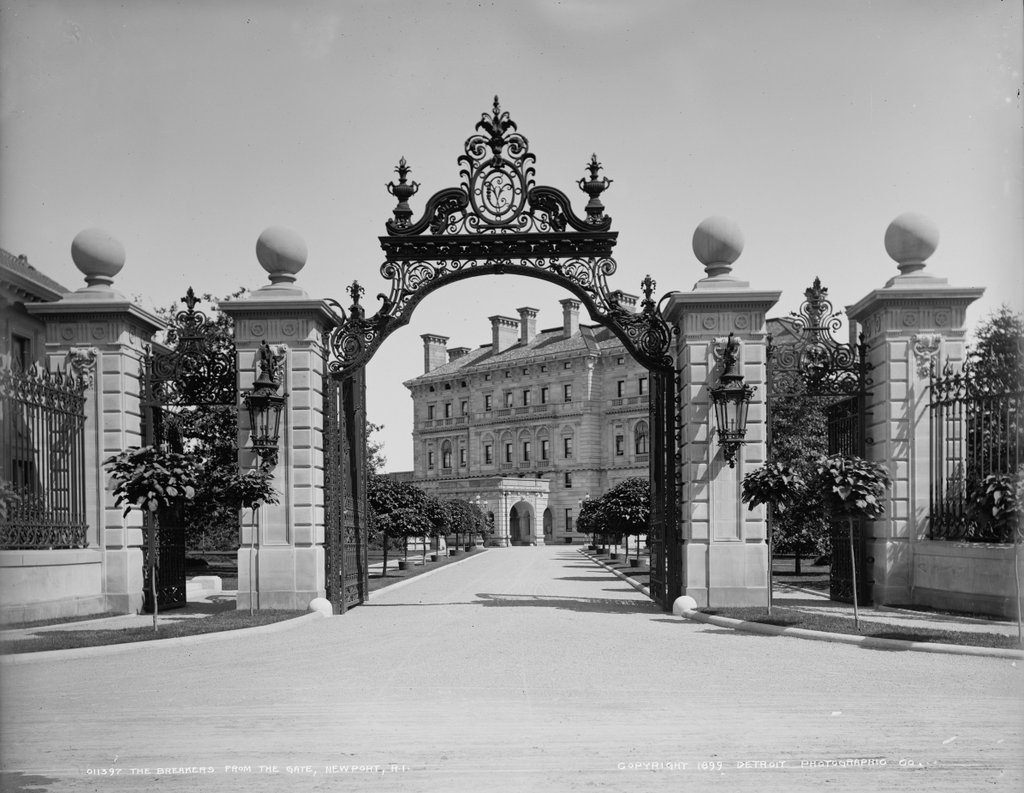
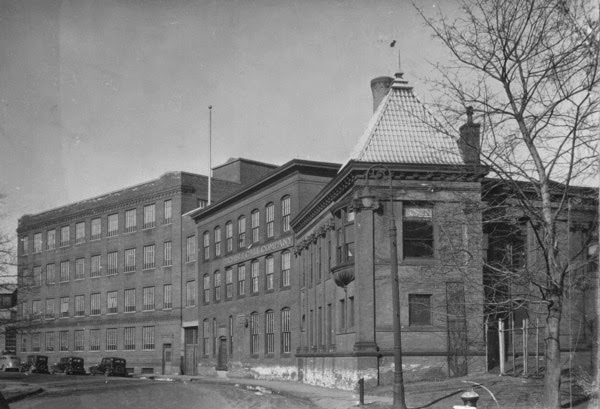
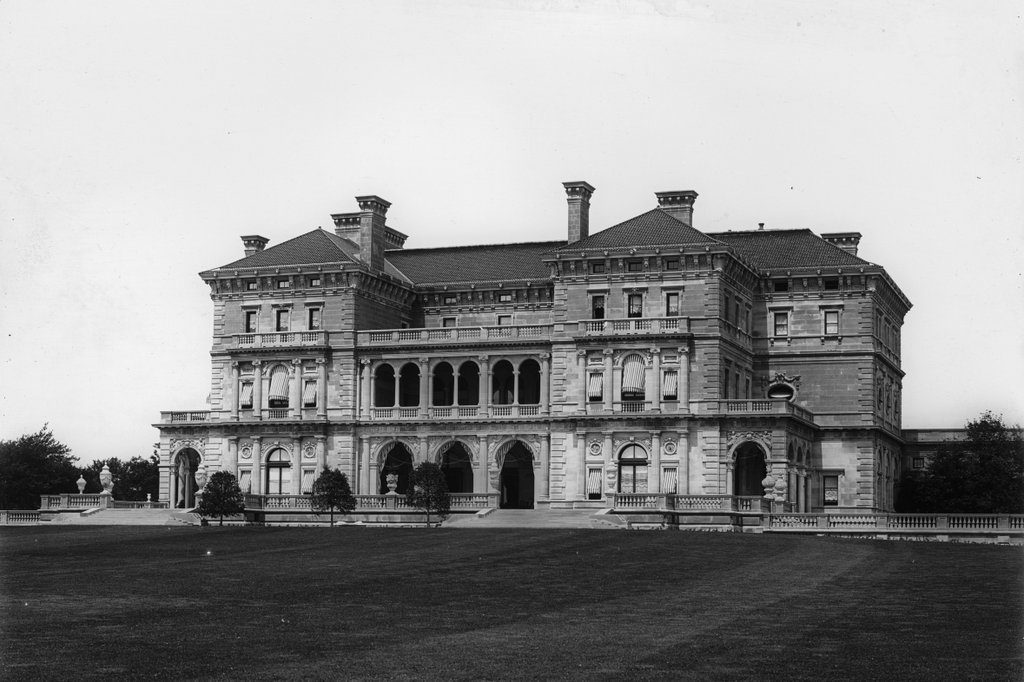
The Breakers, seen from the Cliff Walk in Newport, around 1904. Image courtesy of the Library of Congress, Detroit Publishing Company Collection.

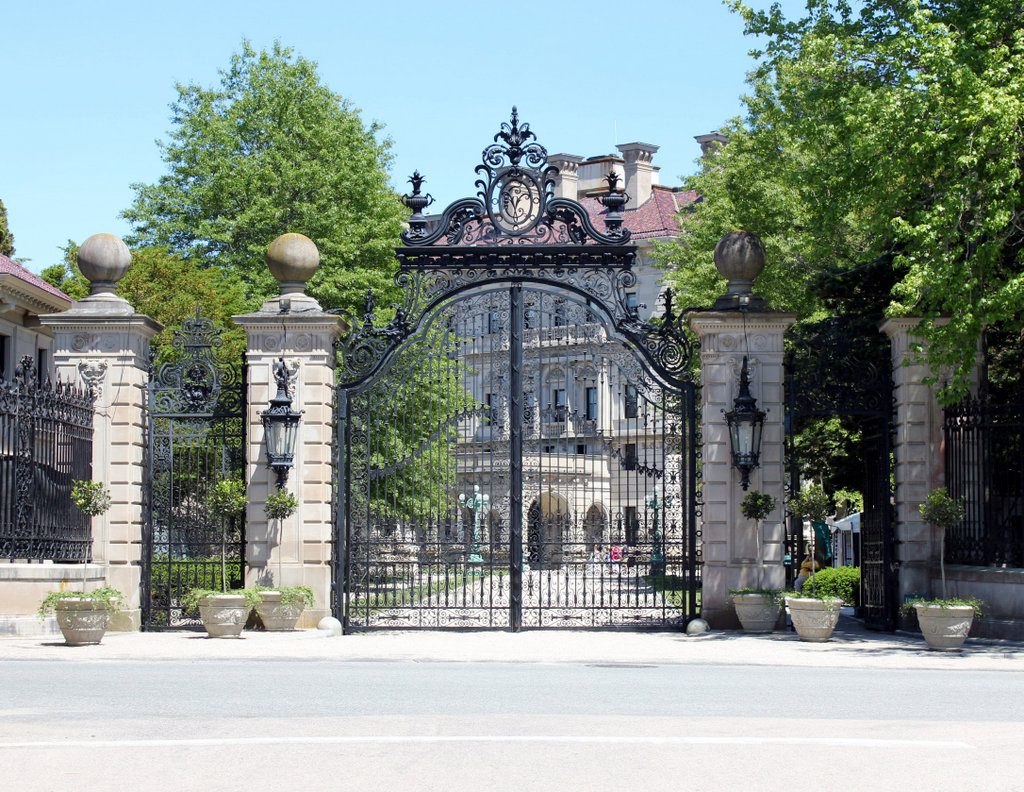
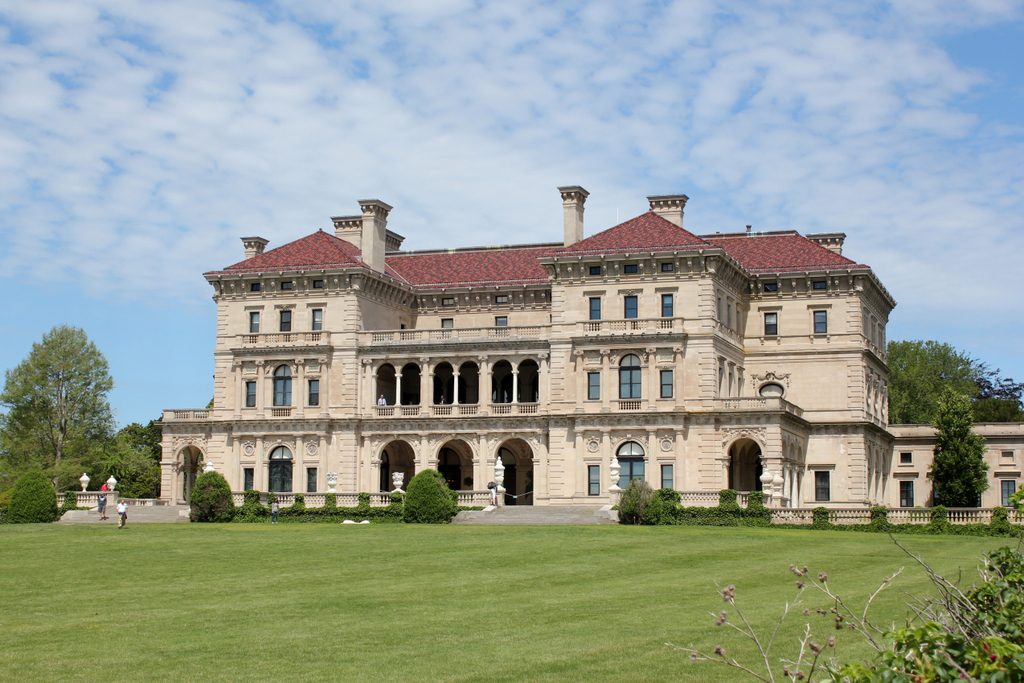
The scene in 2017:

Newport is renowned for its many 19th and early 20th century summer “cottages,” which were built by many of the nation’s wealthiest families and represented some of the finest examples of residential architecture in this era. However, none could quite compare to The Breakers, which was completed in 1895 as a summer home for Cornelius Vanderbilt II, the prominent railroad tycoon who had inherited much of the Vanderbilt family fortune from his father William and grandfather Cornelius. With 70 rooms and over 125,000 square feet, it dwarfed all of the other Newport mansions, and it would go on to epitomize the luxury, grandeur, and excess of the Gilded Age.
