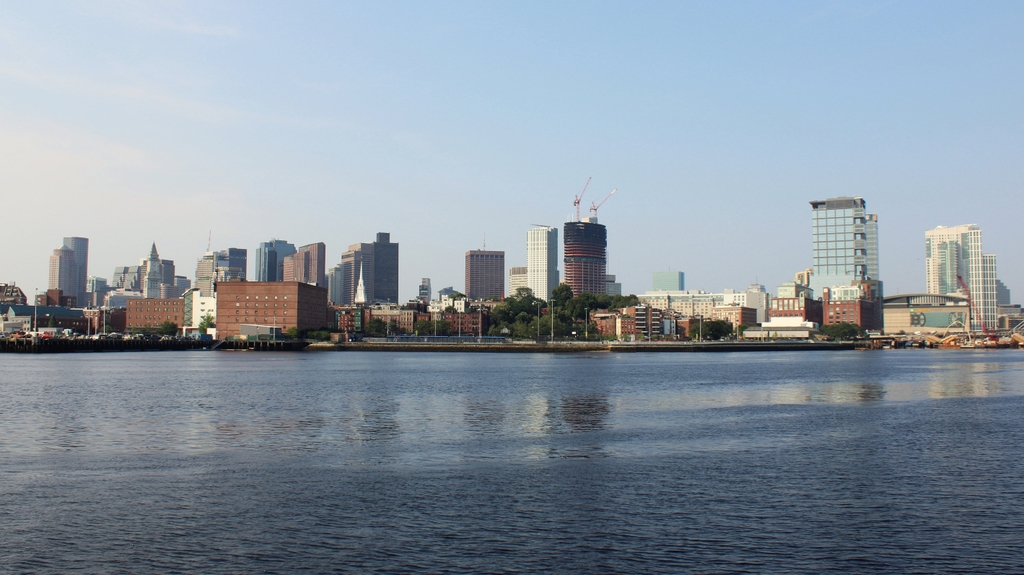
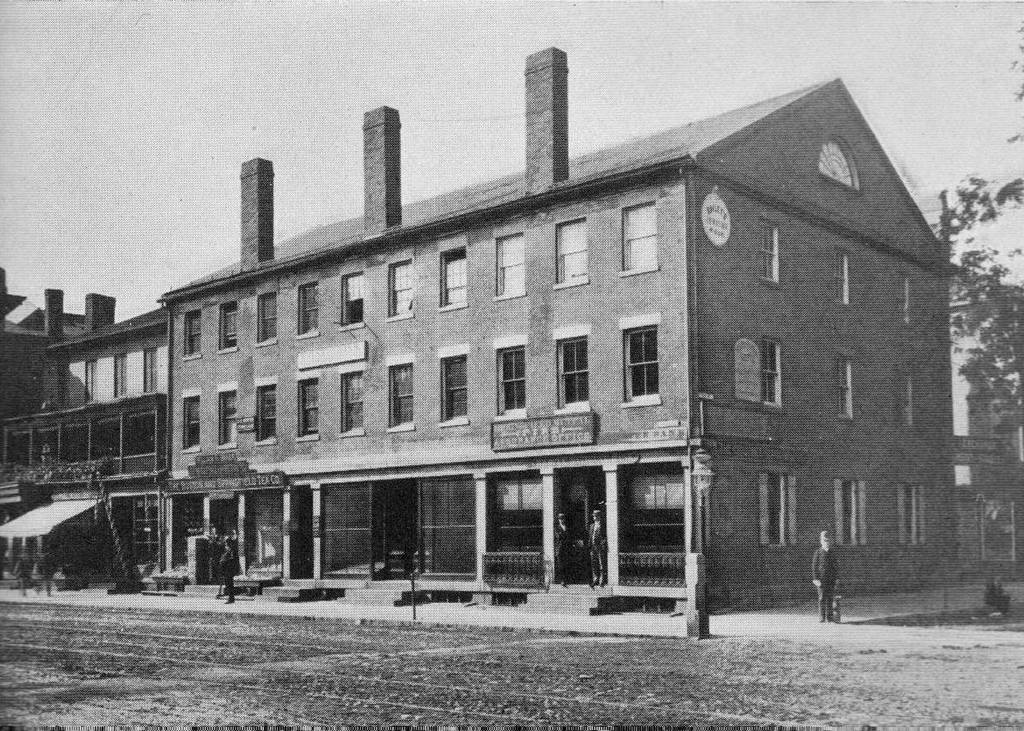
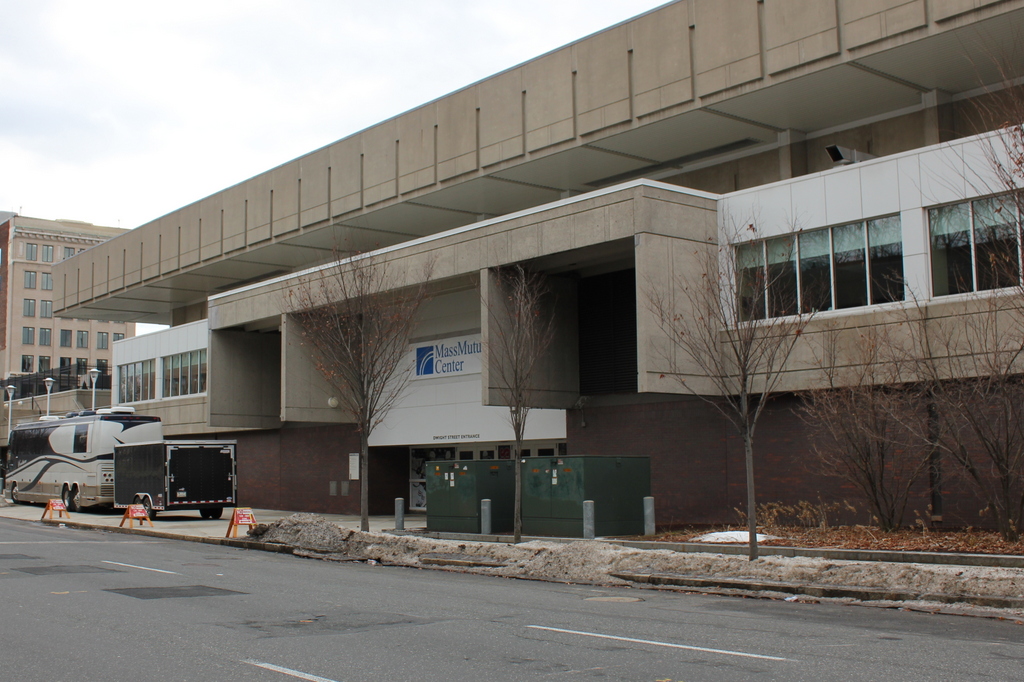
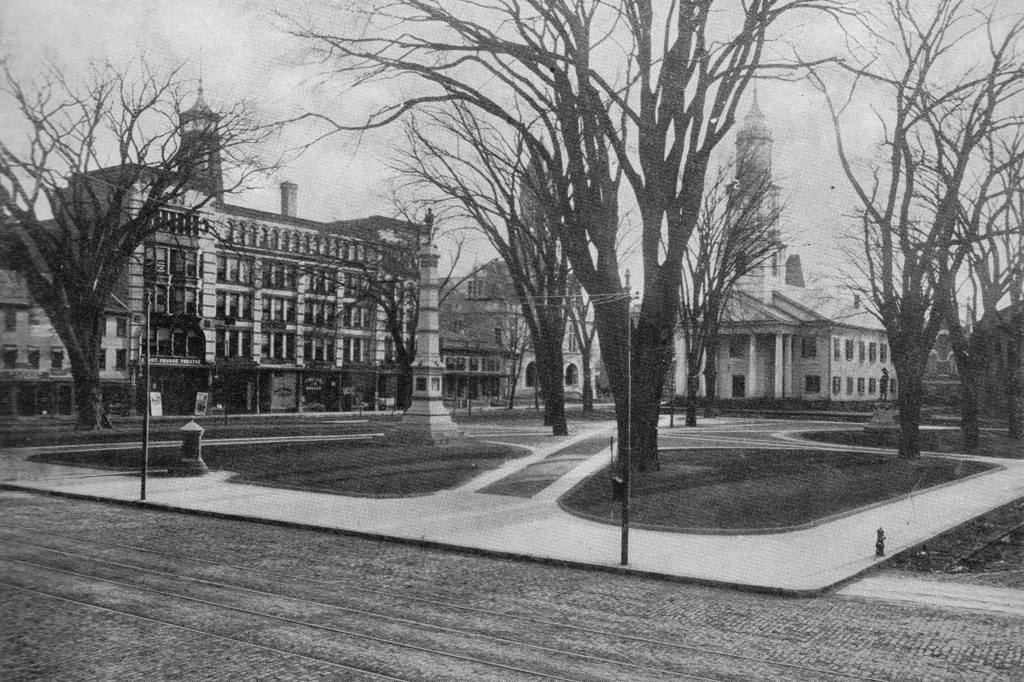
The North End of Boston from the Charlestown Navy Yard, in 1870, with the USS Kearsarge in the foreground. Photo courtesy of Boston Public Library.
