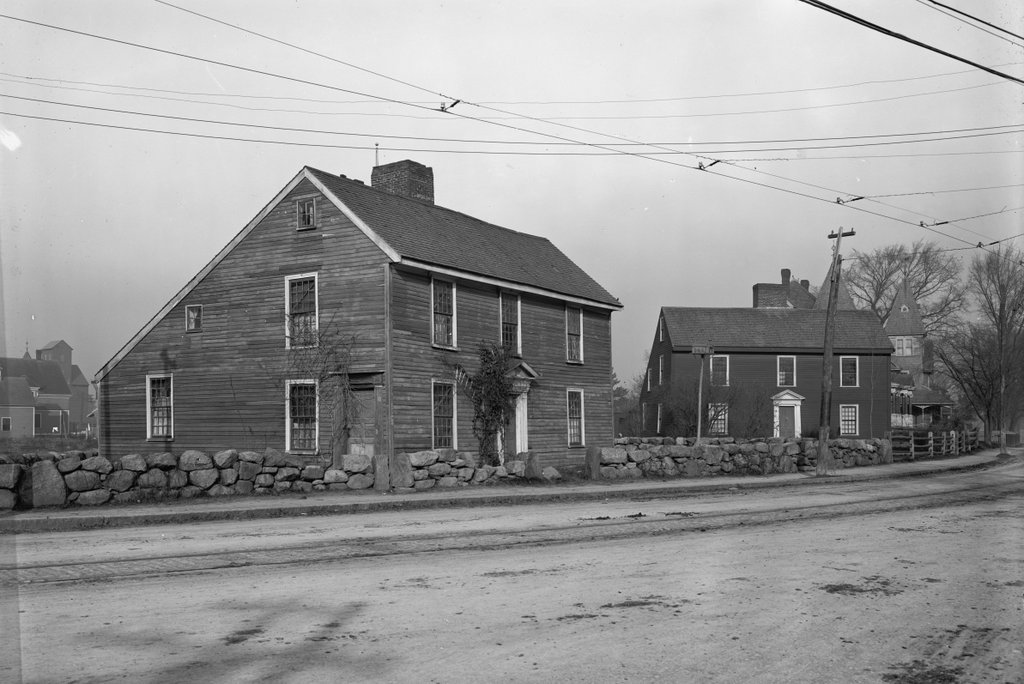
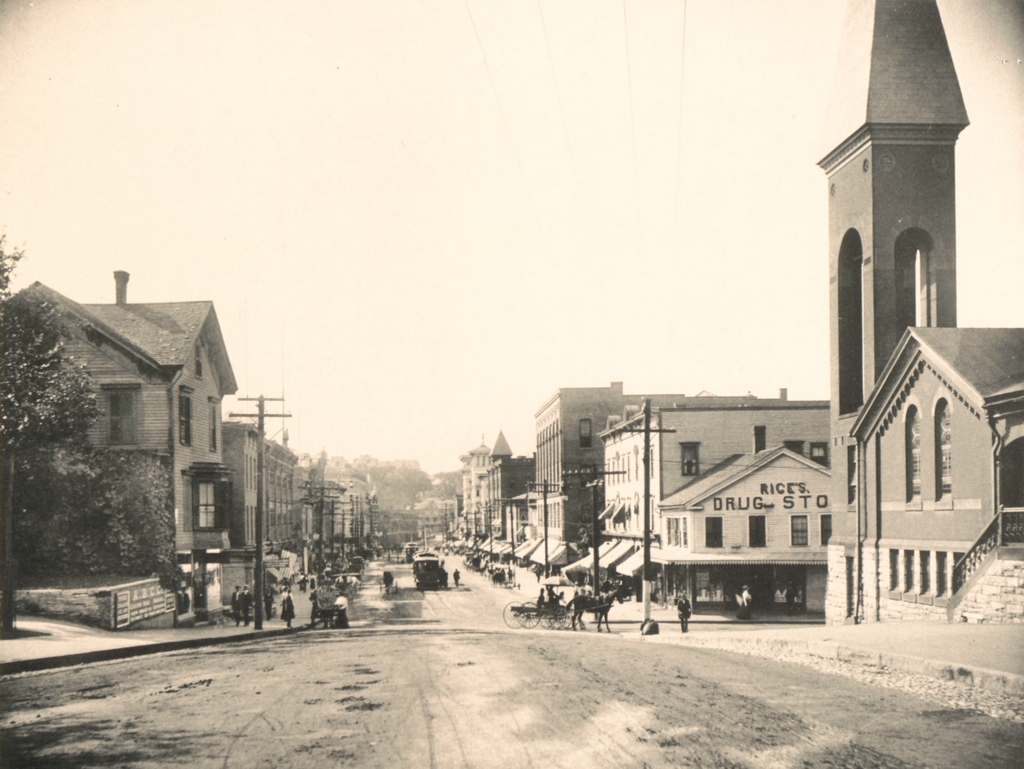
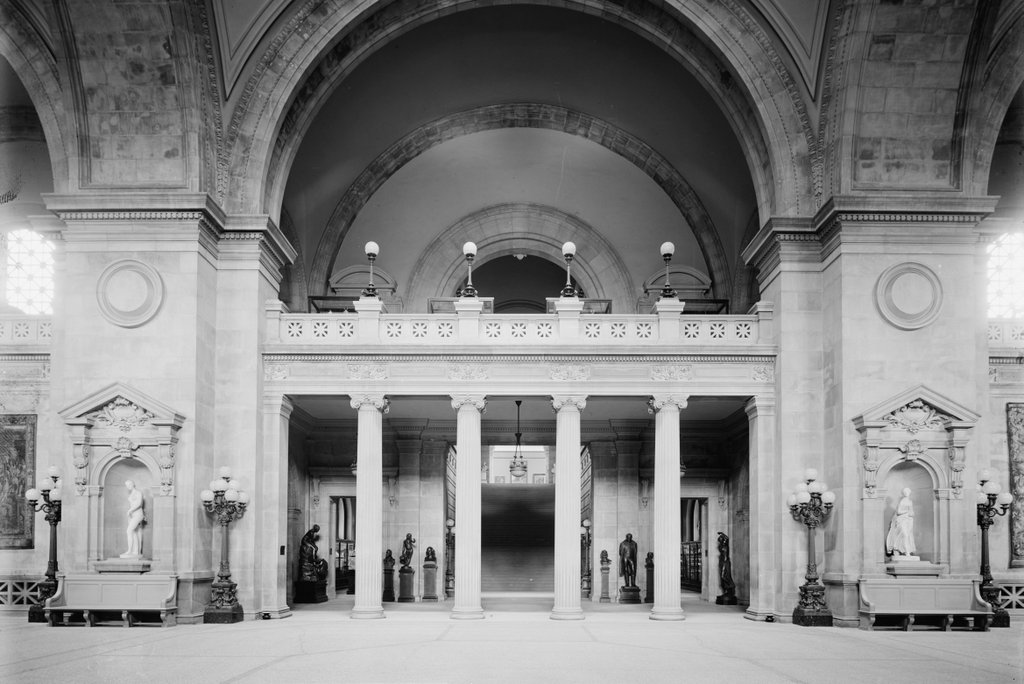
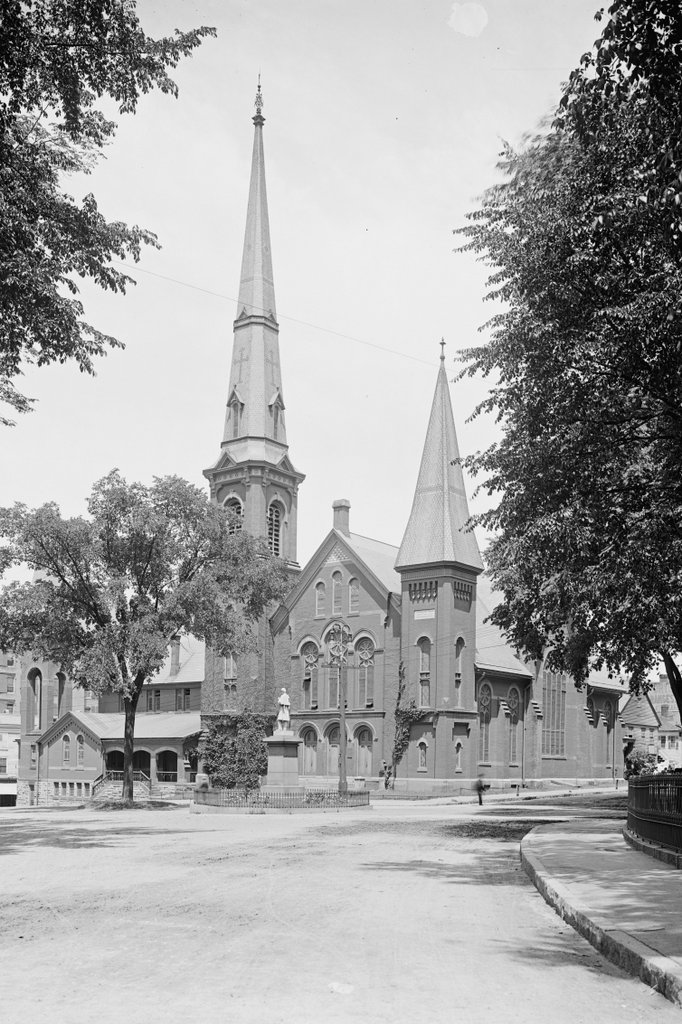The John Adams (right) and John Quincy Adams (left) birthplaces on Franklin Street in Quincy, around 1904. Image courtesy of the Library of Congress, Detroit Publishing Company Collection.
