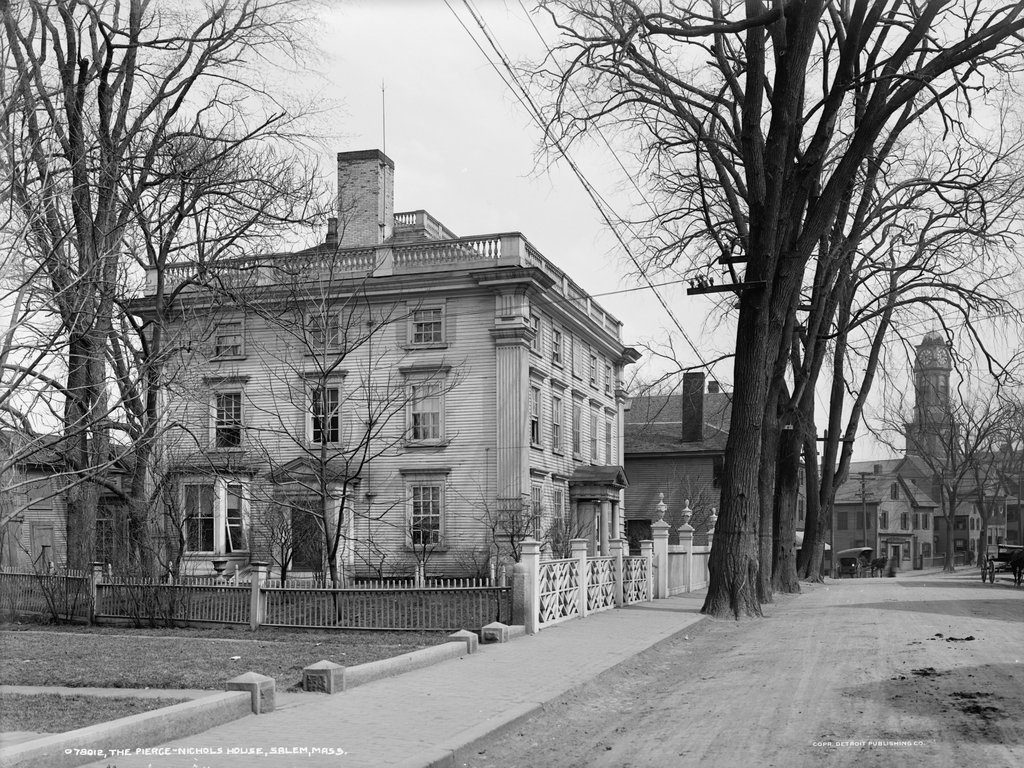
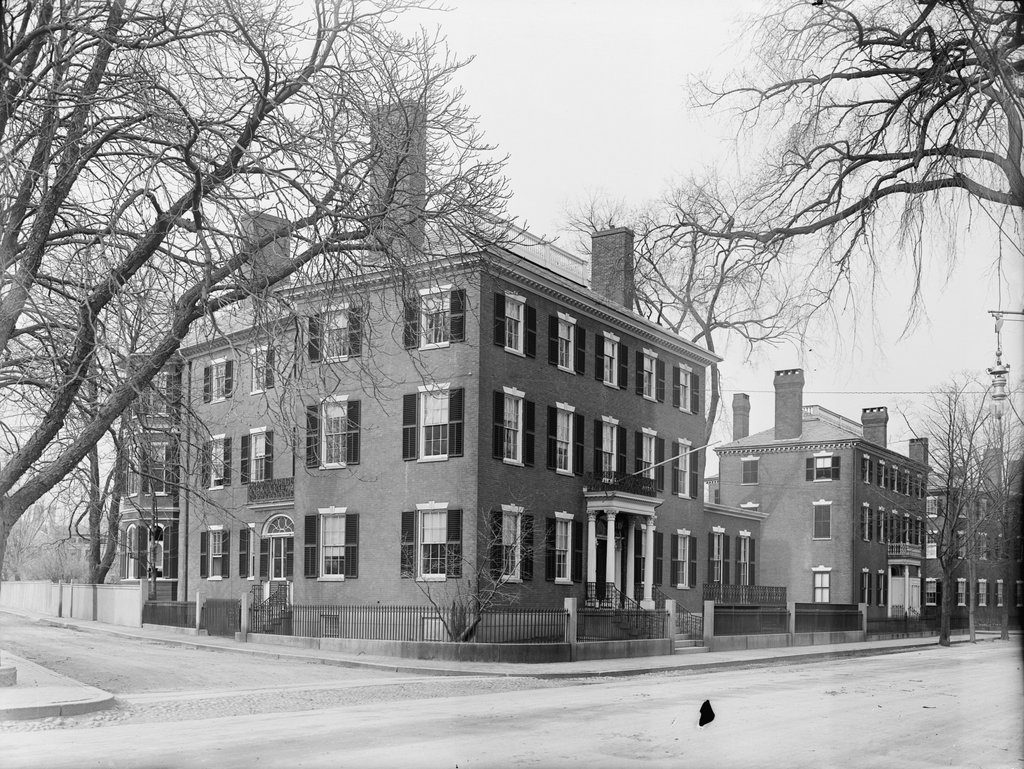
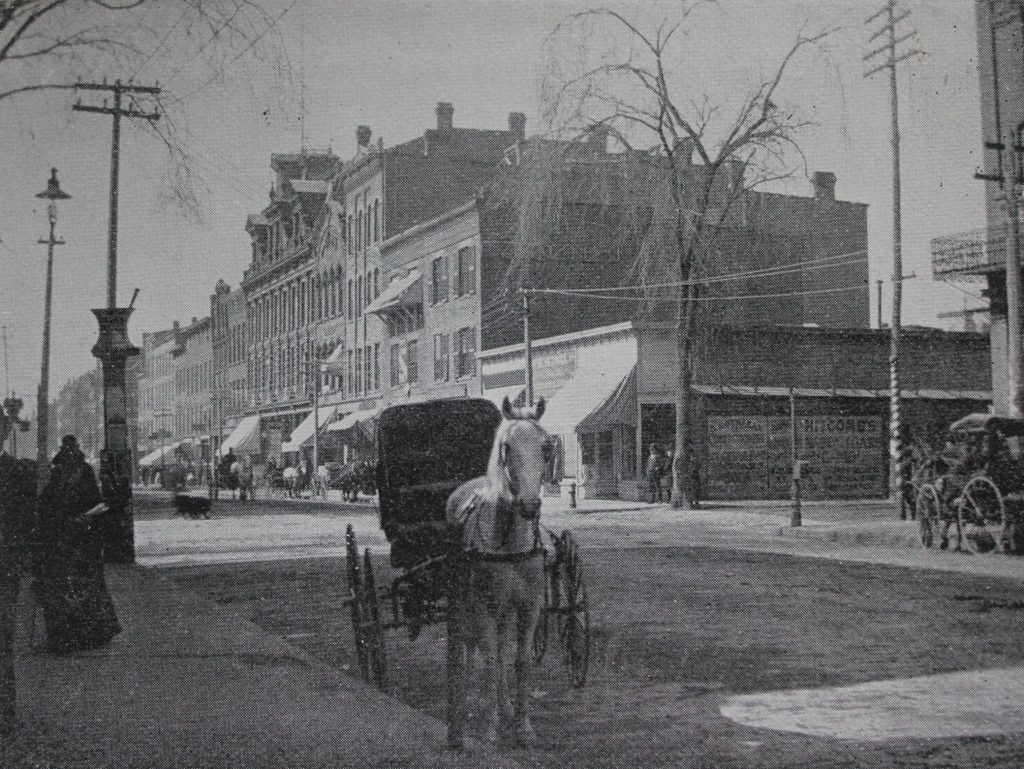The northeast corner of Washington Square North and Mall Street in Salem, around 1910. Image courtesy of the Library of Congress, Detroit Publishing Company Collection.

