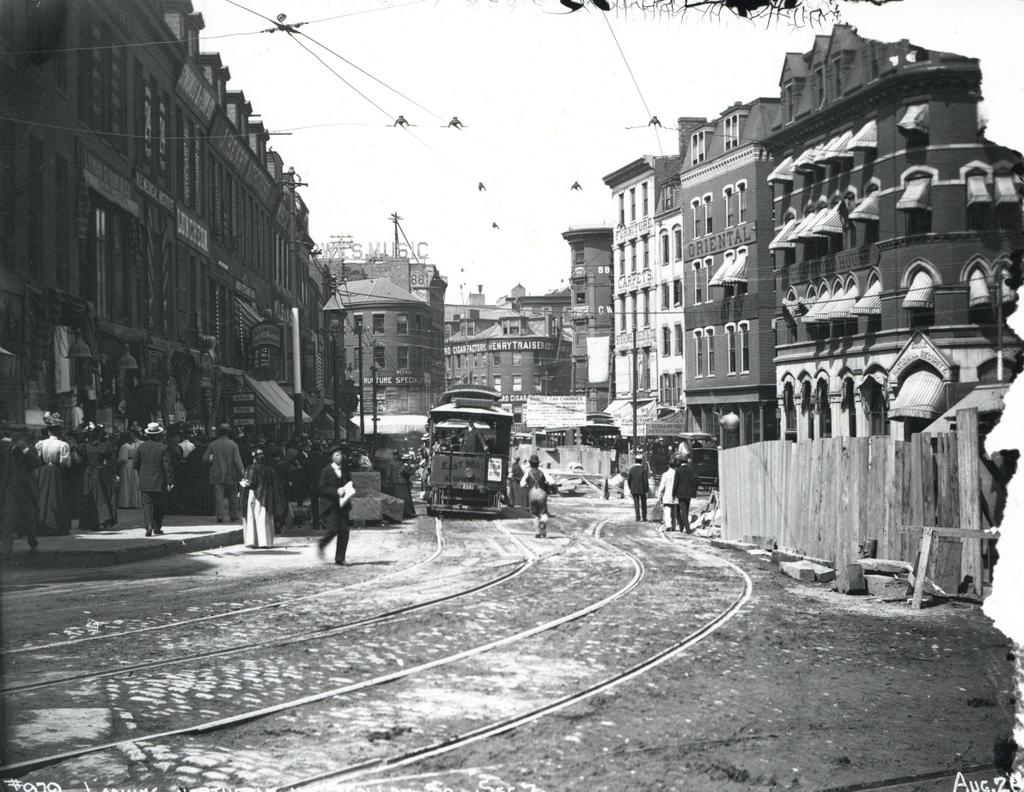
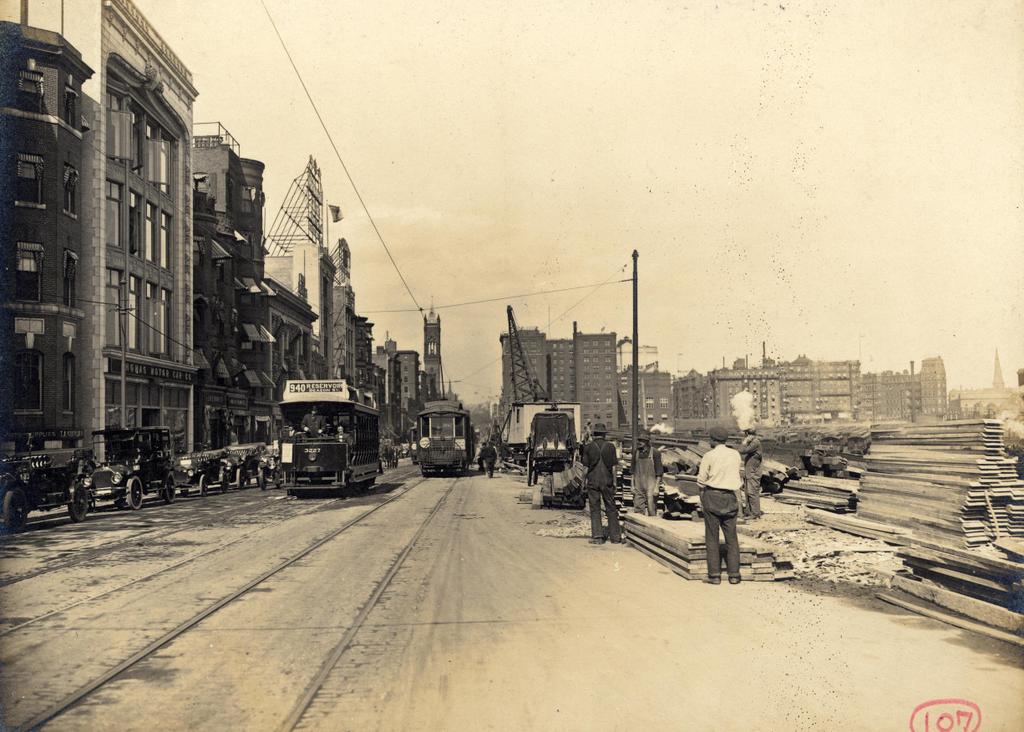
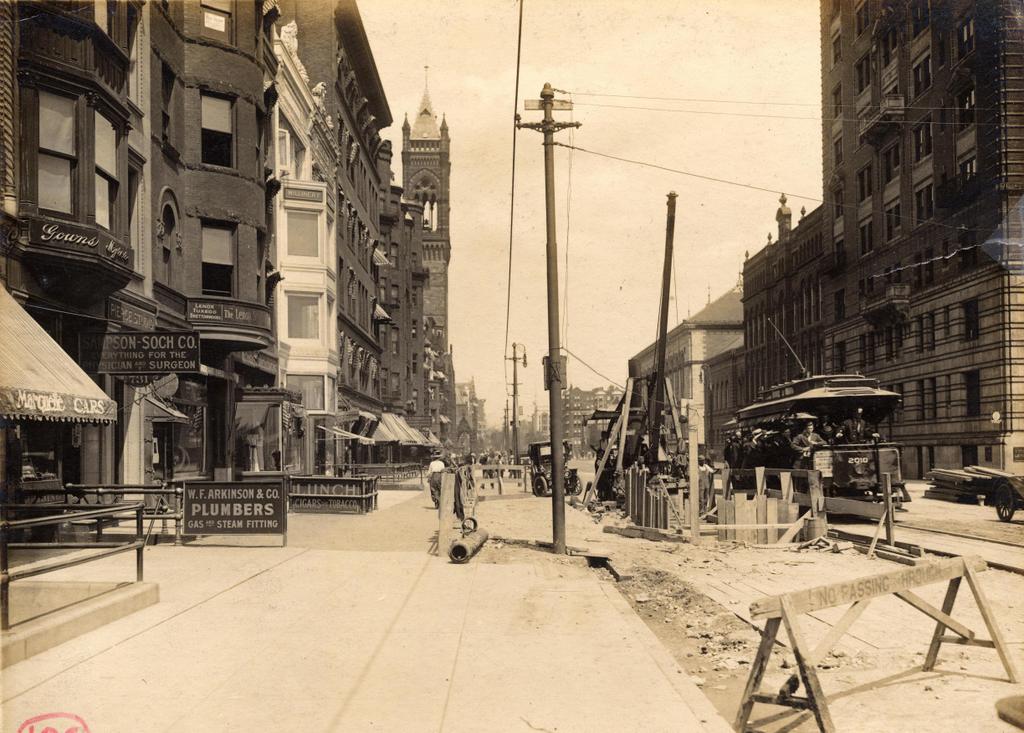
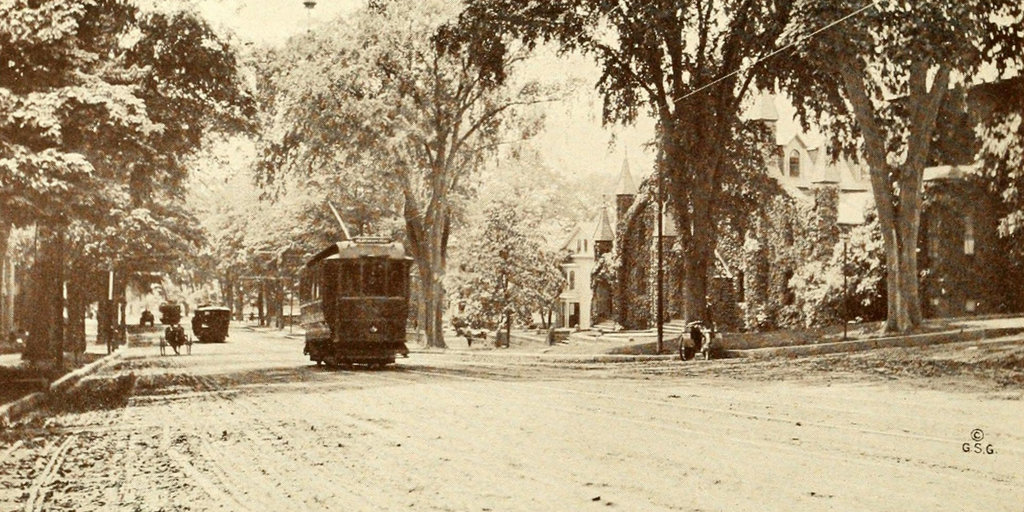Scollay Square, looking north from the corner of Tremont and Court Streets, sometime in the 1860s. Image courtesy of the Boston Public Library.
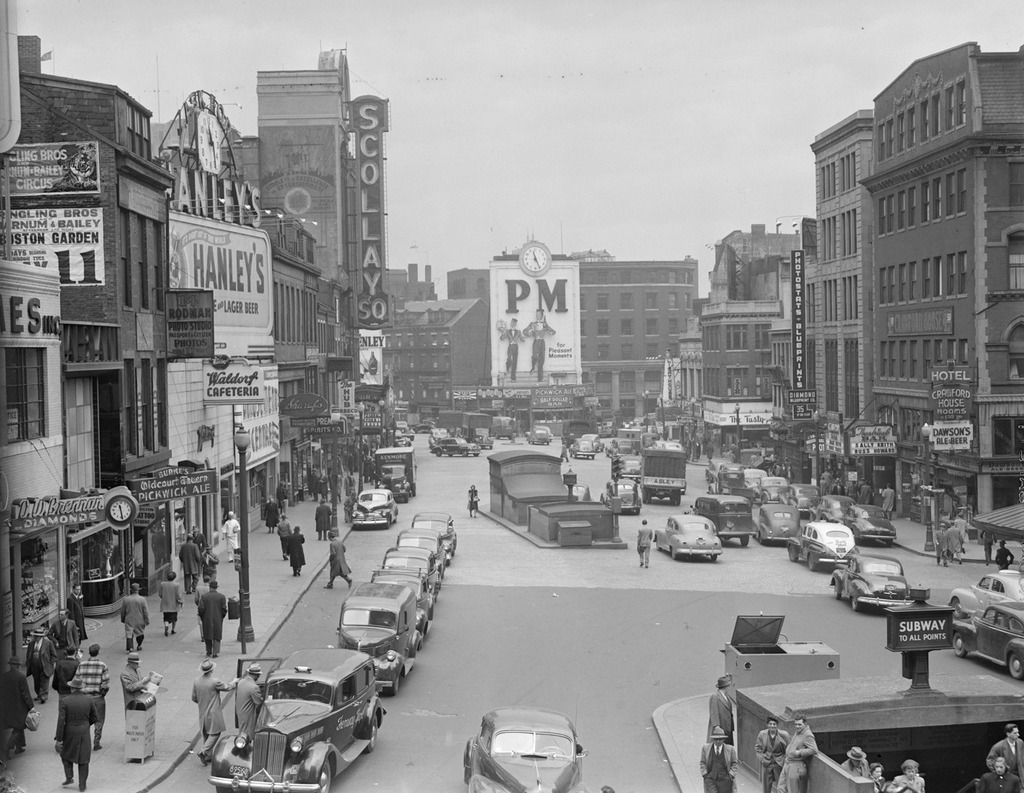
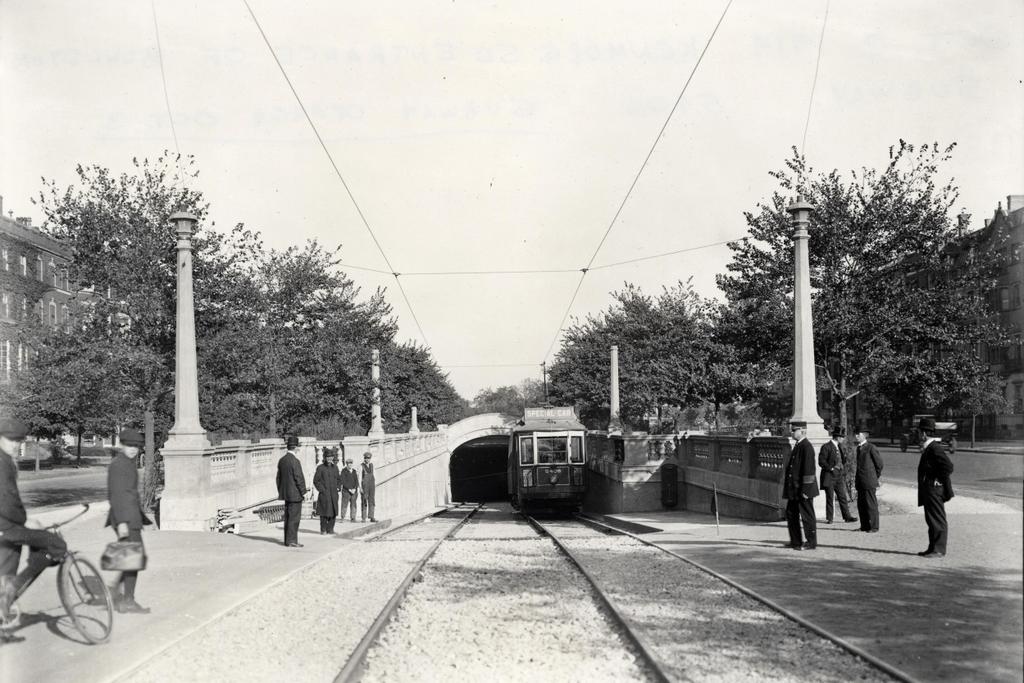
Scollay Square on August 26, 1897. Image courtesy of the City of Boston Archives.
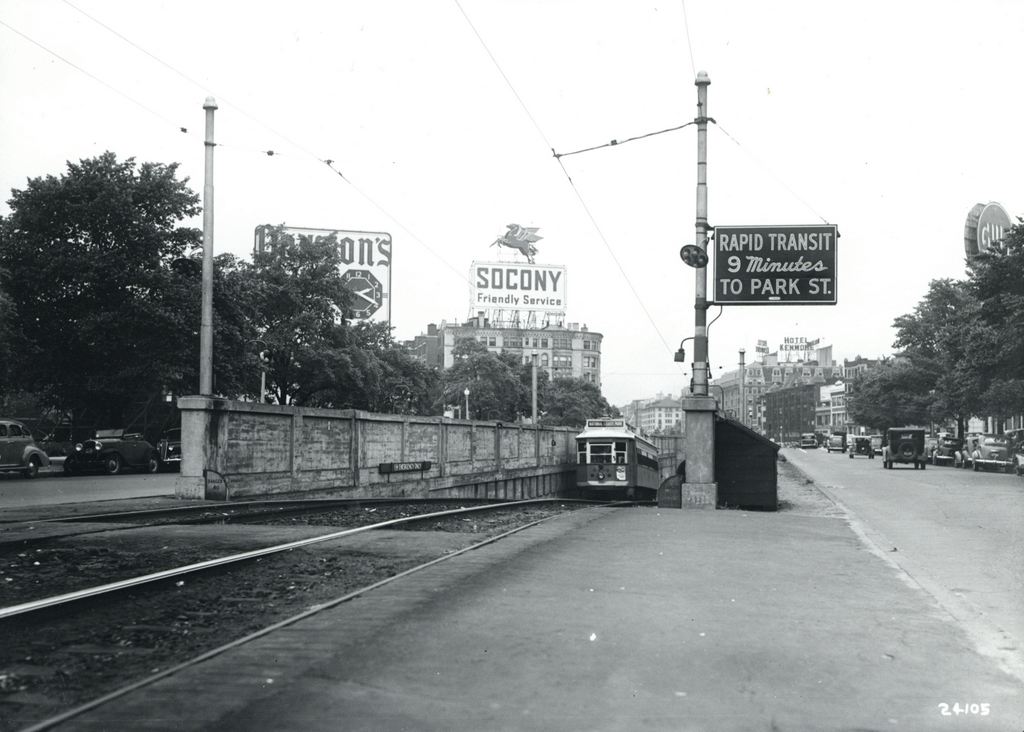
Scollay Square around 1942. Image courtesy of the Boston Public Library, Leslie Jones Collection.