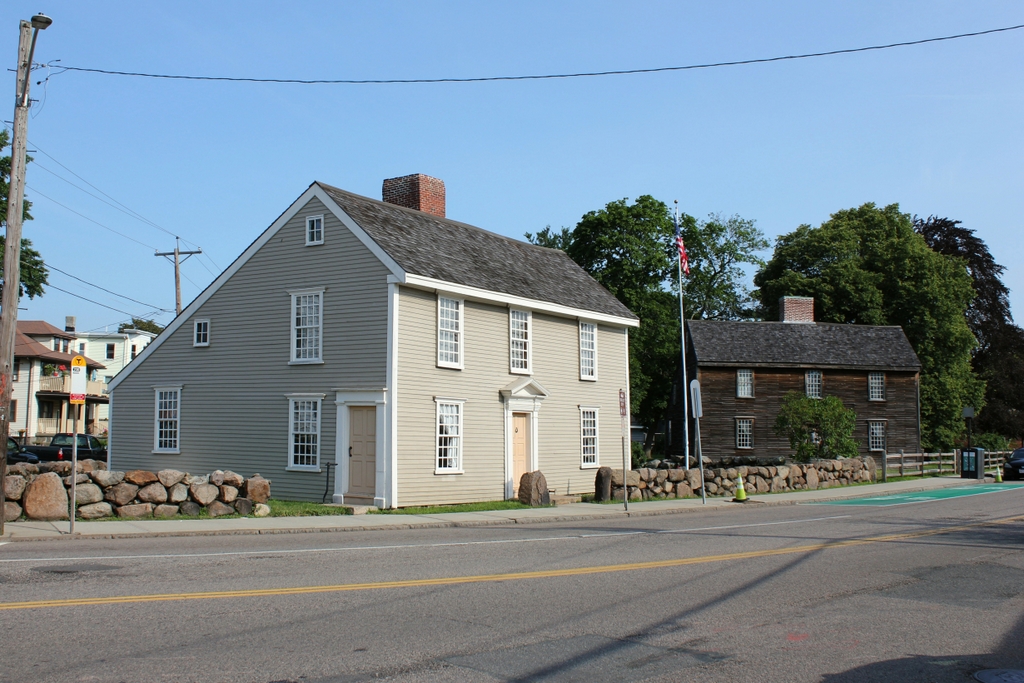
The scene in 2019:
As of 2020, only seven states have been the birthplace of two or more presidents. Massachusetts is among them, with four presidents, and two of these were born here, in this half-acre triangle of land between Franklin Street and Presidents Avenue. John Adams was born in 1735, in the house on the right side of this scene, and his son John Quincy Adams was born 32 years later, in the house on the left in the foreground. Standing only 75 feet apart, these are the two closest presidential birthplaces in the country, and they are also the two oldest surviving ones; no other presidents before William Henry Harrison were born in buildings that still exist.
