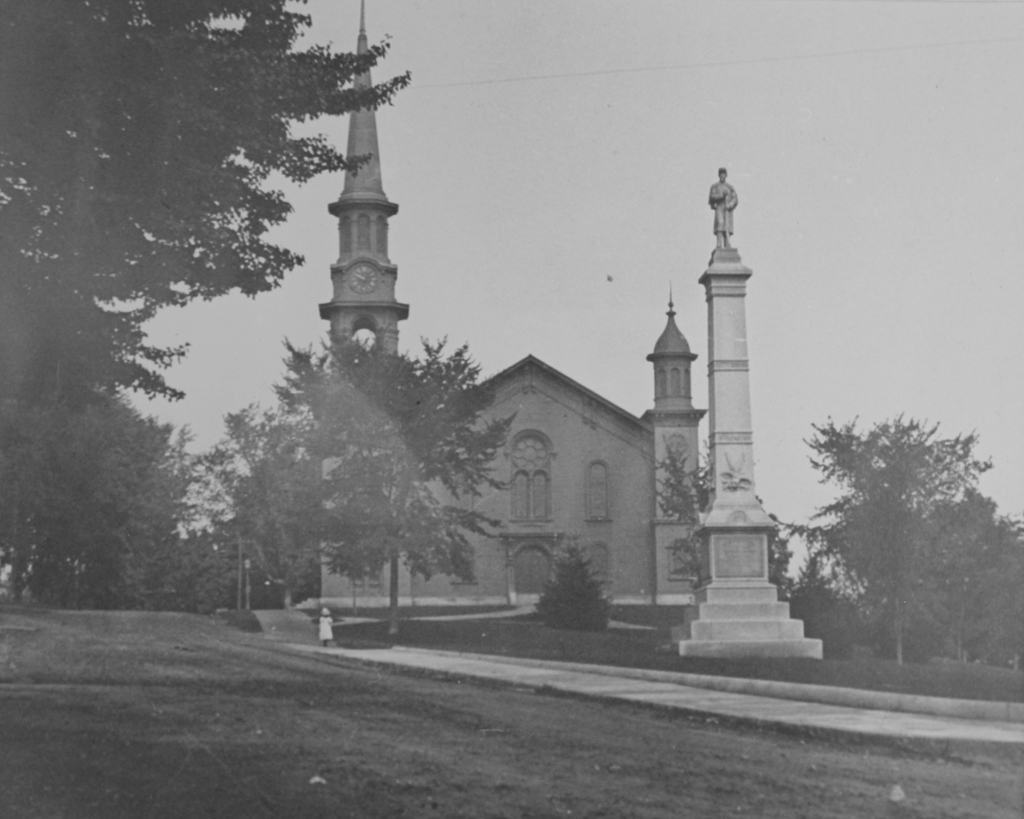
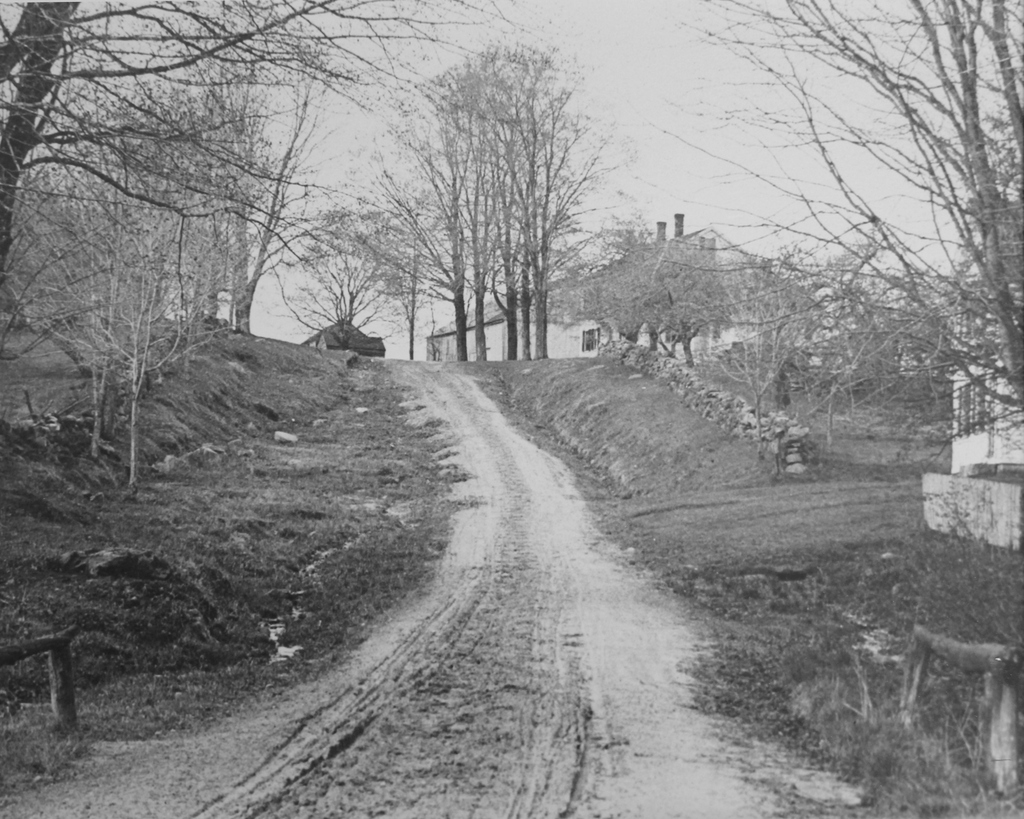
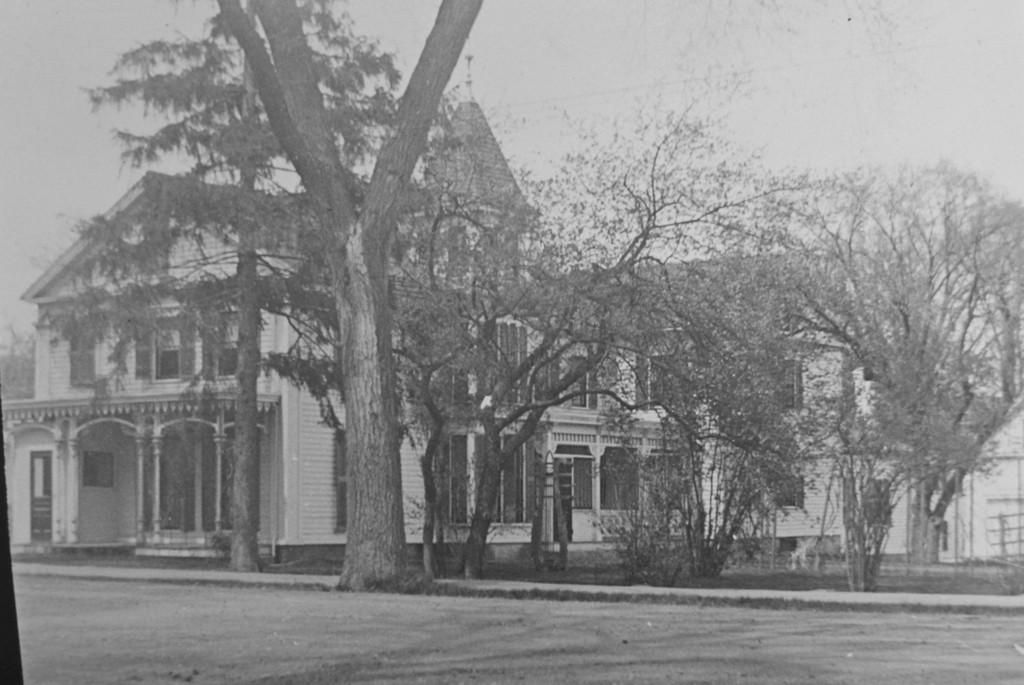Cushman Hall on Main Street in Monson, around 1904-1920. Image courtesy of the Monson Free Library.