The Breakers is situated on Ochre Point, a rocky promontory on Newport’s eastern shoreline, and was built on the site of a previous mansion of the same name. The original Breakers was a wooden, Queen Anne-style mansion that had been designed by the prominent architectural firm of Peabody and Stearns for tobacco merchant Pierre Lorillard IV. It was completed in 1878, but he owned the house for less than a decade before selling it to Cornelius Vanderbilt in 1885 for $450,000, in what was at the time the largest real estate transaction in Newport’s history.
As the favorite grandson and namesake of the family patriarch, Cornelius Vanderbilt II had inherited $5 million after his grandfather’s death in 1877. Nearly all of the remaining family fortune, close to $100 million, had gone to Cornelius’s father, William H. Vanderbilt, who managed to double this amount in jut a few years. However, William died in 1885, just a few months after his son purchased The Breakers, and Cornelius inherited nearly $70 million from his estate, equivalent to nearly $2 billion today.
Cornelius’s younger brother, William K. Vanderbilt, had received a similar inheritance from their father, and he and his socially ambitious wife Alva soon set out to build Marble House nearby on Bellevue Avenue. This lavish mansion far exceeded the original Breakers in opulence, and its $11 million construction costs dwarfed the paltry $450,000 that Cornelius had spent to purchase his summer home. Marble House was completed in 1892, but later that year The Breakers was destroyed in a fire, providing Cornelius with the opportunity to eclipse his brother and sister-in-law in constructing a new summer home.
At the time of the fire here in Newport, Cornelius was just finishing a $3 million expansion of his massive Fifth Avenue mansion, making it the largest private home in New York City’s history. Despite this, he and his wife Alice spared no expense in rebuilding The Breakers. They hired Richard Morris Hunt, the same architect who had designed Marble House, and within six weeks of the fire he had produced preliminary designs for the house. Cornelius and Alice ended up choosing his second design, though, which was inspired by Italian Renaissance-style architecture, and construction began in the spring of 1893.
