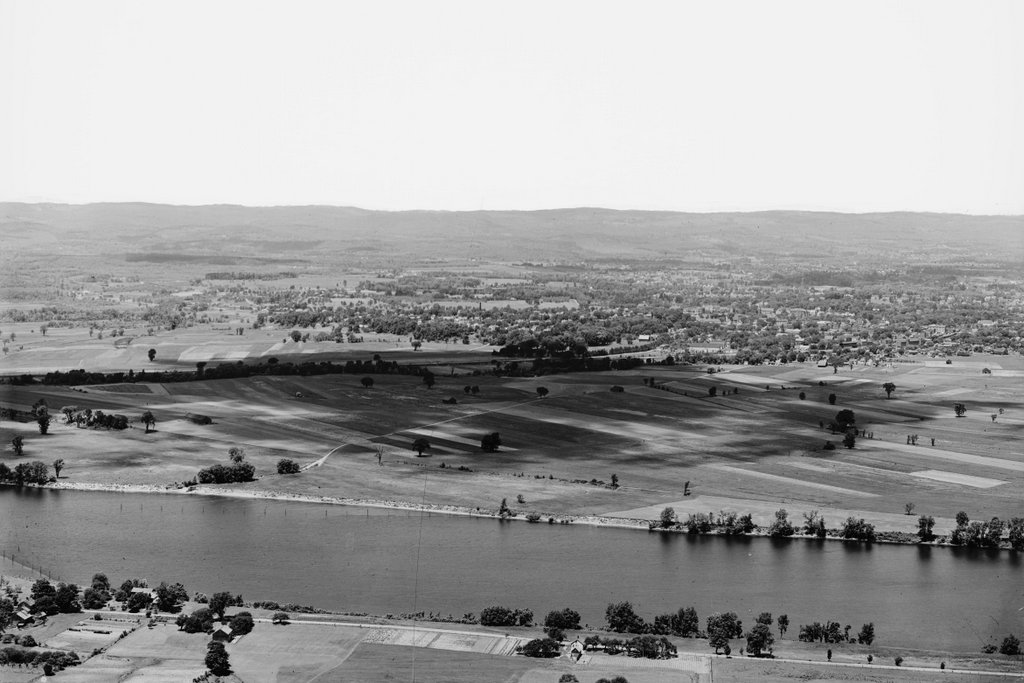
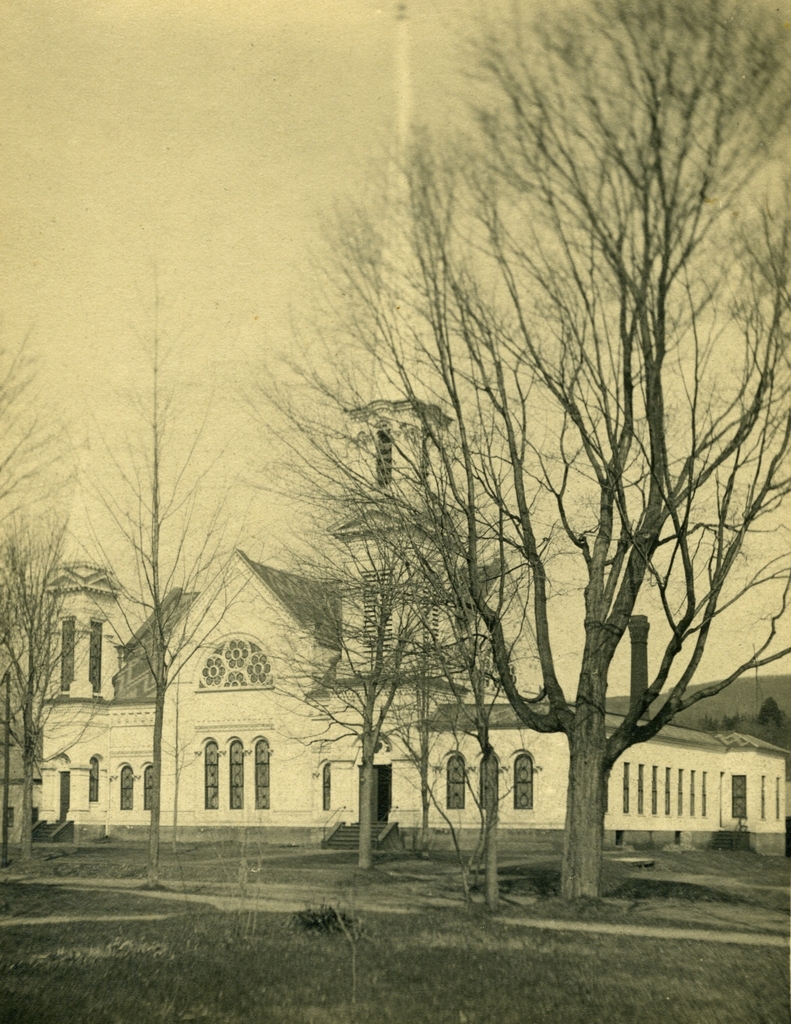
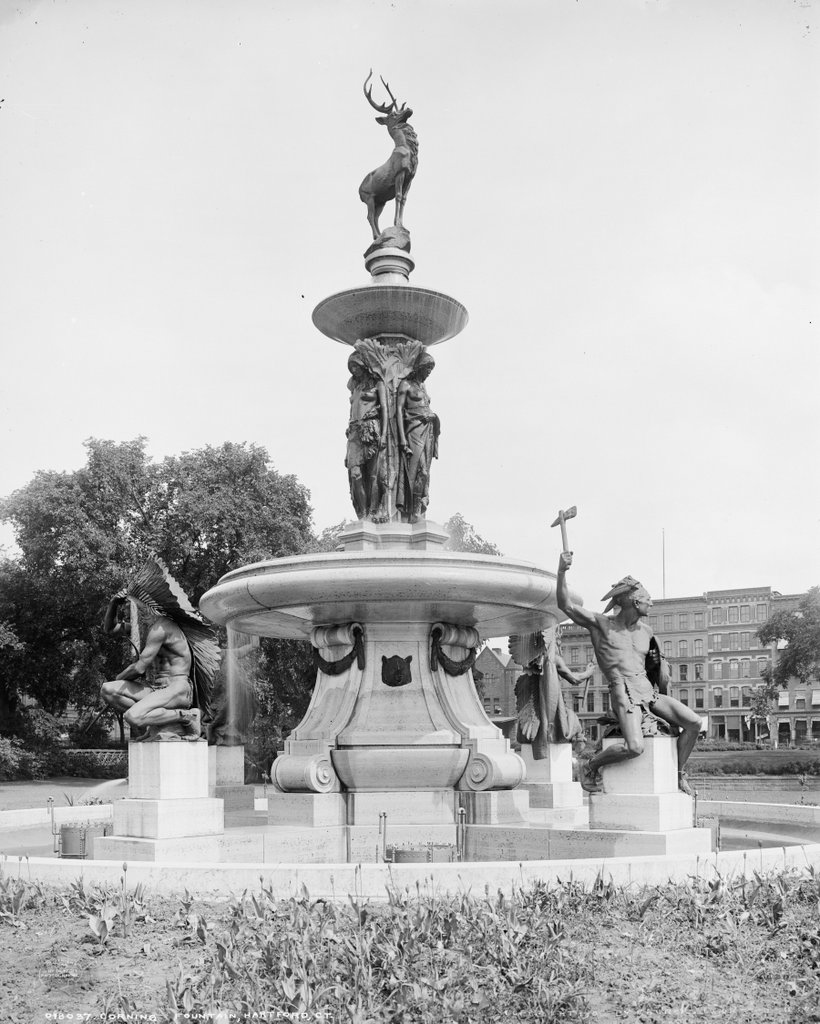The First Congregational Church on Main Street in Wilbraham, probably around 1900. Image courtesy of the Wilbraham Public Library.

