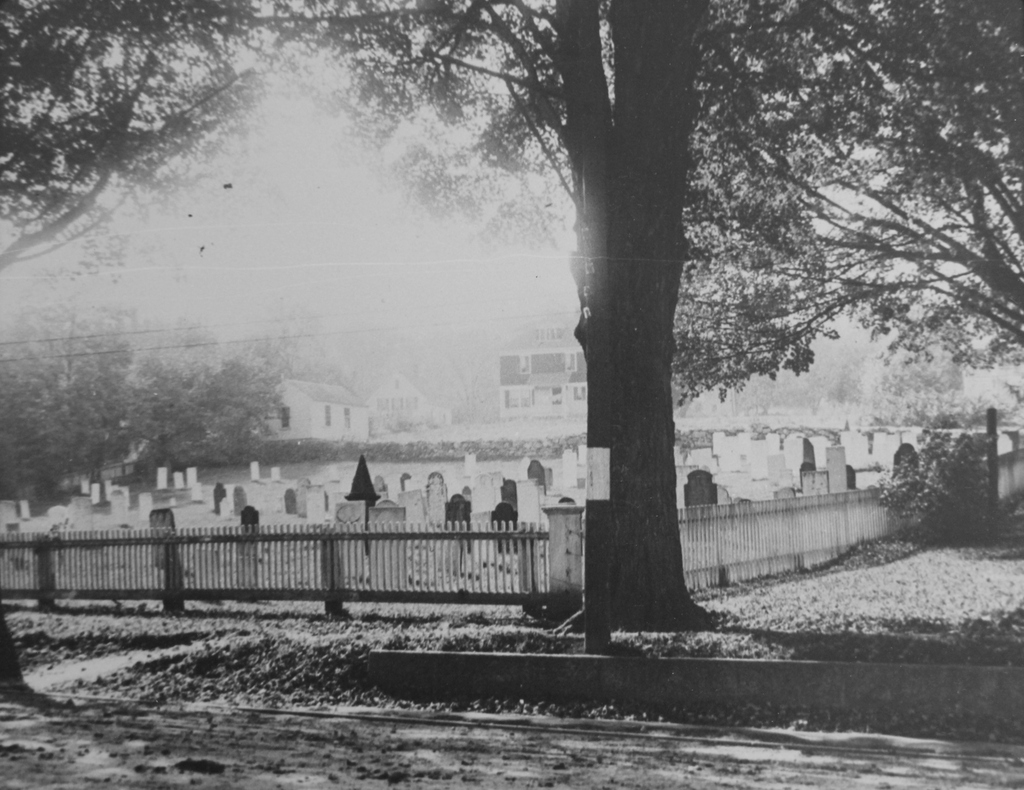
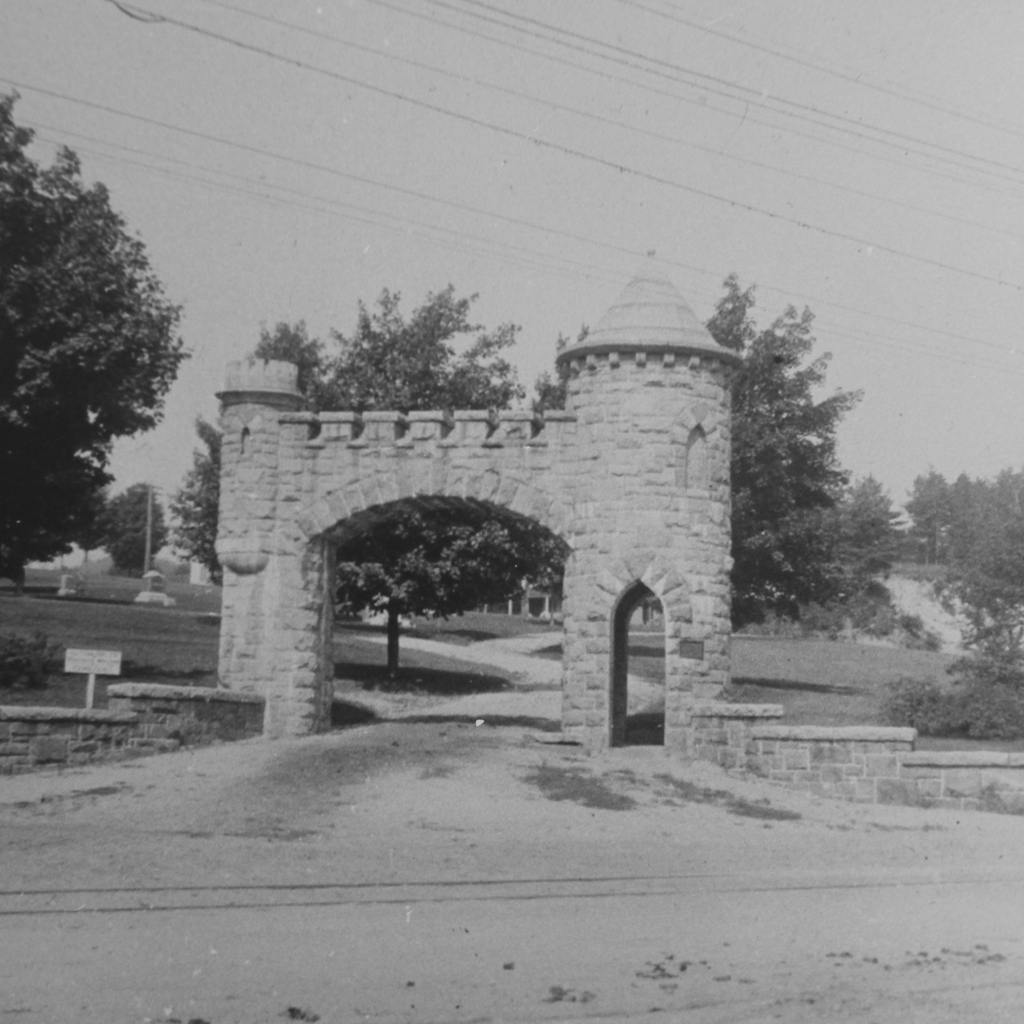
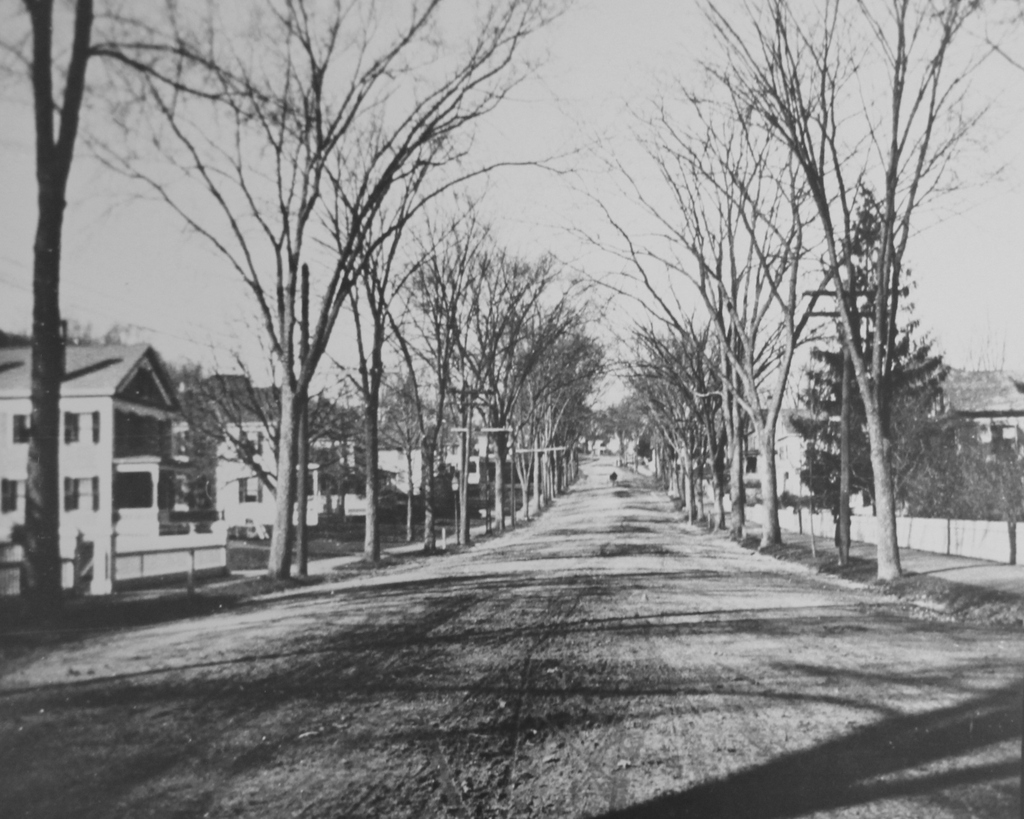
A view of the North Main Street Cemetery in Monson, probably around 1900-1920. Image courtesy of the Monson Free Library.