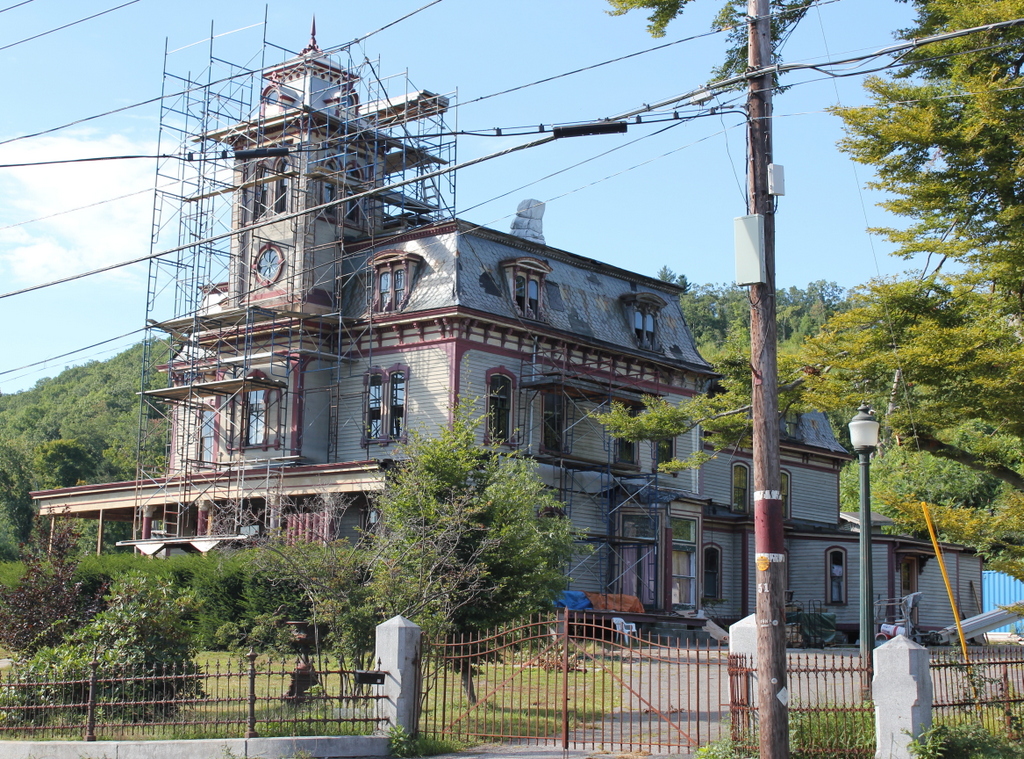
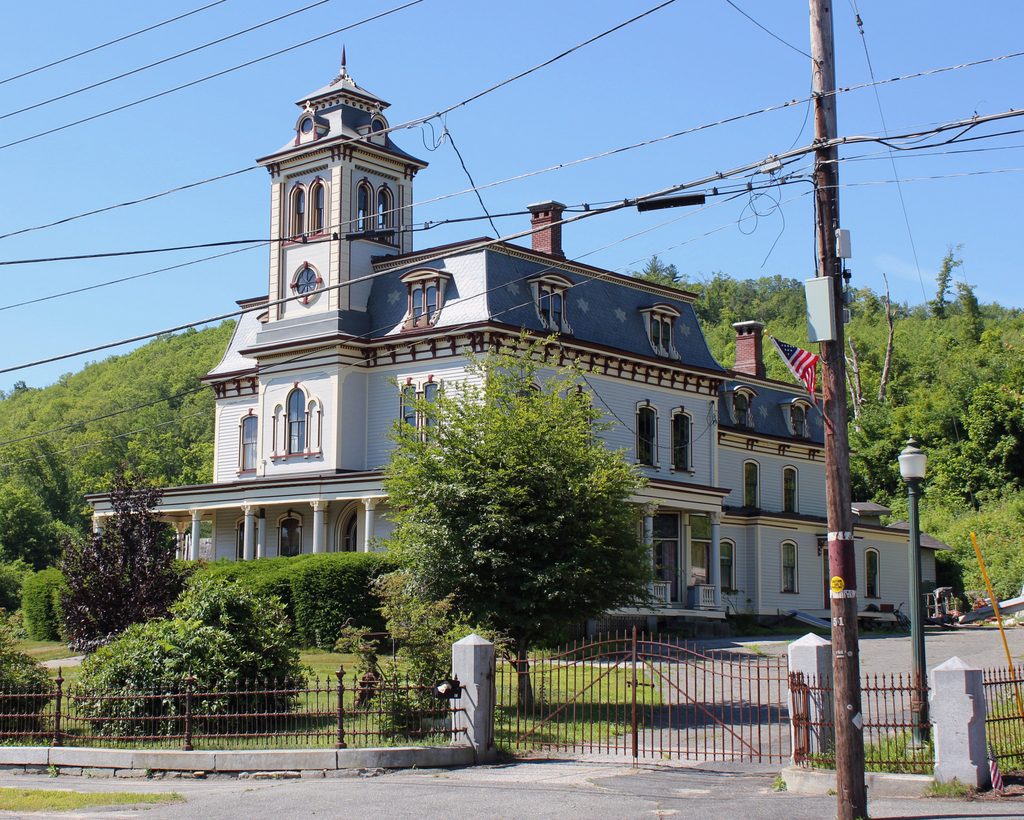
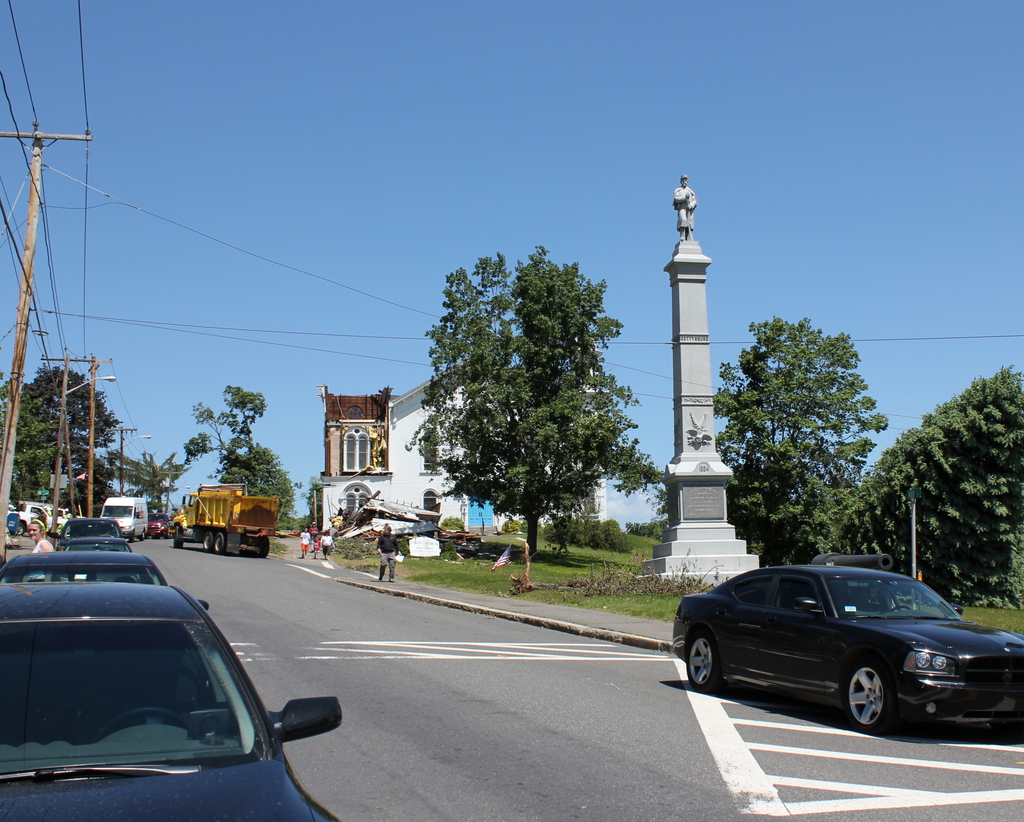
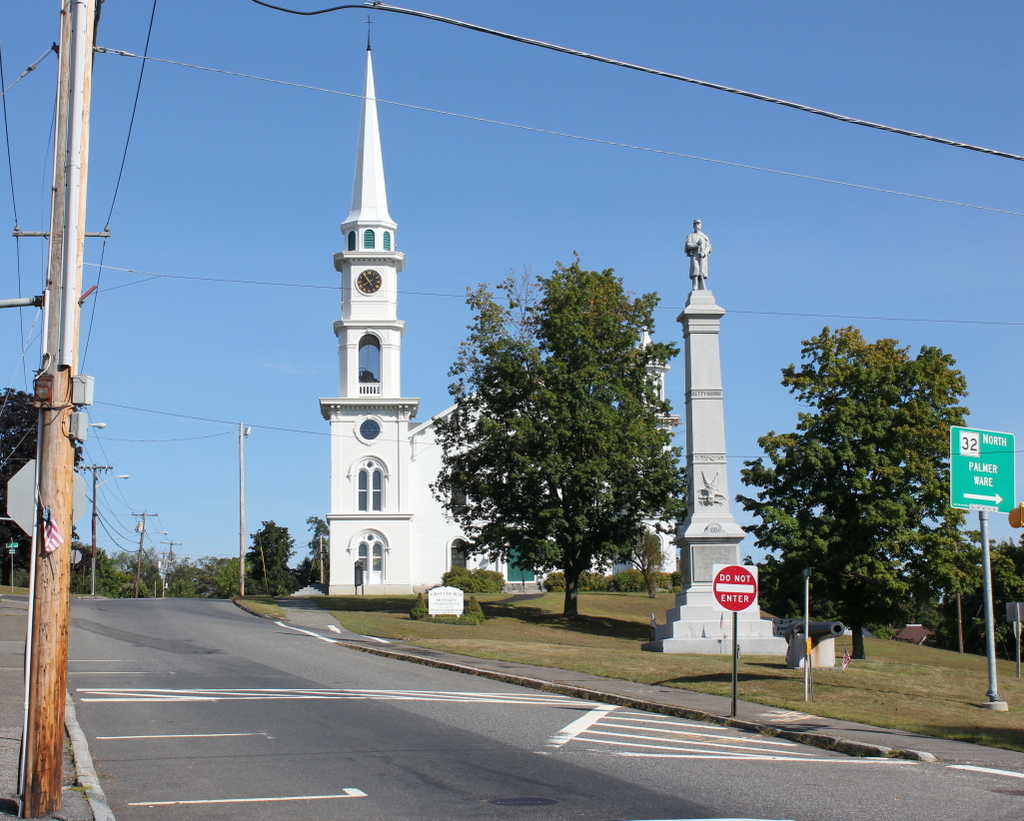
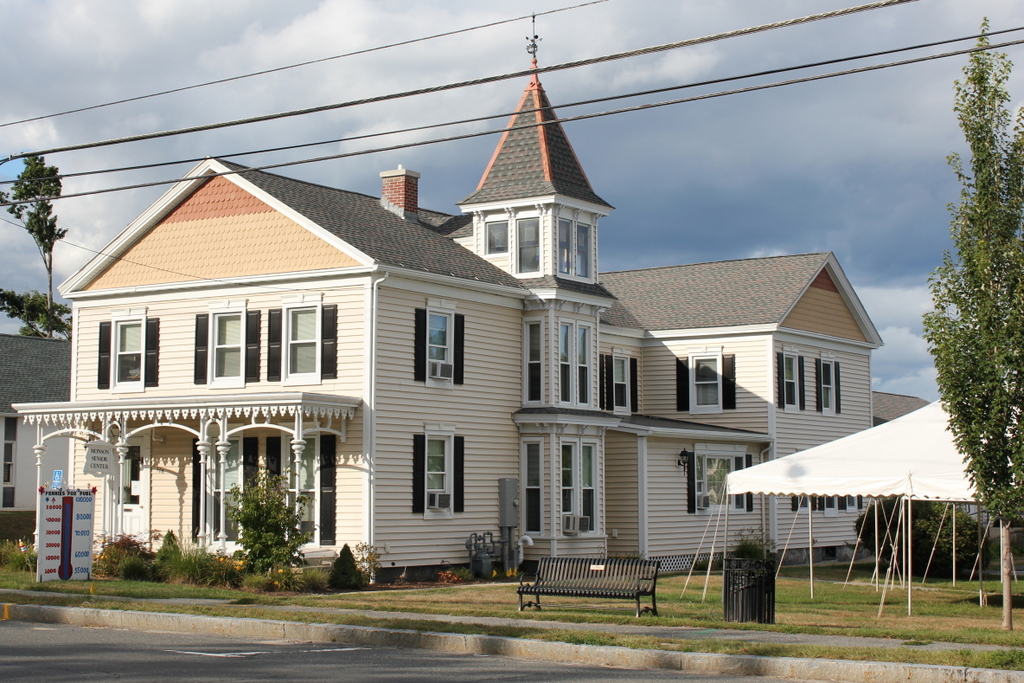
The building in 2015:
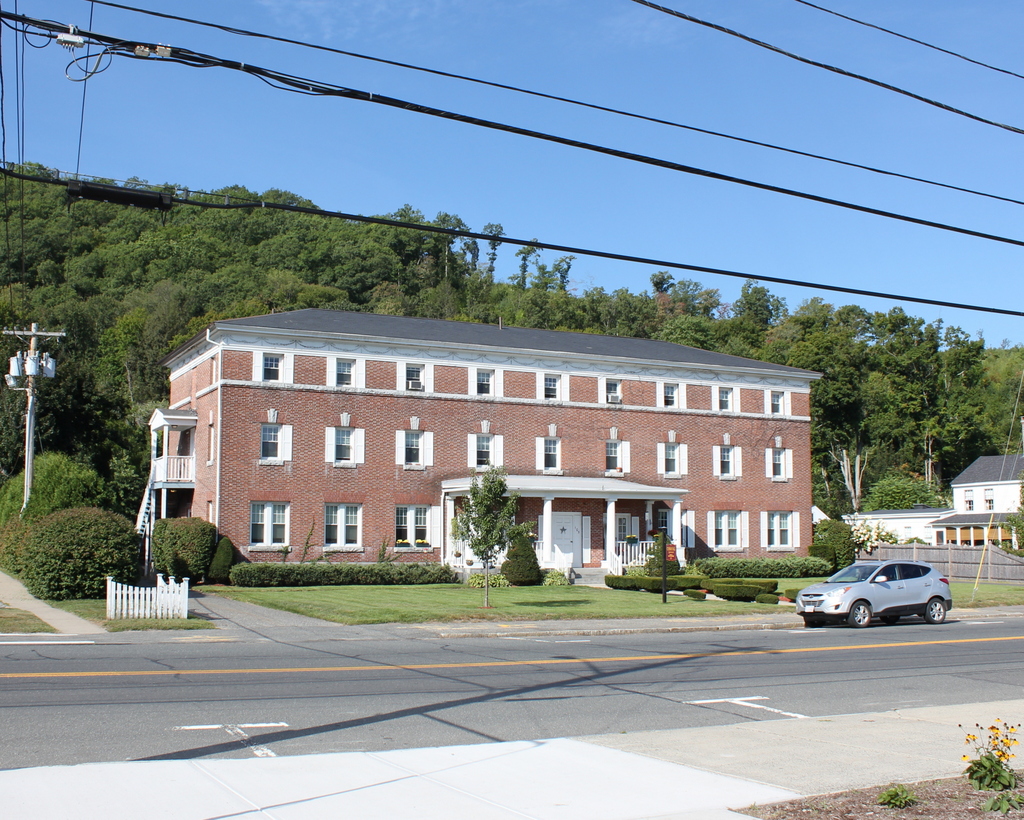

This former dormitory is the last surviving purpose-built structure from the old Monson Academy, which operated here in Monson from 1804 until it merged with Wilbraham Academy in 1971 and moved to their campus. Its construction in 1904 was funded by Thaddeus L. Cushman, and it was named in honor of his nephew, Frank Chapin Cushman, who died the year before at the age of 16.
After the school merger, the former dormitory became an apartment building, and it remains in use today. The 2011 tornado destroyed two of the last three surviving academy buildings, and directly across the street from Cushman Hall the Town Hall/former Monson High School building was damaged beyond repair. However, Cushman Hall sustained minimal damage, and today it is still an excellent reminder of the town’s educational history.