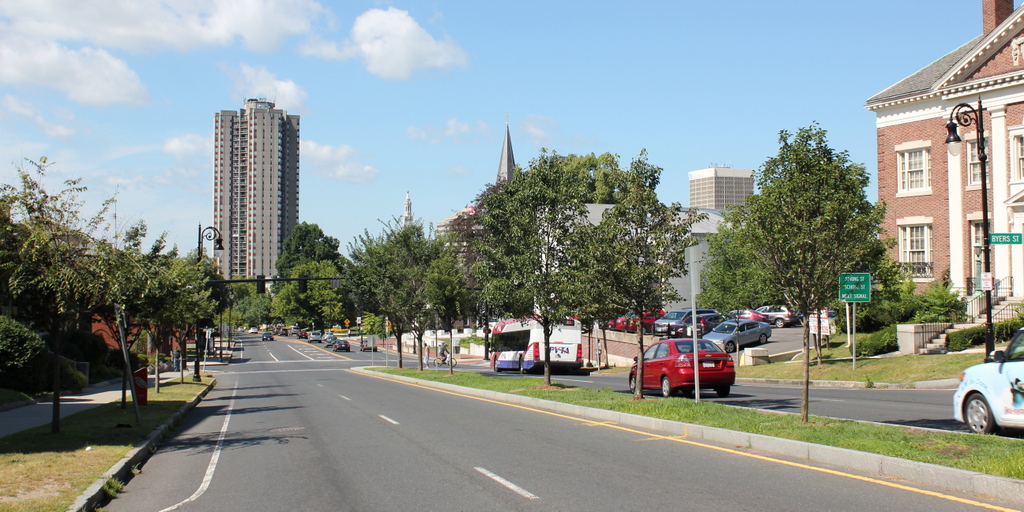
The scene in 2015:
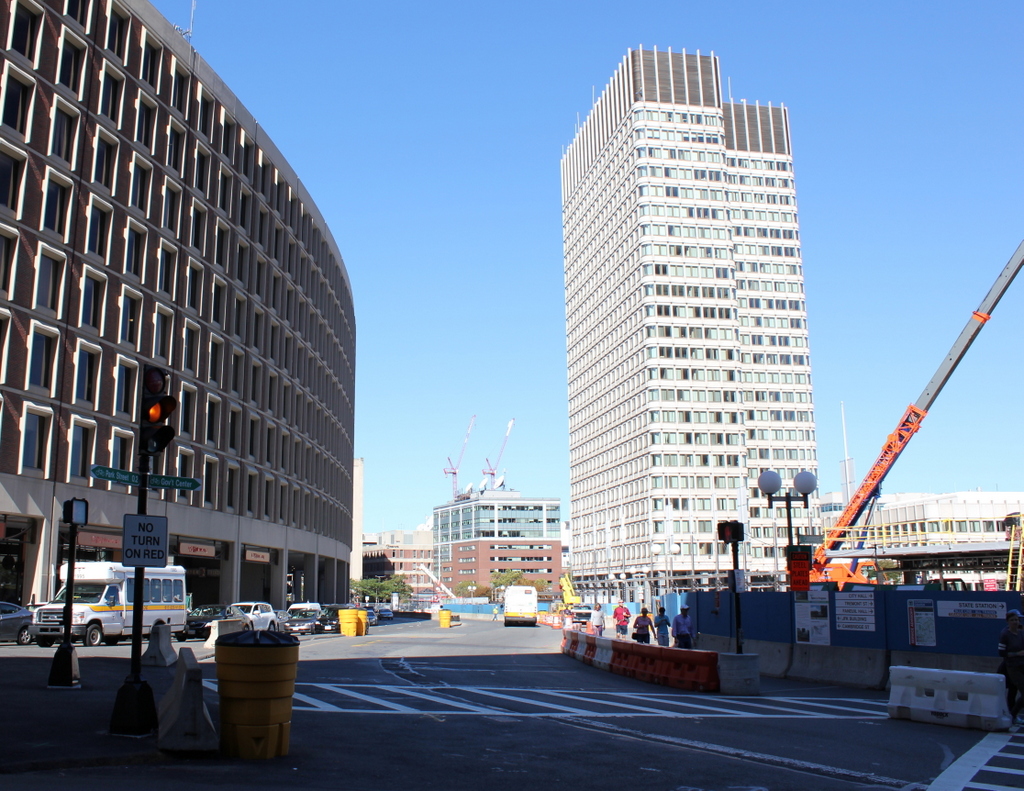

These four photos reveal the dramatic transformations that have occurred at Boston’s Scollay Square over the past 150 years. The square once included a long, narrow row of buildings in the middle, which appear on city maps as early as the 1720s. The construction date for the building in the first photo is unknown, but it was once at the southern end of this row, and in 1795 it was purchased by William Scollay, a real estate developer for whom the square would eventually be