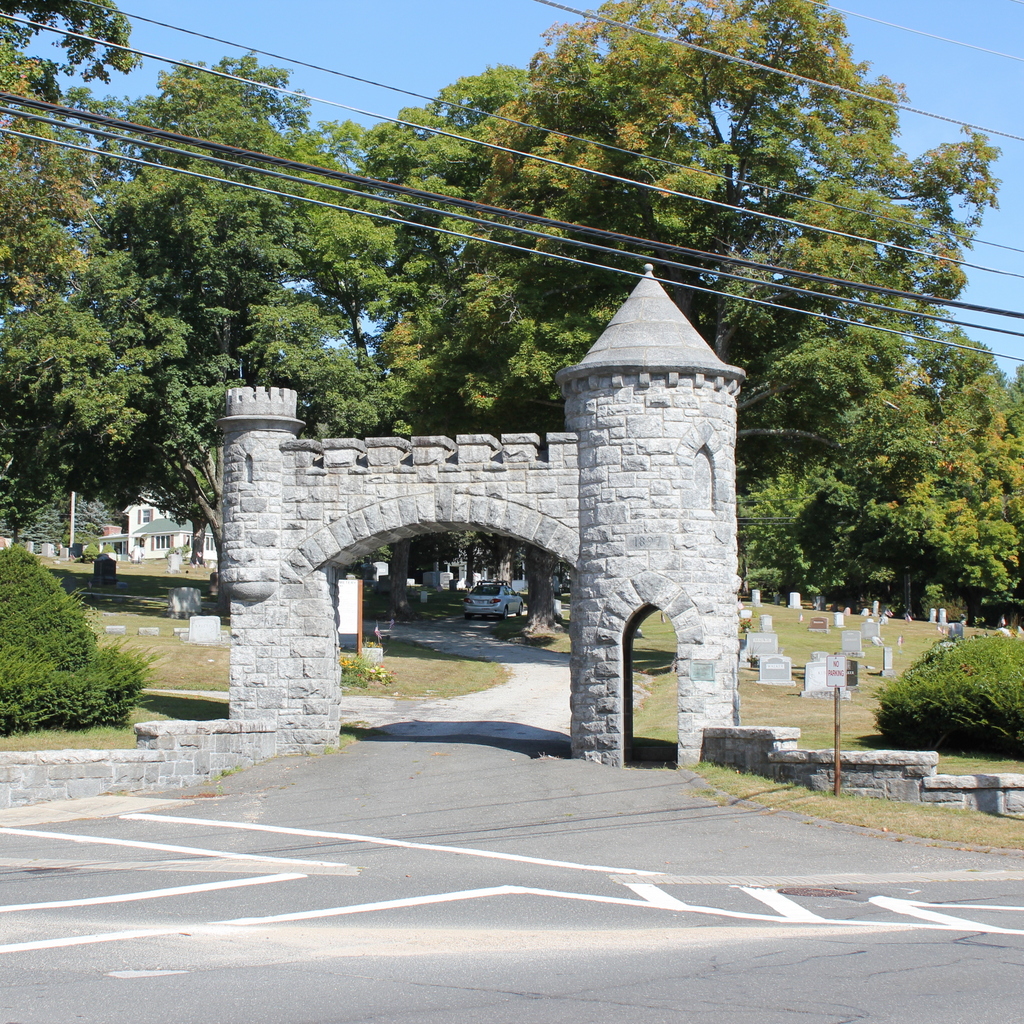
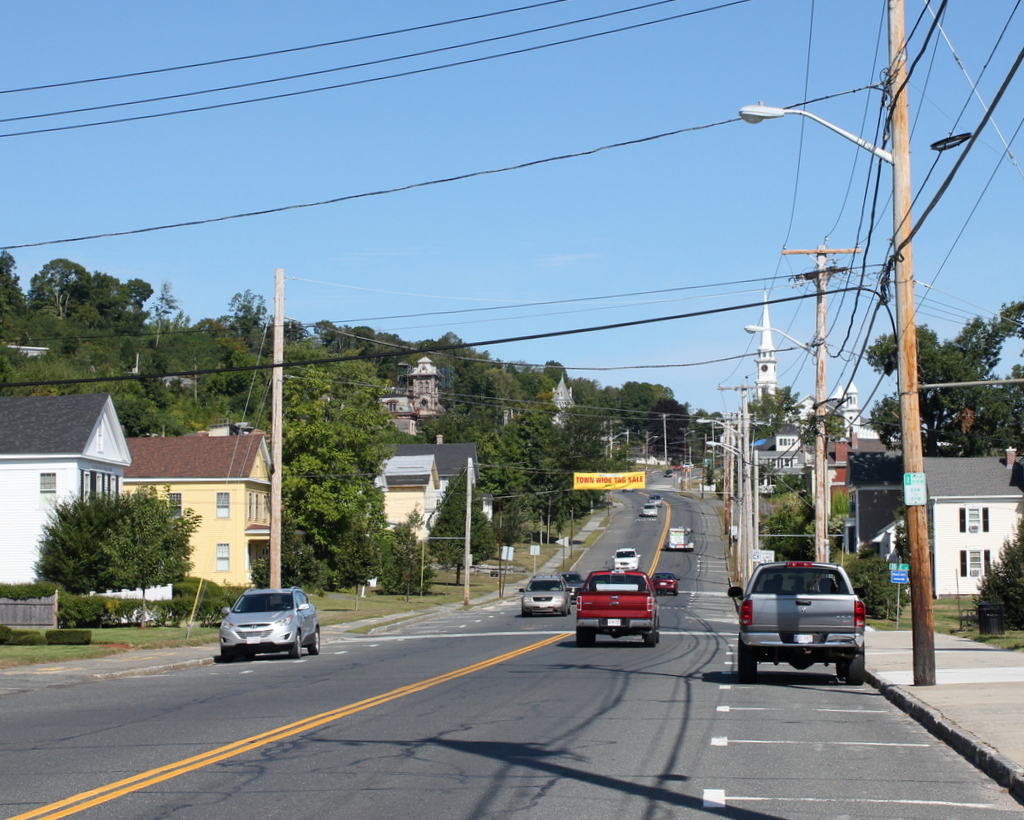
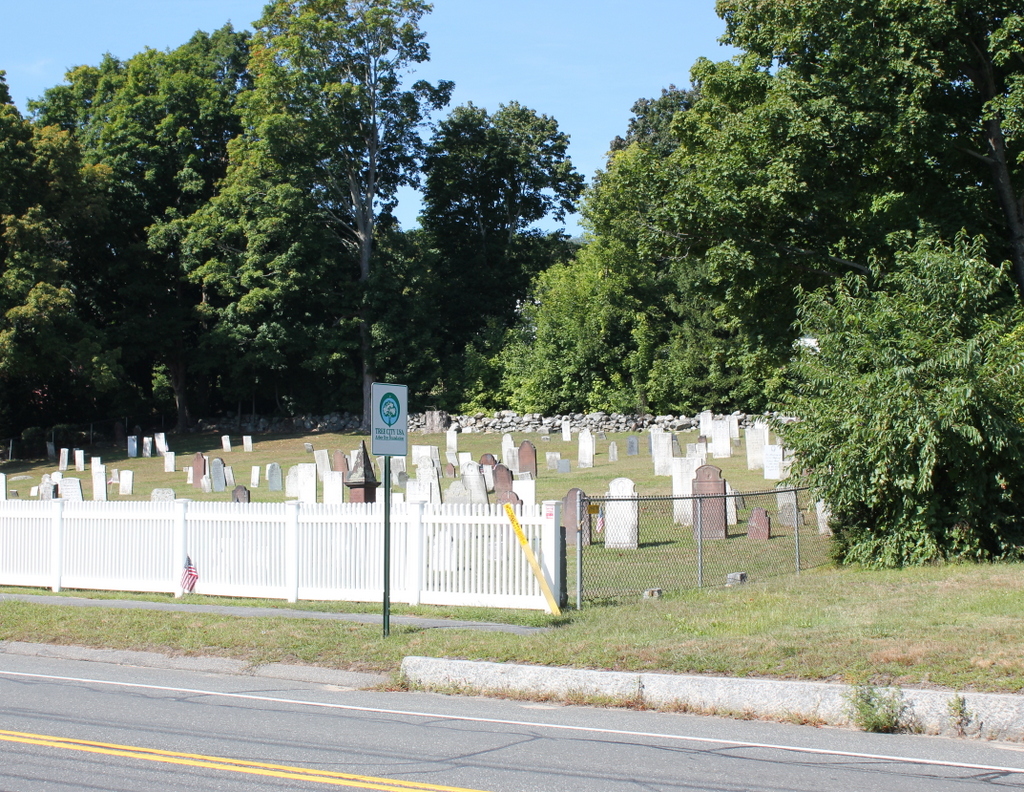
The cemetery in 2015:

The area of present-day Monson was first settled in the early 1700s, but at the time it was part of the town of Brimfield. Among other things, this meant that residents of this area had to bury their dead in Brimfield’s town cemetery, over six miles away from the current center of Monson. The 1960 History of Monson book quotes a petition signed by some of the area’s residents, complaining of “the Badness and length of ye way,” and pointing out that a more convenient burial ground would be of no harm, “it being no matter to the body where it lies when Dead.” Their request was granted, but in any case the point was soon moot when Monson separated from Brimfield in 1760.
The town’s first large cemetery was established here, just a few hundred yards north of the meeting house. The first burial was in 1777, and it was used until 1850, at which point the much larger Hillside Cemetery up the road became the town’s primary public cemetery. Around 250 people were buried here, mostly in the first few decades of the 19th century. The oldest headstones are carved of red sandstone or slate, and have survived the past few centuries in excellent condition. The more recent white marble stones, though, have not weathered as well, and many of the inscriptions are no longer legible.
There has not been a burial here since about 50 years before the first photo was taken, but the cemetery is still well-maintained by the town, and it looks essentially the same as it did a century ago; some of the headstones are even still leaning in the same direction today.