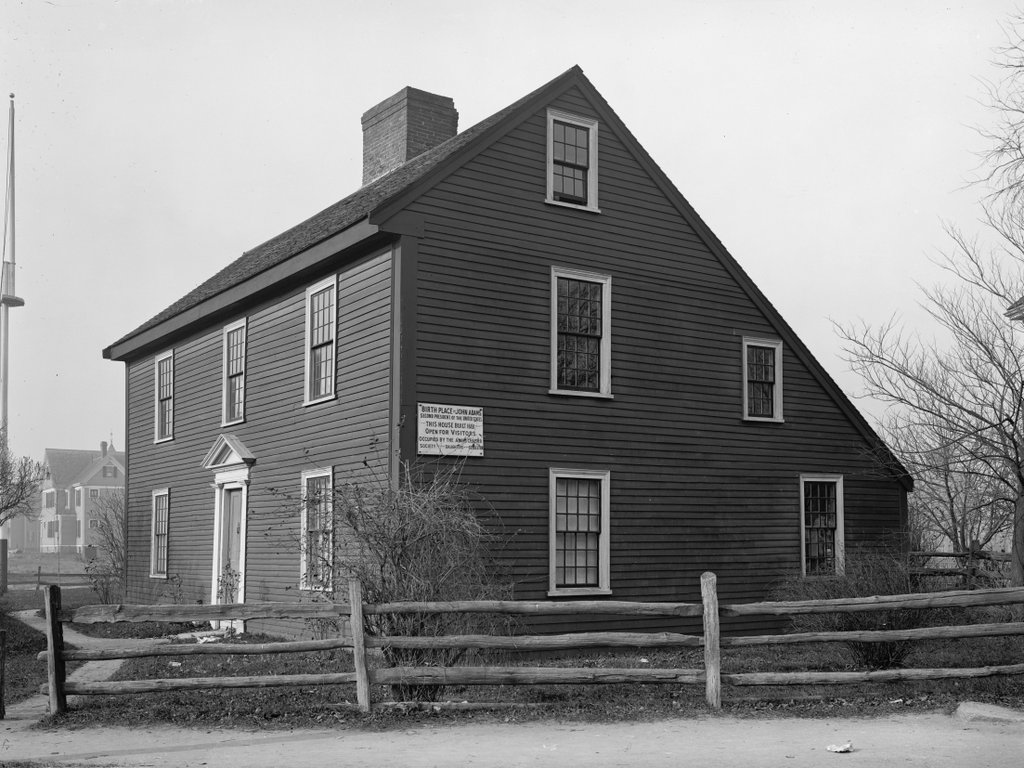
The house on the right, where John Adams was later born, was built in 1722 by the future president’s father, Deacon John Adams. At the the time, this area was part of the town of Braintree, as the present-day city of Quincy would not be incorporated as a separate municipality until 1792. Deacon Adams had purchased the property, which included seven acres of farmland, in 1720, and he subsequently built the house, apparently reusing timbers from an earlier house that had stood here. Adams married his wife Susanna Boylston in 1734, and a year later their first son John was born here. John spent his childhood here, along with his younger brothers Peter and Elihu, although he left home in 1751 at the age of 16, in order to attend Harvard.
