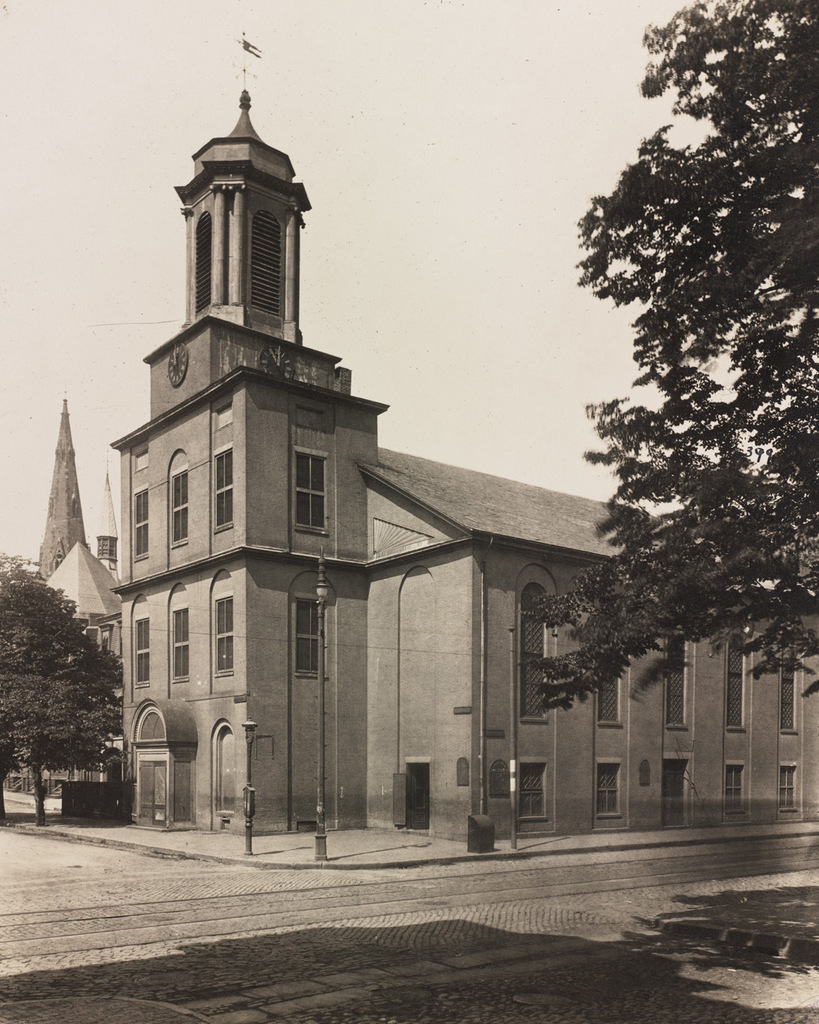
The Charles Street Meeting House, at the corner of Charles and Mt. Vernon Streets in Boston, around 1889. Image courtesy of the Boston Public Library.
The church in 2015:
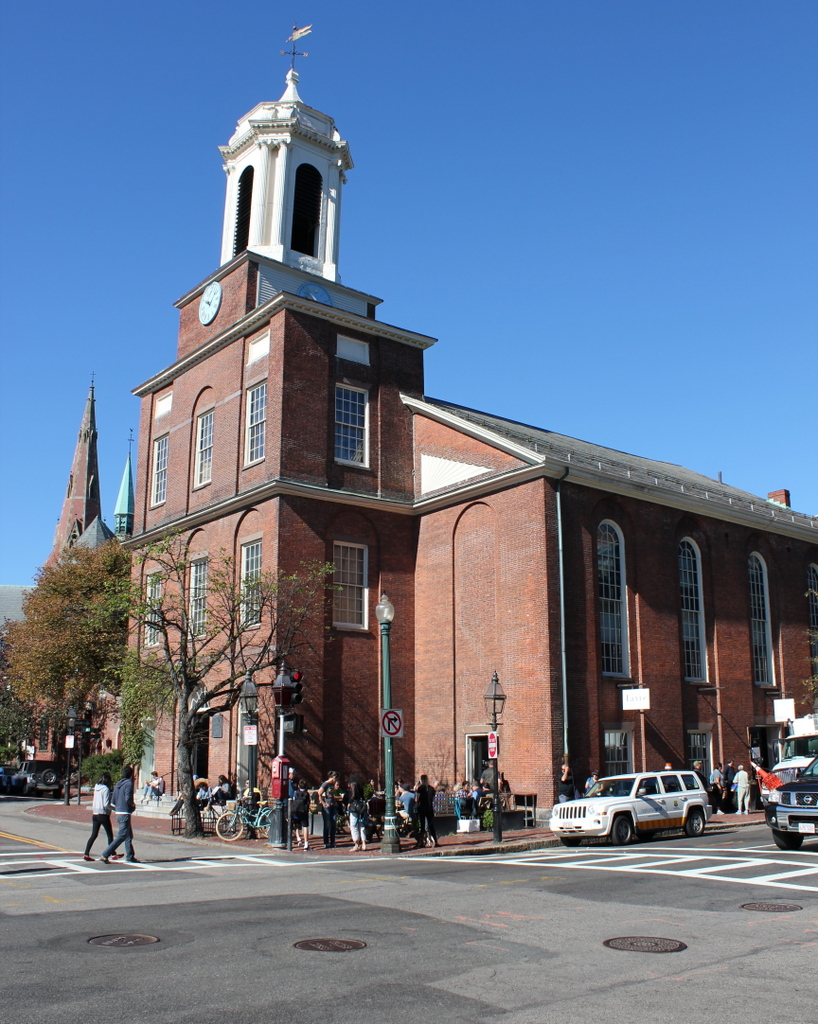

This historic church in the Beacon Hill neighborhood was built in 1807 as the Third Baptist Church. It was designed by Asher Benjamin, a New England native who was one of the leading American architects of the Federal era, and at the time it was located right along the waterfront. The building hasn’t moved in the past two centuries, but the shoreline has; Charles Street once ran along the Charles River at the western edge of the city, but after widespread landfill projects in the 19th century the church is now a considerable distance from the water.
Prior to the Civil War, this church was prominent in Boston’s abolitionist movement, and it hosted speakers such as Frederick Douglass, Wendell Phillips, Charles Sumner, and Sojourner Truth. After the war, though, the congregation declined, and merged with the First Baptist Church by 1876. The building was sold to the First African Methodist Episcopal Church, and became the Charles Street A.M.E. Church.
When the first photo was taken around 1889, the A.M.E. Church still owned it, and they remained here until 1939. By then, Boston’s black population had shifted away from its historic roots in Beacon Hill, and the congregation relocated to Roxbury. The building was later used as an Albanian Orthodox church and later as a Unitarian Universalist church until the late 1970s. A few years later, it was converted into offices. The interior was completely renovated, but the exterior was preserved, and today it is a part of the National Park Service’s Boston African American National Historic Site.