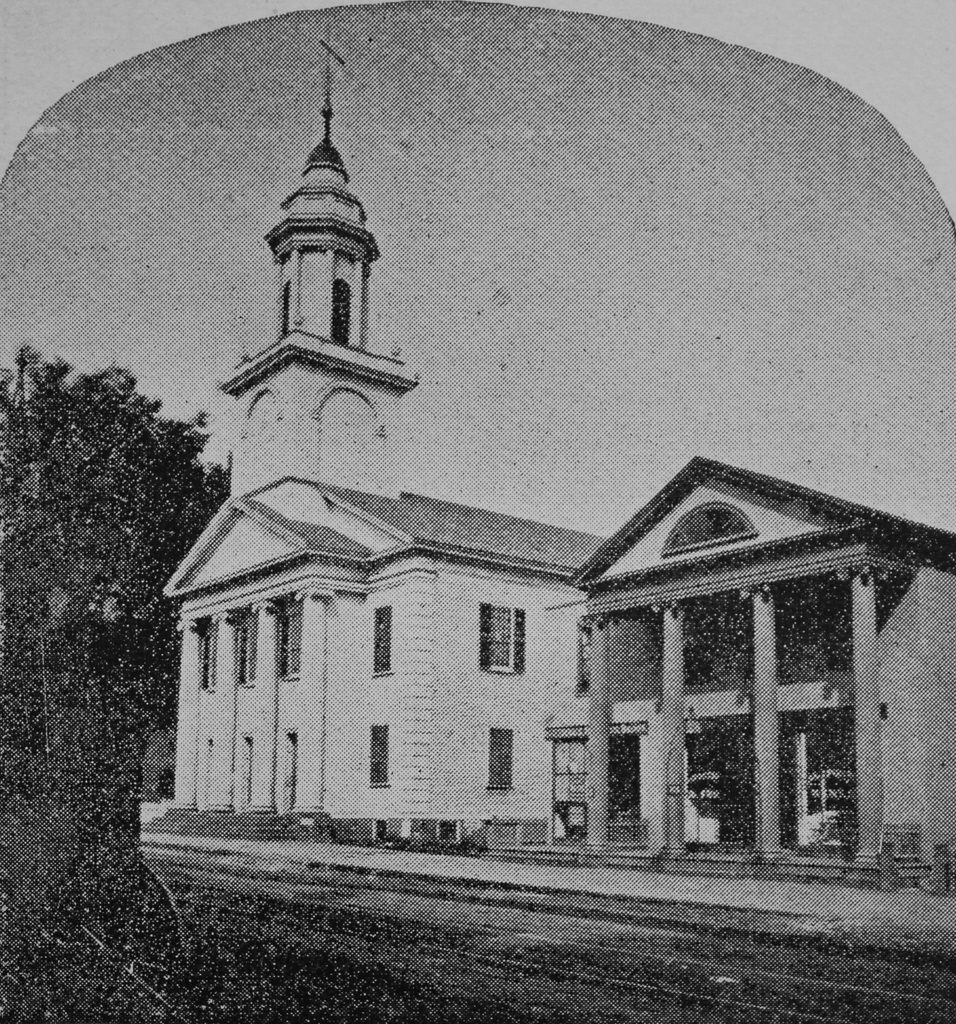
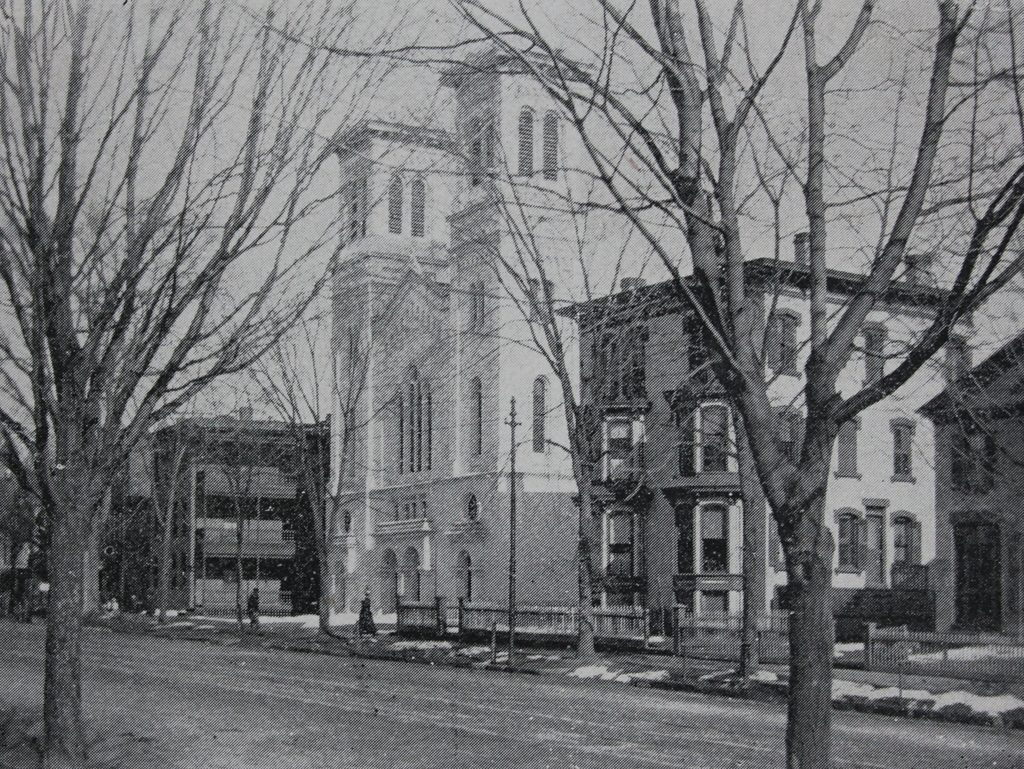
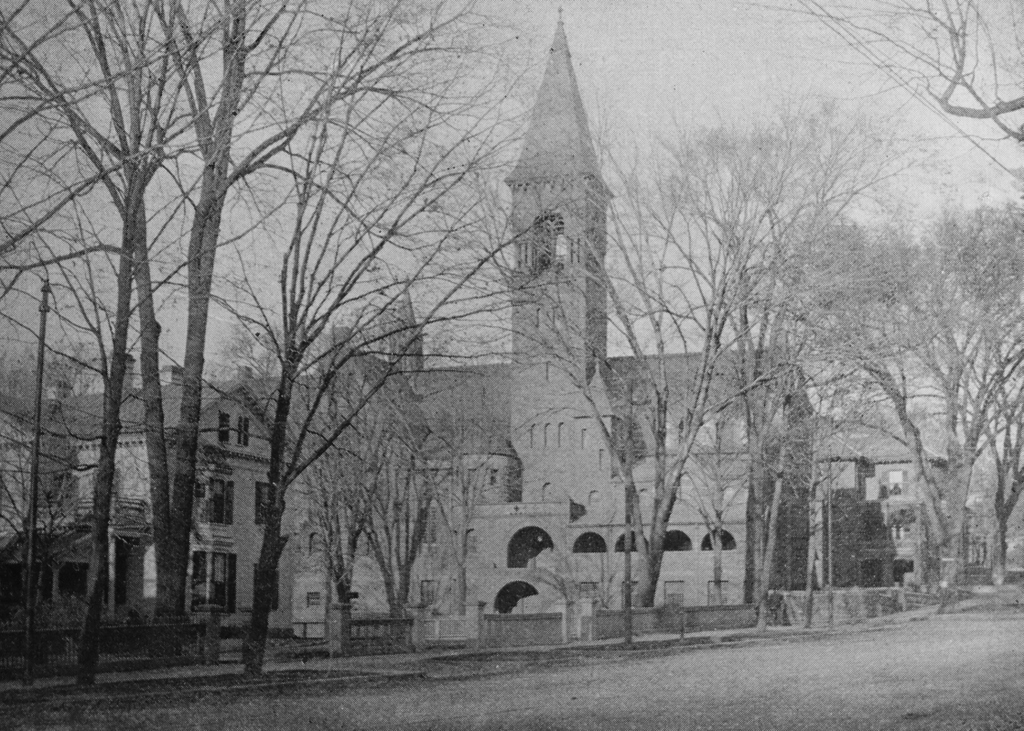The Unitarian church at the corner of State and Willow Streets in Springfield, probably sometime in the 1860s. Image from Picturesque Hampden (1892).