In sending his son to Harvard, Deacon Adams had hoped that John would become a minister, but after graduation he moved to Worcester, where he worked as a schoolteacher before deciding to study law. John ultimately returned here to his family home in 1758, and a year later he was admitted to the bar and began practicing law. Two years later, Deacon Adams died at the age of 70, and his son Peter inherited the old family home, with John receiving the house next door on the left side of the scene, which Deacon Adams had acquired in 1744.
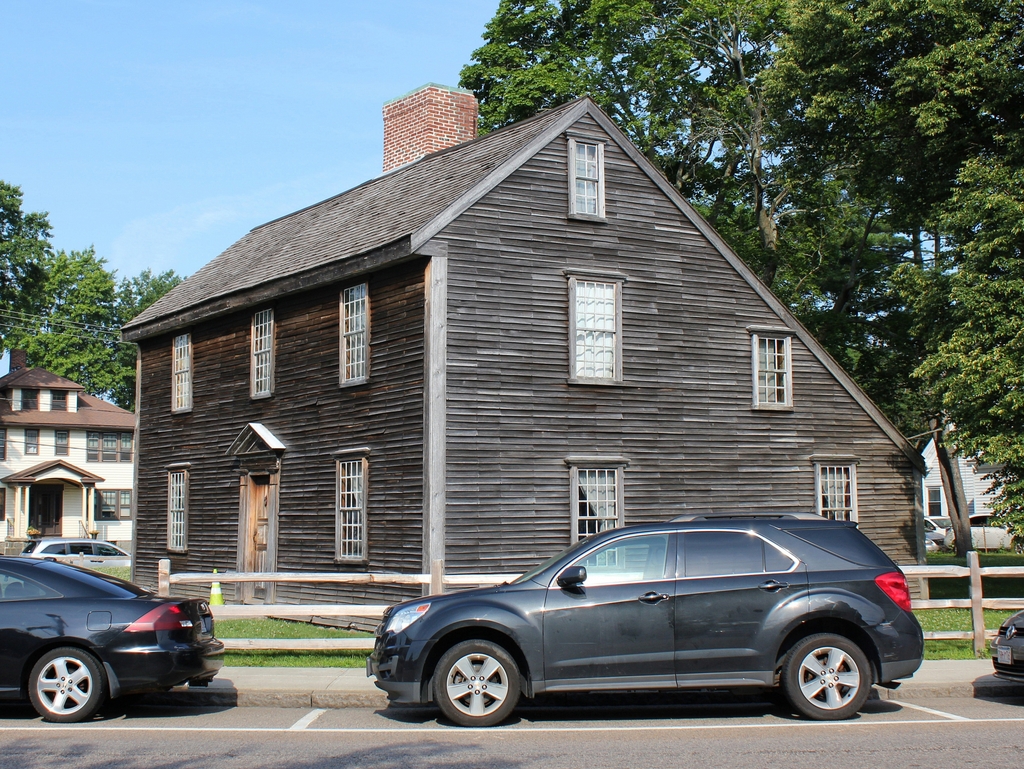
John Adams married Abigail Smith in 1764, and the couple moved into the house here on the left side. Although John’s father had only owned it for 20 years at that point, it was actually even older than the other house. It was definitely built by 1717, but it apparently incorporated parts of an earlier house that had been built here on this site in 1663. In either case, the house was expanded at some point after it was built, possibly during Deacon Adams’s ownership, and in its current form it is architecturally very similar to the house on the right. Both are good examples of the traditional New England saltbox style, with three window bays on the front facade, a central chimney, two front rooms on both the first and second floors, and two additional rooms on the first floor of the lean-to.
