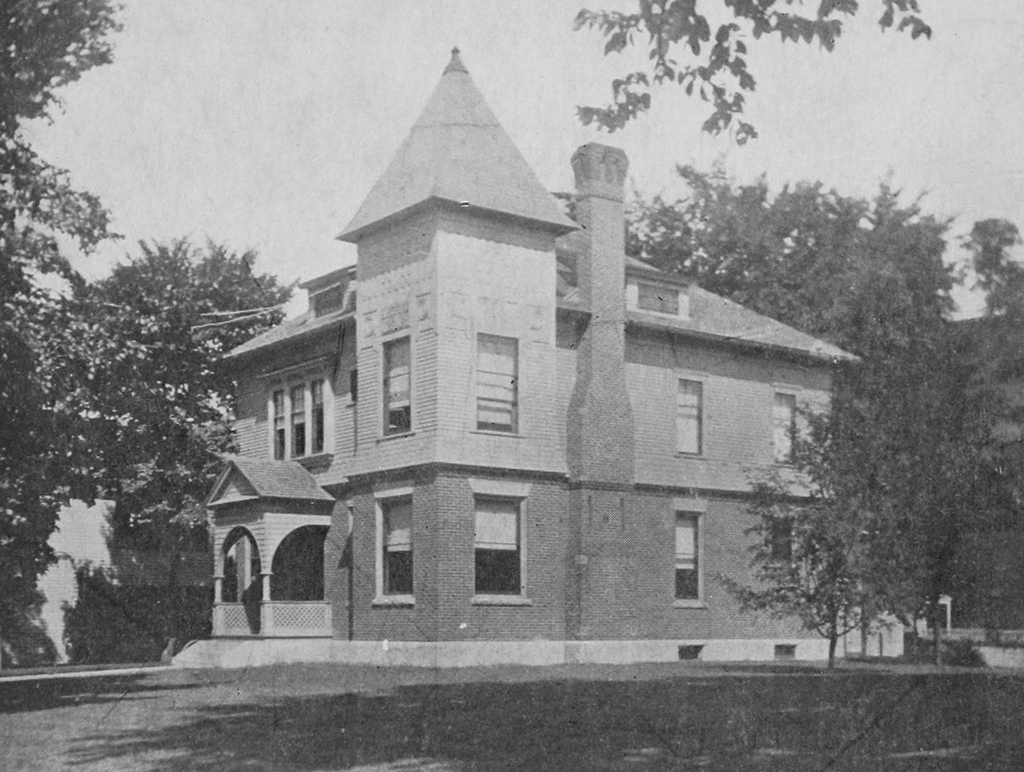
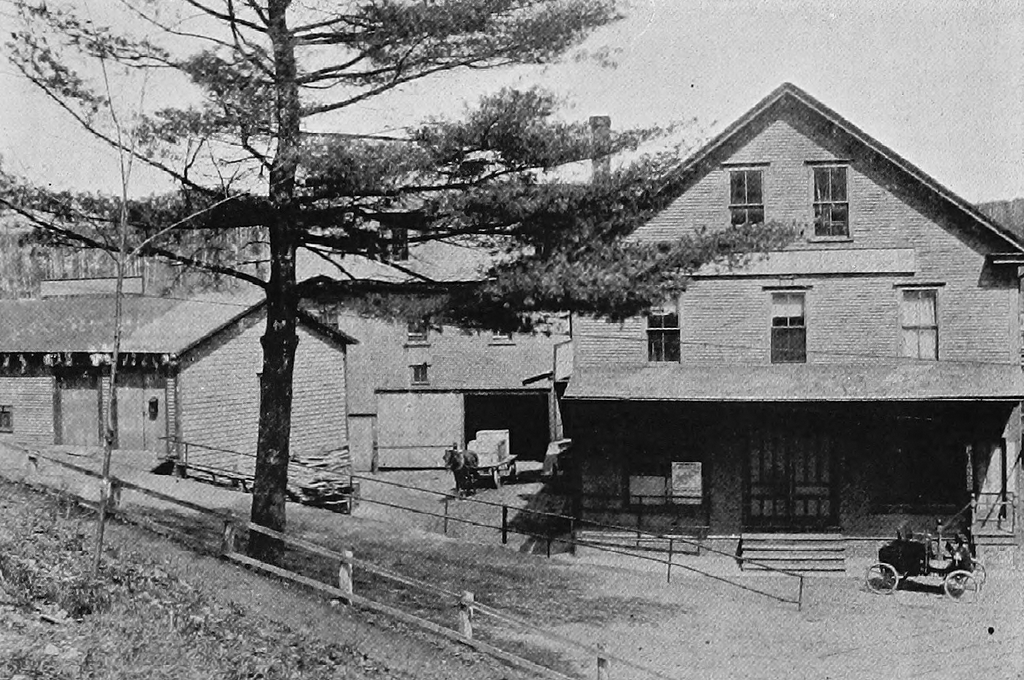
The Hartford Library on Main Street (now named Maple Street) in Hartford, around 1900. Image from The Old and the New.