The scene in 2017:
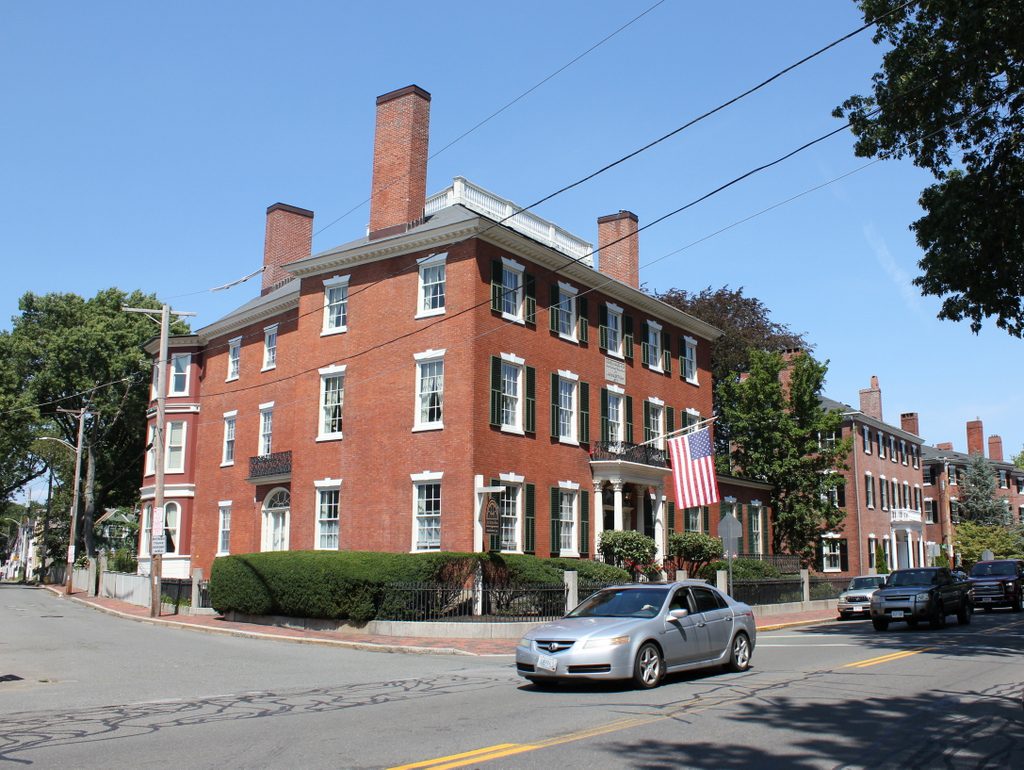

This scene shows a row of three elegant Federal-style brick homes that were built along the north side of the Salem Common in the early 19th century. The houses were originally owned by three wealthy merchants, each of whom married a daughter from the prominent Story family. Starting in the foreground, at the corner of Mall Street, 29 Washington Square North was built in 1818-19 as the home of John Forrester and his wife, Charlotte Story. Beyond it, house number 31 was built in 1811 for Stephen White and his wife Harriet Story, and furthest in the distance is house number 33, which was also built around 1811 and was the home of Joseph White, Jr. and his wife Eliza Story.
Charlotte, Harriet, and Eliza were all daughters of Dr. Elisha Story, a noted physician who had been a member of the Sons of Liberty and had participated in the Boston Tea Party. He became an army surgeon after the start of the American Revolution, including seeing combat at the Battle of Bunker Hill, and after his service in the Continental Army he practiced medicine for the rest of his life. He had eight children – one of whom died soon after birth – with his first wife Ruth, and eleven with his second wife Mehitable, including the three sisters who lived in these houses. Another child from this second marriage was Joseph Story, a lawyer who went on to serve on the U. S. Supreme Court from 1812 to 1845.
In 1810, Charlotte Story married John Forrester, who was the son of prominent merchant Simon Forrester and the first cousin of author Nathaniel Hawthorne. John received a substantial inheritance after his father’s death in 1817, and he soon began building the house in the foreground of the scene. The old house on this site – itself a fine mansion – was relocated to 91 Federal Street, where it still stands today, and construction of the new house was underway by June 1818. It was nearly finished by September of the following year, when prominent local pastor William Bentley described it in his diary, writing:
Capt. John Forrester is now preparing the front of his house on the north side of the Common, with a southern front. He has the best situation. Everything is well done about this house which will soon be ready for him. It comes nigher in its appearance to our usual style of building in brick, but probably is not behind in any of the materials or workmanship upon the plan he has adopted.
John and Charlotte Forrester moved into the house in December 1819, along with their five children. They would go on to have five more children, and they lived here in this house until 1834. By this point, John had suffered a significant reversal of his fortune, with business failures that forced the family to sell the house and move into decidedly more humble quarters around the corner at 9 Oliver Street. John died three years later, but Charlotte outlived him by 30 years, living in Salem until her death in 1867.
In the meantime, the house just beyond the Forrester house was, for many years, the home of Charlotte’s sister Harriet and her husband Stephen White. They were married in 1808, and moved into this house upon its completion three years later, where they raised their four children. Stephen White was a prominent merchant who was also involved in politics. He held a number of elected offices throughout the 1820s, including serving in the state House of Representatives in 1821 and 1828; the state Senate in 1825, 1826, and 1830; the Governor’s Council in 1824; and as a presidential electors in 1828. He was also a personal friend of Daniel Webster, and his daughter Caroline later married Webster’s son Fletcher. Aside from Webster’s other prominent visitors to this house included President James Monroe, who attended a reception here on July 11, 1817. Reverend Bentley also described this event in his diary, writing:
[I]n the evening [Monroe] was at Capt. Stephen White’s & there was received by a very brilliant assembly of Ladies, who were attended by The gentlemen of the Town. As this would probably be the last interview, it collected more than any former one but with less comfort from over stowing. The President however may have done too much as he hardly had time to breathe. But the question was everywhere, have you seen him? And this eager curiosity it would have been cruel to indulge & even gratify. I presented him the Gold headed walking Cane of the late Gen. Knox, Sec. of War, & the very elegant Tobacco box of Silver, with a wrought China top, received from China.