The house was completed in just two years, thanks to the efforts of some 2,000 workers who worked in shifts, both day and night, to ensure that it was completed as soon as possible. It was much larger, and had been built in far less time than Marble House, but at $7 million it had actually cost significantly less to build, with William having spent $7 million just on marble alone. It would be Richard Morris Hunt’s magnum opus and, as it turned out, his last major commission, as he died in Newport while supervising the finishing touches in the summer of 1895. The house’s completion came none too soon for Cornelius Vanderbilt, though, who was only able to enjoy one summer at the house in good health before suffering a debilitating stroke in 1896.
Cornelius, Alice, and their children would continue to spend several more summers here at The Breakers, but Cornelius never fully recovered his health and he died of a cerebral hemorrhage in September 1899, a day after returning to New York City from Newport. Alice would outlive him by 35 years, and became known as “Alice of the Breakers” for her long ownership of the house. However, the Gilded Age was rapidly drawing to a close at the turn of the 20th century, as was the Vanderbilt family’s wealth and prominence. William H. Vanderbilt’s children, including Cornelius, had done little to grow the family fortune, but excelled at spending it, particularly on lavish mansions in New York and summer houses such as The Breakers, Marble House, and the Biltmore Estate.
By Alice’s death in 1934 at the age of 89, the family fortune had been squandered and divided among so many descendants that it was essentially gone. Most of the New York City mansions, including her own Fifth Avenue home, were gone, replaced by modern high-rises, and the many summer homes in Newport and elsewhere were already antiquated white elephants from a long-gone era. During Alice’s later years, taxes alone on The Breakers amounted to $83,000 per year, plus operating expenses that included paying nearly 60 servants and other employees, along with 150 tons of coal to heat the house each winter. She eventually took to alternating years spent in Newport and New York, so that both houses were never open simultaneously.
Of Alice’s seven children, she outlived all but three of them. Her first child, Alice, had died as a child in 1874, and she subsequently lost her oldest son William to typhoid fever in 1892 while he was in college. Alfred died aboard the RMS Lusitania, when it was sunk by a German submarine during World War I, and Alice’s youngest son, Reginald, was a compulsive gambler and alcoholic who died of cirrhosis in 1925, a year after the birth of his daughter, future fashion designer Gloria Vanderbilt. Her only other son, Cornelius Vanderbilt III, was disinherited by his father for his unapproved marriage, and neither he nor his sister, the famous sculptor Gertrude Vanderbilt Whitney, had much interest in acquiring The Breakers.
As a result, the mansion ultimately went to Alice’s youngest child, Gladys, who was 47 at the time and married to a Hungarian count, László Széchenyi. She owned the property for the rest of her life, until her death in 1965, but in 1948 she began leasing the house to the Preservation Society of Newport County, and for the first time it was opened to the public. She would continue to maintain an apartment on the third-floor, as would her daughter Sylvia, but otherwise the rest of the house was preserved as a museum. Sylvia ultimately sold The Breakers to the Preservation Society in 1972 for just $365,000, substantially less than what her grandfather had paid for the original house 87 years earlier, although the sale included a stipulation that she be allowed to continue to use the third floor apartment for the rest of her life.
After Sylvia’s death in 1998, the third floor continued to be used by her children, Paul and Gladys Szápáry, for the next 20 years, but in early 2018 the Preservation Society asked them to leave, citing safety concerns. This move came shortly after the Szápárys voiced their opposition to the Preservation Society’s controversial decision to build a welcome center on the property, which many critics argued would mar its original landscape and historic appearance. Their departure ends four generations and nearly 123 years of the Vanderbilt family living here, but it also gives the Preservation Society the opportunity to restore the third floor and make it accessible to the public for the first time.
Today, The Breakers is one of the nine historic Newport homes that are owned by the Preservation Society and open to the public. Aside from the colonial-era Hunter House, all of these are Gilded Age mansions that represent some of the finest examples of residential architecture in 19th century America, including William and Alva Vanderbilt’s Marble House. However, The Breakers remains, by far, the largest and most impressive of these homes, and has been well-preserved over the years, as these two photos show. Because of its architectural significance, it was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1994, and it is now one of Rhode Island’s most popular tourist destinations, attracting over 400,000 visitors per year.