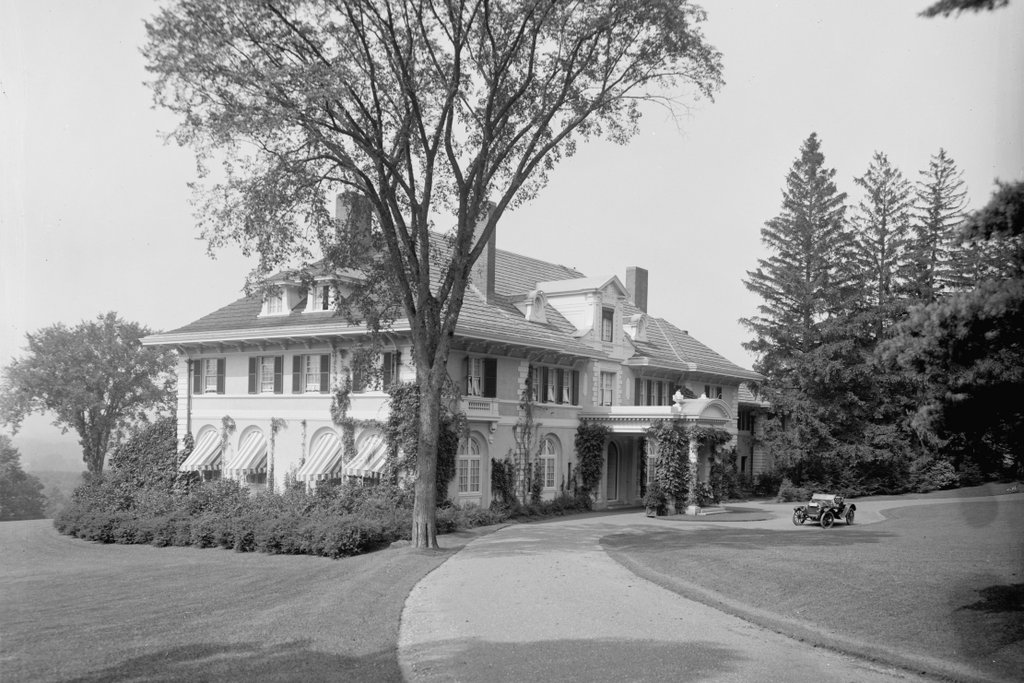
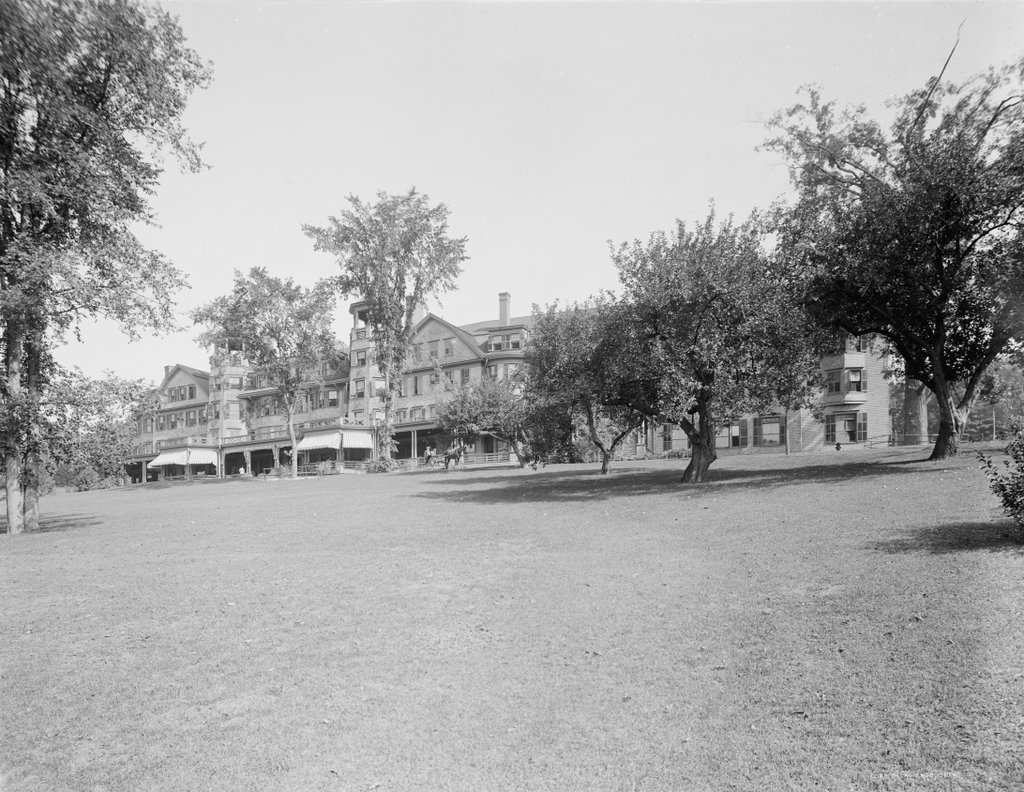
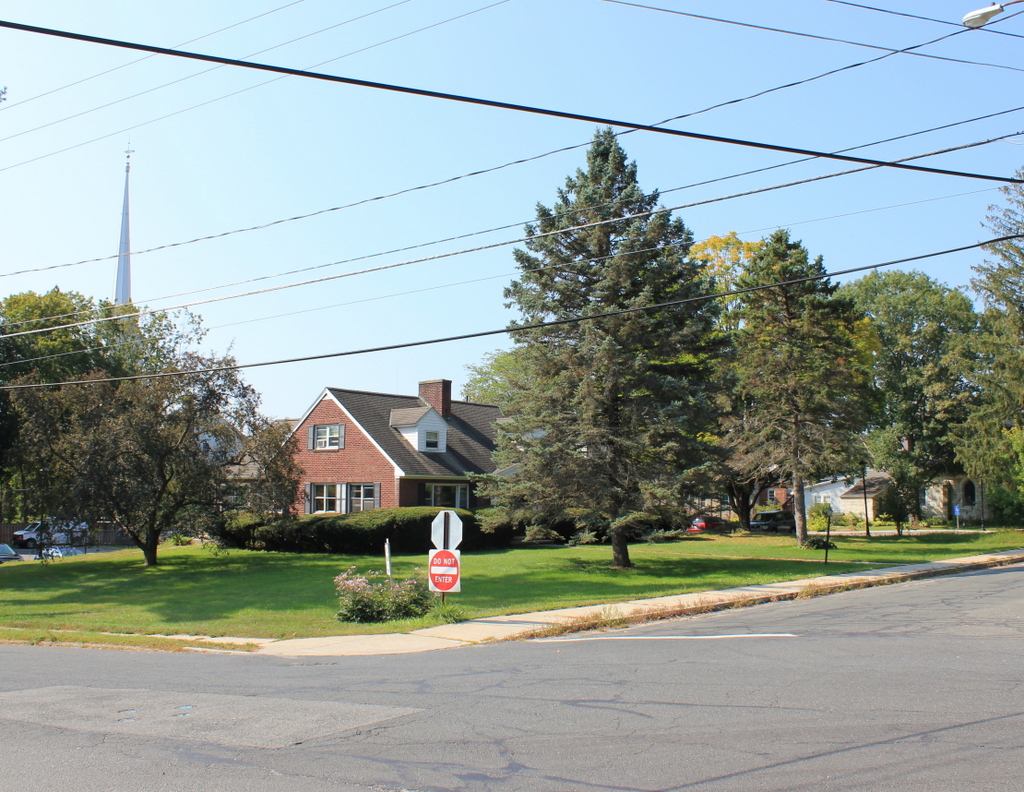
The Spring Lawn estate on Kemble Street in Lenox, around 1910-1920. Image courtesy of the Library of Congress, Detroit Publishing Company Collection.
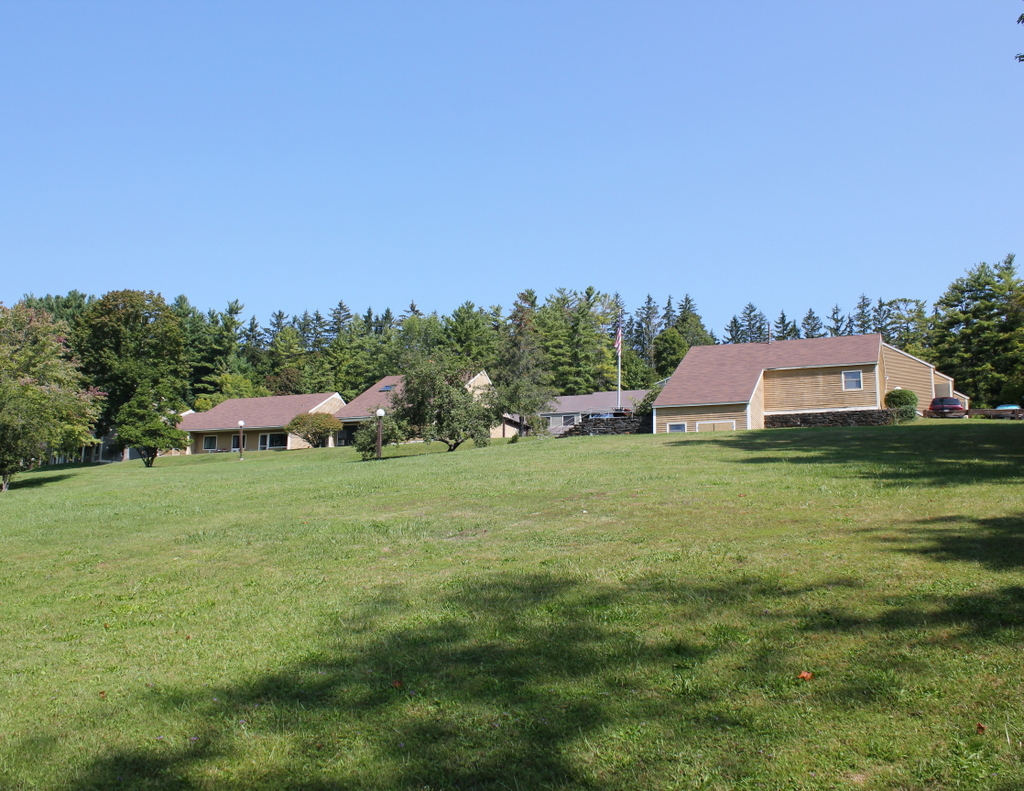
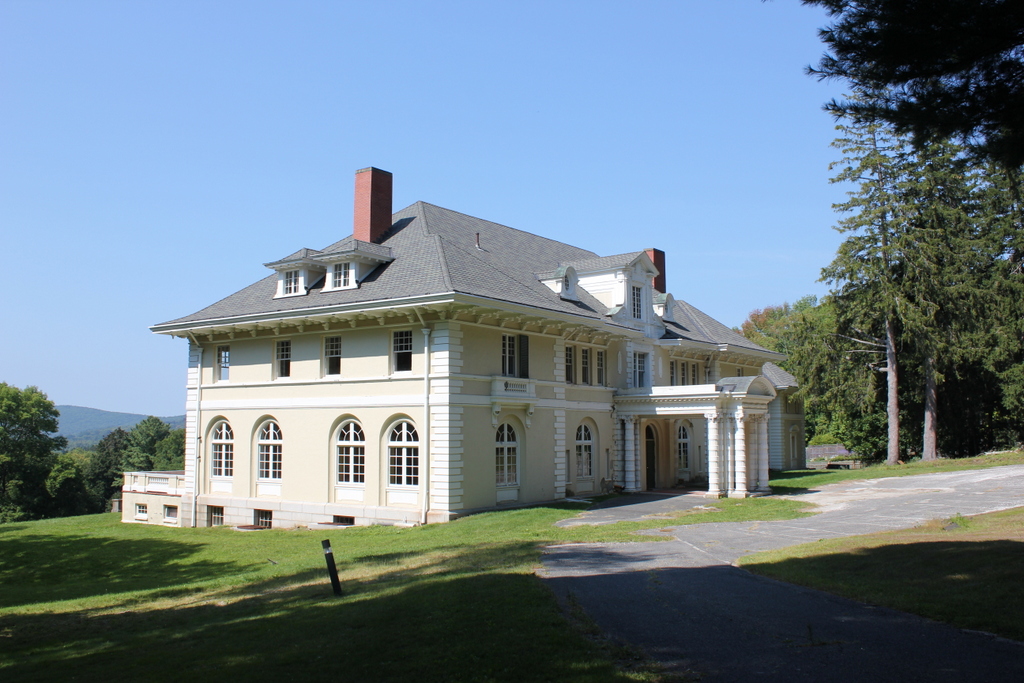
The building in 2015:

Spring Lawn was one of many summer “cottages” built in the Berkshires in the late 1800s and early 1900s, when towns like Lenox were popular resorts for the wealthy during the Gilded Age. This mansion was built in 1904, replacing The Hive, which had been the home of Charles and Elizabeth Sedgwick and the site of Elizabeth’s prestigious school for girls. Her students included Ellen Emerson, the daughter of Ralph Waldo Emerson; Mary Abigal Fillmore, the daughter of president Millard Fillmore; and Jennie Jerome, the mother of Winston Churchill.
The school closed after Elizabeth Sedgwick’s death in 1864, and the property changed hands several times before being purchased by New York businessman John E. Alexandre, who demolished the old house and built Spring Lawn, as seen here. It was one of the first buildings designed by noted architect Guy Lowell, who later went on to design the New York State Supreme Court Building, the Museum of Fine Arts in Boston, and the Charles River Dam in Boston.
Alexandre didn’t have much time to enjoy his new house, though. He died here in 1910, and it was sold to another prominent New York City resident, Mrs. Arthur F. Schermerhorn, who renamed it “Schermeer.” The house was later owned by the Lenox School for Boys and Bible Speaks College, and it has since gone through a number of other owners. As of the 2015 photo, the house is vacant, but in 2013 the owners announced a plan to restore the historic home as part of a proposed 14-building resort on the property.