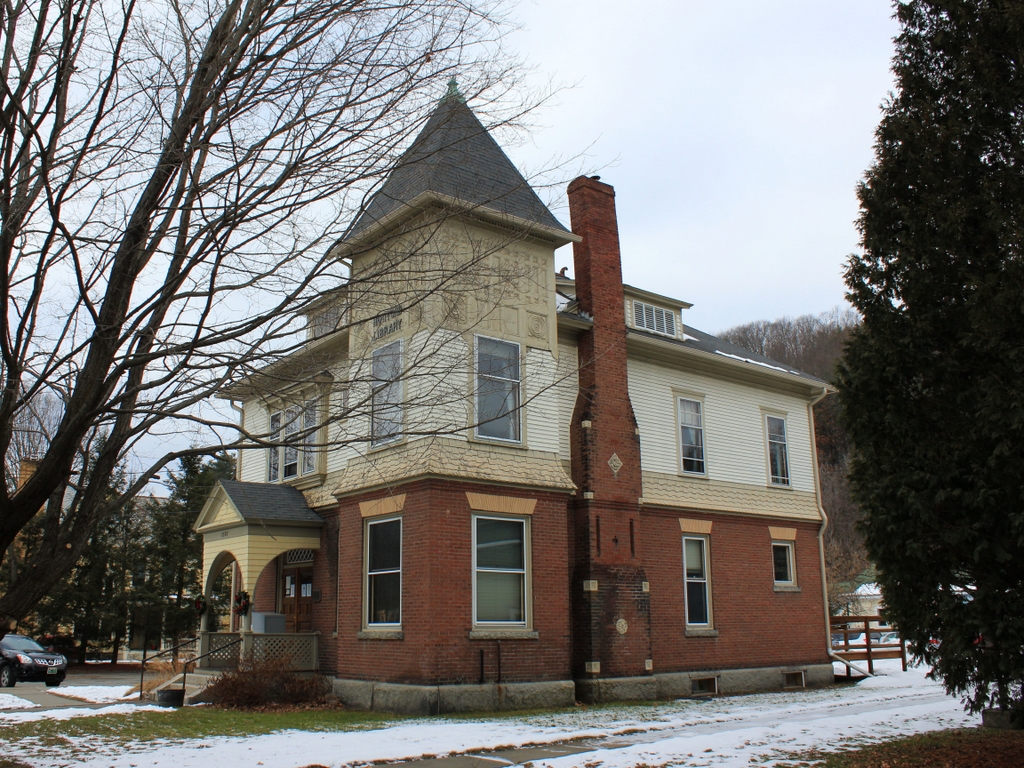
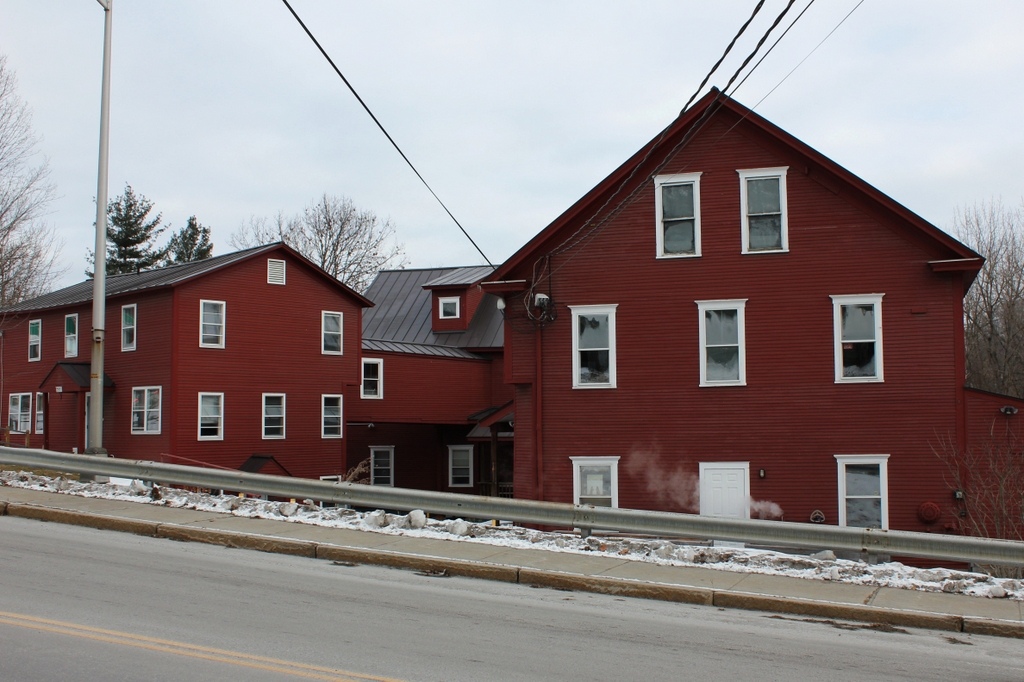
The building in 2018:
This Queen Anne-style library building was constructed in 1893, in the center of the village of Hartford. It was built thanks to the efforts of several prominent locals, including Horace and Seraph Pease, who donated a parcel of land adjacent to their home, and Ephraim Morris, a woolen manufacturer who gave $5,000 to construct it.
The library was dedicated on September 16, 1893, in a ceremony that included remarks by former governor and Civil War Medal of Honor recipient Samuel E. Pingree. He was a Hartford resident and one of the founders of the library, and he also served on its board of trustees. His comments were followed by the keynote speaker, Dartmouth College President William Tucker, who spoke on “Uses of a Library.”
Upon completion, the library consisted of a reading room on the first floor, and a lecture room, known as Library Hall, on the second floor. At the time, it had about 2,000 books in its collections, but by the early 20th century it had grown to some 4,000. A total of 4,503 books were checked out from the library in 1908, and during its first 15 years in operation the library served 1,550 different patrons here.
The first photo was taken around this time, but very little has changed here in this scene more than a century later. It remains in use as a public library, with around 17,000 items in its collections today, and it is now one of four libraries in the town of Hartford. The exterior of the building has remained well-preserved throughout this time, and in 1994 it was added to the National Register of Historic Places. Four years later, it also became a part of the Hartford Village Historic District, which encompasses many of the buildings here in the traditional town center of Hartford.