named. By the time the first photo was taken, all of the other buildings in the middle of the square had been demolished, and Scollay’s building was taken down soon after, around 1870.
The second photo shows a very different scene. Some of the buildings along the square are still standing, but the Scollay Building is gone, as are the horse-drawn trolleys from the first photo. Instead, they have been replaced by electric trolleys, like the one shown in the photo. However, these would not last long, at least not on the surface. The second photo was taken only about a week before the Tremont Street Subway opened, and the photo shows some of the construction activity as the workers prepared the Scollay Square station for its opening day on September 3. The station itself is not visible, but its ornate entrance can be seen in this post, which shows the scene from a slightly different angle.
Scollay Square had long been a major commercial center in the city, but by the time the third photo was taken in the 1940s, it had seen a dramatic decline. Many of the old buildings were still standing, but the businesses had become seedier. The 1942 photo shows a number of bars, liquor stores, cheap restaurants, and burlesque theaters, and the area was particularly popular among sailors on leave from the Boston Navy Yard and college students from the many nearby schools. One prominent hotel and theater in both the second and third photos was the Crawford House on the far right. It was built in 1865 and underwent several renovations, including one in 1926 that completely altered the front. The building burned in 1948, and all but the first two floors were demolished a few years later.
By the 1950s, the area was being targeted for urban renewal. Looking to replace the area with something more respectable, the Boston Redevelopment Authority demolished over a thousand buildings in the vicinity to build the Government Center complex, which includes the Center Plaza to the left, the John F. Kennedy Federal Building in the center, and the Boston City Hall, just out of view to the right. The old Scollay Square subway station was also extensively renovated and renamed Government Center. When the last photo was taken, the station was undergoing a another renovation, so if there is one thing that the second and fourth photos have in common, it is subway station construction.