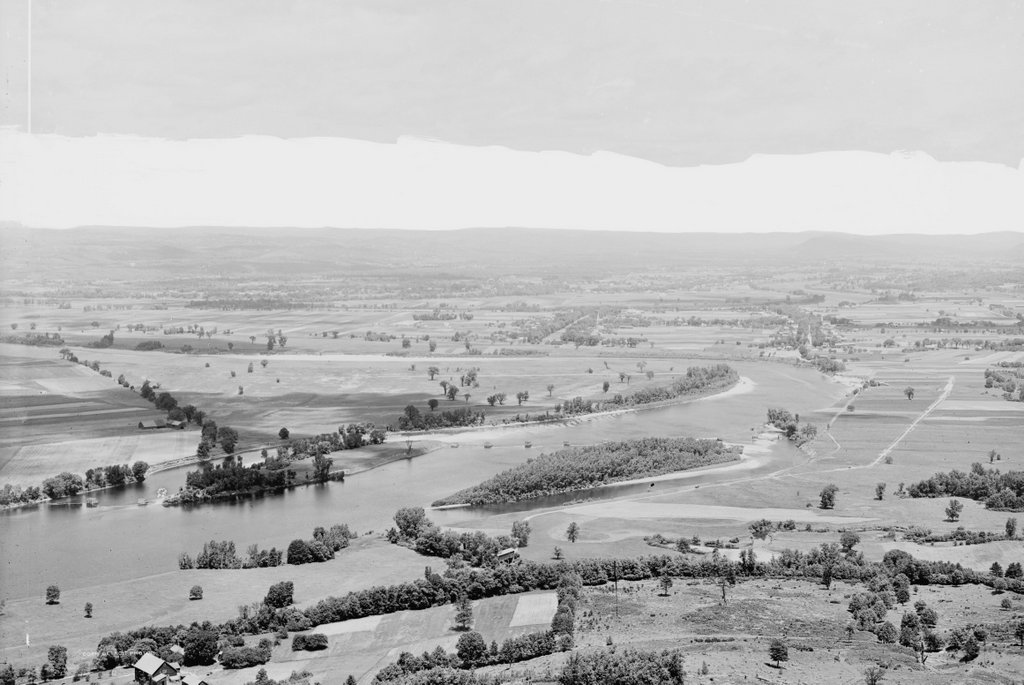
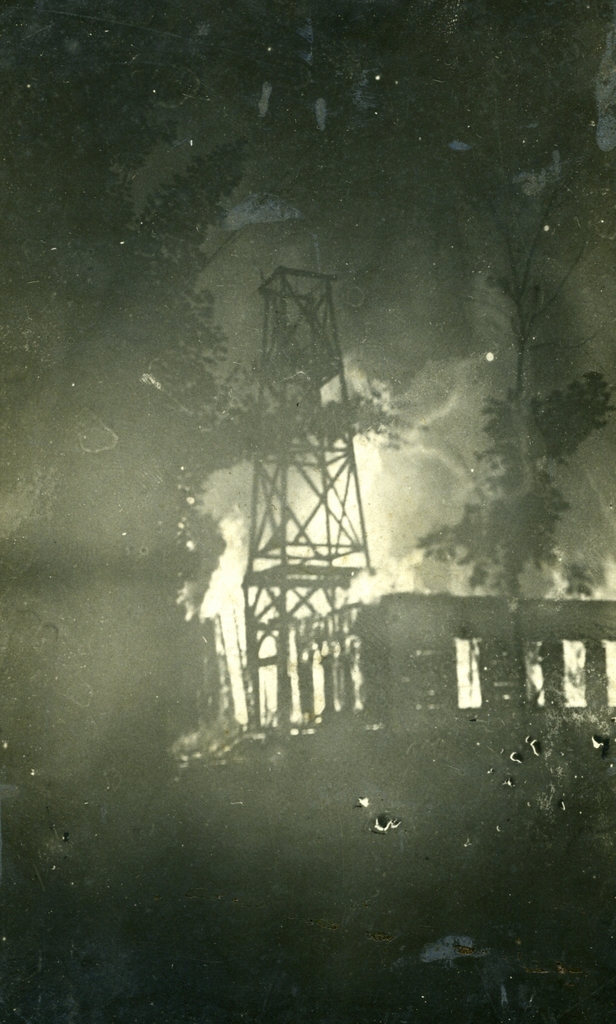
The church on fire after being struck by lightning on July 5, 1911. Image courtesy of the Wilbraham Public Library.