Stephen White lived in this house on Washington Square North throughout the 1820s. His wife Harriet died in 1827 at the age of 40, and around 1831 he moved to Boston. By this point Salem had already peaked in its prosperity as a major port, and it would continue to decline throughout the 19th century, while Boston enjoyed steadily growing wealth and population. White sold his Salem mansion in 1831 for $7,000 – only about $160,000 in today’s dollars – and lived in Boston until his death a decade later in 1841, at the age of 54.
The house furthest in the distance of both photos, at 33 Washington Square North, was built around 1811, the same year as Stephen White’s house, and was even constructed by the same builder, Joshua Upham. It was originally the home of Stephen White’s older brother, Joseph White Jr., and his wife Eliza Story, who was the older sister of Stephen’s wife Harriet. Joseph was a merchant, and he was named after his uncle, Joseph White, Sr., a wealthy merchant who was the victim of an infamous 1830 murder in Salem. However, the younger Joseph did not live long enough to see this happen; he died in 1816, only a few years after his house was completed, leaving his widow Eliza and three young daughters. She lived here in this house until 1831, when she sold the property and joined her brother-in-law Stephen in moving to Boston.
Overall, despite their wealth and prominence, the Forrester and White families’ ownership of these houses was marked by catastrophic business failure and untimely deaths. However, the houses would continue to be home to some notable Salem residents of the mid and late 19th century, including Colonel George Peabody, who purchased John Forrester’s house in the foreground in 1834. He was about 30 years old at the time, and was the son of wealthy Salem merchant Joseph Peabody. He would go on to have a successful business career as well, including serving as president of the Salem Bank and the Eastern Railroad. Along with this, he was a colonel in the militia, and served several terms as a city alderman. Peabody lived here until his death in 1892, and during this time he had several prominent visitors to the house, including poets Henry Wadsworth Longfellow and James Russell Lowell, biologist and geologist Louis Agassiz, and Civil War General George McClellan.
By the time the first photo was taken around 1910, the Forrester-Peabody House was used as the home of the Salem Club, a private men’s club. Around the 1920s, it became the Bertram Home for Aged Men, as indicated by the panel that is now located above the second floor window in the present-day scene. The house was renovated in 1990, becoming an assisted living facility, and it is still in use today as the John Bertram House. However, despite these many changes in use, the exterior of the house has remained well-preserved in more than a century since the first photo was taken, and the only notable change is the panel on the front facade.
Just beyond this house, Stephen White’s former house changed hands several times in the mid-19 century. Merchant John W. Rogers lived here from 1831 to 1844, followed by another merchant, Thomas P. Pingree, who lived here from 1844 to 1858 before selling it to attorney Nathaniel Lord. It would remain in his family for the next 90 years, until it was finally sold in 1948. However, like its neighbors, this house is also well-preserved today, with no significant differences between the two photos.
The house of Joseph White, Jr., on the far right of both photos, was owned by the prominent Silsbee family from 1831 until the early 1880s, and its residents included merchant and banker Benjamin H. Silsbee, who was the president of the Merchants’ National Bank in Salem. Later in the 1880s, the house became the parsonage for the Tabernacle Congregational Church. Its pastor at the time was DeWitt S. Clark, a native of Chicopee, Massachusetts who began his ministry at the Salem church in 1878. His father had been the longtime pastor of the First Congregational Church in Chicopee, and DeWitt Clark had a similar tenure here in Salem. He was still serving as pastor when the first photo was taken around 1910, and that year’s census shows him living here with his wife Emma and their four children. Reverend Clark died in 1916, but his family later purchased the house and continued living here for many years, eventually selling the property in 1969.
Today, almost two centuries after William Bentley described the finishing touches on the Forrester House in his diary, this scene has hardly changed. Although no longer inhabited by prosperous merchant families, these three houses are among the many fine early 19th century homes that still stand in Salem,and serve as reminders of the city’s golden age as one of the wealthiest communities in the country. All three houses, along with the rest of the surrounding neighborhood, are now part of the Salem Common Historic District, which was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1976.