Upon moving into the house on the left, John Adams converted the southeast room on the ground floor—at the corner closest to the foreground in this scene—into his law office. From the exterior, the only change was the door here at the corner, which allowed clients to come and go without using the main entrance. On the other side of the house, in the northeast corner, was the parlor, and the kitchen was located behind it in the lean-to section. There were two bedrooms upstairs, and future president John Quincy Adams was born in the northern bedroom, on the right side in this scene.
Aside from John Quincy Adams (1767-1848), John and Abigail Adams had five other children: Abigail “Nabby” (1765-1813), Susanna (1768-1770), Charles (1770-1800), Thomas (1772-1832), and Elizabeth (stillborn in 1777). This was their home throughout this time, although John was frequently away from here during and after the American Revolution. From 1774 to 1777, he was a delegate at the First and Second Continental Congresses in Philadelphia, and then from 1777 to 1779 he was overseas as an envoy in France. This was followed by an even longer stay in Europe during the 1780s, when he served as Minister to the Netherlands and Minister to Great Britain.
During John Adams’s long periods away from home, he and Abigail exchanged hundreds of letters, a substantial number of which have survived. Although she lacked formal education, the letters reveal Abigail’s role as an influential advisor and confidant to her husband, and these letters have become a part of the American literary canon. Abigail wrote many of the letters from here at their house, including her famous 1776 exhortation to John to “Remember the Ladies, and be more generous and favourable to them than your ancestors” when creating a new government.
As it turned out, a few years later John Adams would almost singlehandedly create the Massachusetts state government here in his law office in this house. In 1779, during his brief return to America between diplomatic assignments, he found himself on the three-man drafting committee at the state constitutional convention. Like any group project, the other two members of the committee, in turn, assigned him the actual task of writing the text of the new constitution, much of which was done here.
This document was ratified a year later in 1780, and it remains in effect today, making it the world’s oldest written constitution. Its structure also served as a model for the United States Constitution, which was written seven years later. However, perhaps Adams’s single most famous contribution to the constitution was the seemingly-innocuous statement that “All men are born free and equal, and have certain natural, essential, and unalienable rights.” Although largely echoing Thomas Jefferson’s words from the Declaration of Independence, the “born free and equal” phrase became the legal basis for the abolition of slavery in Massachusetts in 1781, when the state Supreme Judicial Court ruled that slavery was incompatible with the words of the constitution.
John Adams returned to Europe in late 1779, shortly after he finished drafting the constitution. He and Abigail would be separated for the next five years, until she and Nabby joined him and John Quincy in Paris in 1784. They would remain overseas until 1788, and during this time they grew accustomed to the more lavish residences that they enjoyed in Europe, in contrast to their decidedly modest farmhouse back home. As a result, in 1787, while he was still in Europe, he purchased a mansion a little over a mile north of here, which was situated on 40 acres of land. Upon returning home a year later, he named it Peacefield, and set about expanding and renovating it.
John and Abigail would live at Peacefield for the rest of their lives, and the home would remain in the Adams family for several more generations. During this time, though, the family also retained these houses here on Franklin Street. These were generally used as rental properties throughout most of the 19th century, although John Quincy Adams did live here in his birthplace and childhood home from 1805 to 1807, during part of his single term as a United States senator.
By the late 19th century, both of these houses were occupied by local historical groups, with the Quincy Historical Society in the John Quincy Adams birthplace on the left, and the Adams Chapter of the Daughters of the American Revolution in the John Adams birthplace on the right. Around this same time the houses were also restored to their 18th century appearances, including uncovering the side door to John Adams’s law office, which had long been boarded over. The first photo was taken soon after, probably around 1904, with the colonial-era homes contrasting with the modern trolley tracks and overhead wires In the foreground.
The Adams family ultimately owned these properties for more than two centuries, until selling them to the city of Quincy in 1940. Both houses were designated as National Historic Landmarks in 1960, and in 1978 the city transferred them to the National Park Service. Today, remarkably little has changed in this scene since the first photo was taken, and both houses remain well-preserved. Along with the nearby Peacefield mansion, they now form the Adams National Historical Park, and they are open to the public for guided tours.