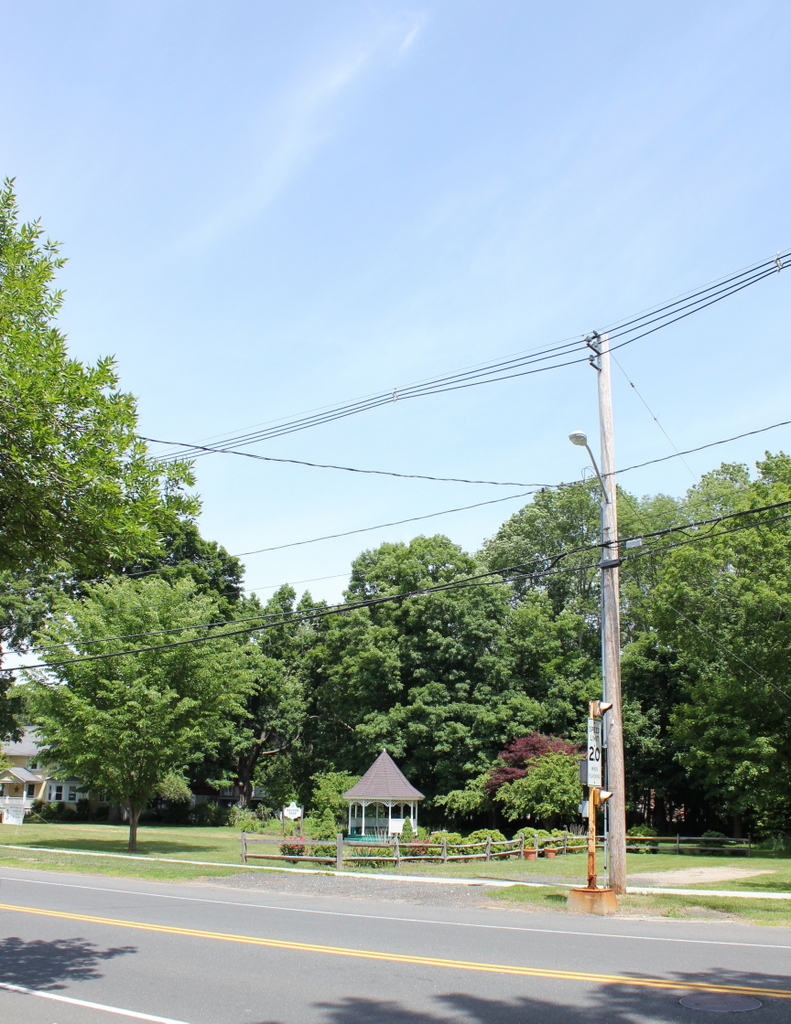
The site of the church in 2015:

In many New England towns, one of the main features of the town center is a historic 19th century Congregational church, usually painted white and complete with a tall steeple. However, that isn’t the case in Wilbraham, in part because of a series of fires that destroyed the first three meetinghouses that were located on this site. The First Congregational Church in Wilbraham was established in 1741 as an offshoot of the Springfield church. As was the case in many other towns, however, the location of the meeting house became a major political issue. In the days before automobiles, it was particularly advantageous to live near the meeting house, and in Wilbraham the settlers in both the northern part of town (present-day Wilbraham) and the southern part (present-day Hampden) wanted a meeting house location that was convenient for them. Eventually, a compromise was reached and the meeting house was built on Wigwam Hill, halfway up a mountain in a sparsely-populated location that presumably only worked because it was equally inconvenient to everyone.
Eventually, however, it began to make sense to have a meeting house in the center of town, so in 1794 the church moved to this location on Main Street. It wasn’t just the congregation that moved, though. In true Yankee frugality, the building itself was moved down the mountain and over to this site, where it stood until 1857, when a new church building was completed. The old meeting house was moved and used as a stable until 1877, when both generations of Wilbraham churches were destroyed in a fire.
The third meeting house, which is shown in the first photo here, was completed in 1878 and was used until 1911, for reasons that the second photo makes very clear. On July 5, 1911, the steeple was struck by lightning, and the resulting fire consumed the entire church. I don’t know how long it had been burning by the time the photograph was taken, but it is a ghostly image, with the skeletal remains of the steeple silhouetted against the flames in the background.
Following the fire, the church merged with the Methodist church to form the Wilbraham United Church. They alternated between the rebuilt church at this site and the Methodist church next to the Wilbraham Academy campus until 1935, when the church here became their full-time home. However, the congregation began to outgrow that building, so a fifth-generation Wilbraham church was built a short distance away in 1958; this building is still in use today. The 1911 church was demolished in 1962, and today the site of the first four Congregational churches in Wilbraham is now a public park.