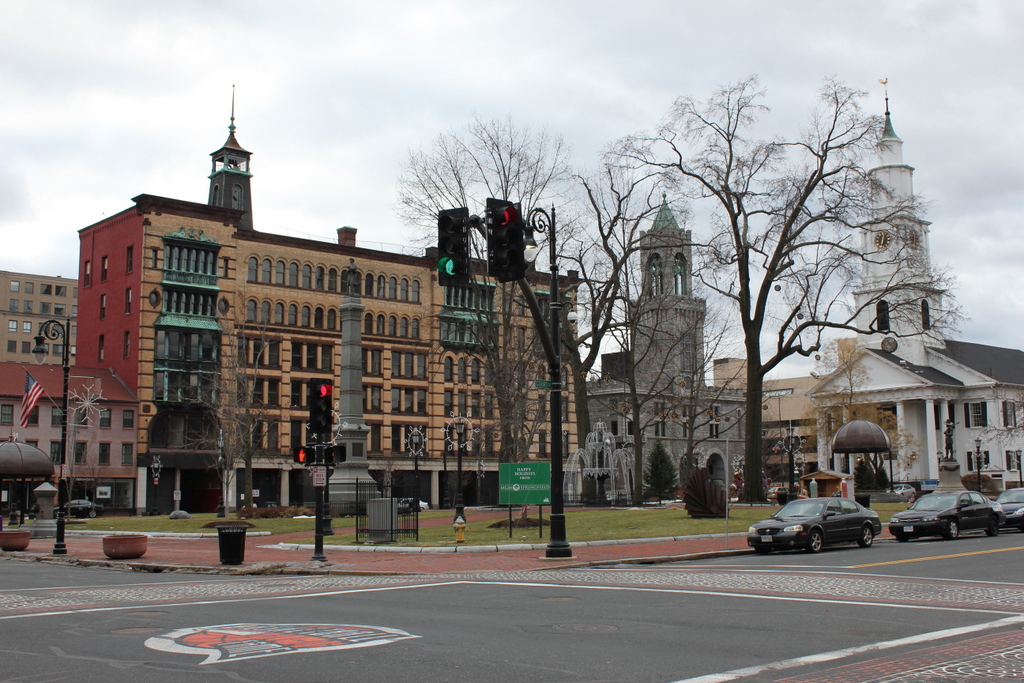
The scene in 2021:
Boston’s skyline has obviously changed significantly over the past 150 years, but at least one constant remains in both photos: Old North Church, which is barely visible behind some masts, just to the left of the Kearsarge, in the 1870 photo. The Kearsarge was a famous ship by this point – during the Civil War, she defeated the infamous Confederate commerce raider CSS Alabama. After she was decommissioned, a US battleship was named after her; she is the only non-state to have a US Navy battleship named after her.