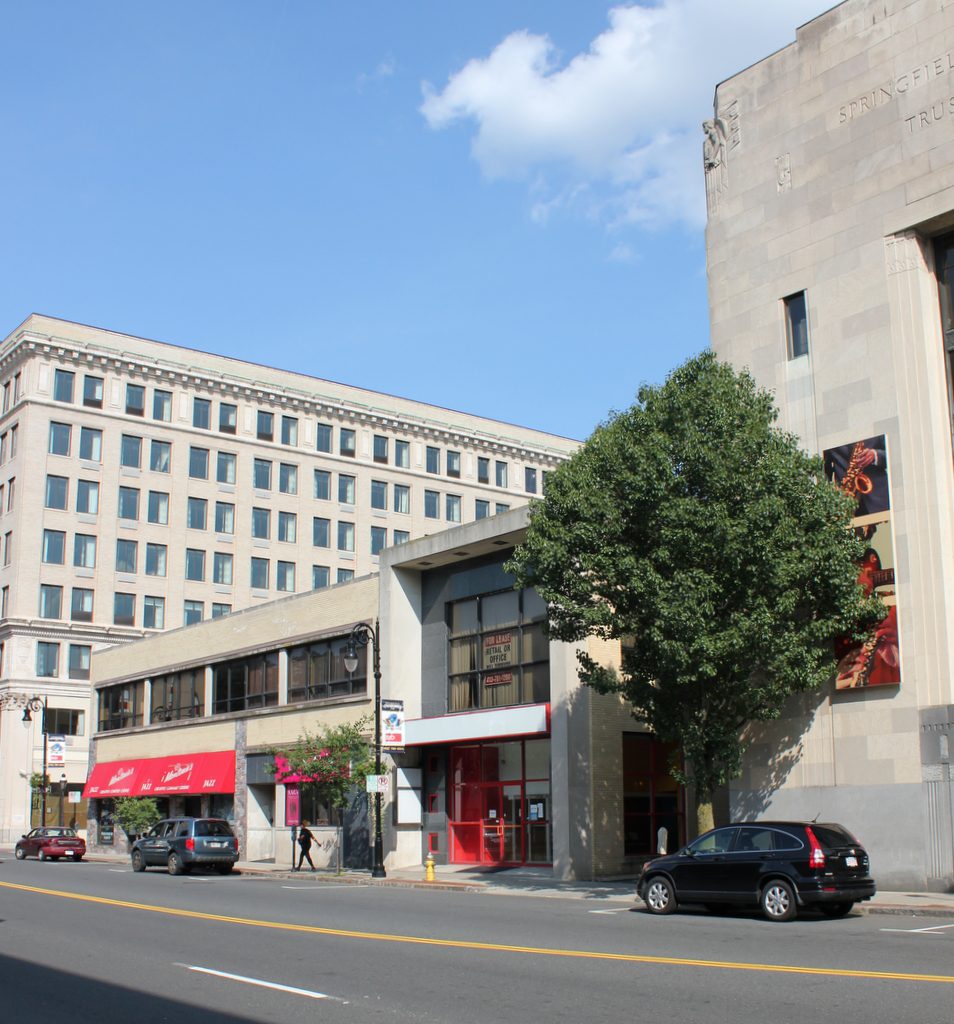
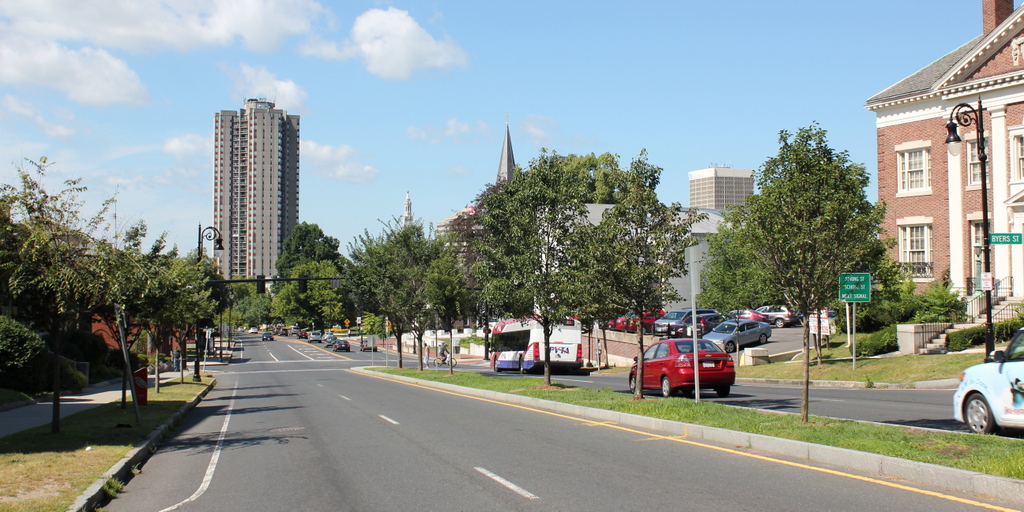
The scene in 2017:
For nearly 200 years, the Congregational Church was essentially the only church in Springfield. Aside from small groups of religious minorities such as Baptists and Methodists, who arrived at the turn of the 19th century, nearly all of Springfield’s residents were affiliated with the First Church. However, this hegemony began to break apart in the early 19th century, when the New England Congregationalists saw a schism between the traditional Trinitarians and the newer, theologically-liberal Unitarians.
Here in Springfield, the First Church had two fairly liberal pastors throughout much of the 18th century, beginning with Robert Breck, who served from 1736 to 1784. Breck’s ordination had been highly controversial, due to the perceived unorthodox beliefs of the young clergyman. He was popular among the Springfield congregants, but many of the pastors of surrounding towns – including Jonathan Edwards of Northampton – had advised against him, and some of his opponents had Breck arrested for heresy on the day of his scheduled ordination.
The charges against Breck were ultimately dropped, and he was duly ordained, serving the church for nearly 50 years. After his death, he was replaced by another young liberal pastor, Bezaleel Howard, who served for 18 years before announcing his resignation in 1803, due to poor health. He agreed to remain with the church until his replacement was found, but this process likely took longer than Howard had anticipated. By this point, the Unitarian-Trinitarian controversy had become the dominant issue in New England churches, and it took six years – and 37 candidates – before Samuel Osgood was selected as pastor in 1809.
Osgood, a 24-year-old Dartmouth graduate, had been the unanimous choice of the congregation, who had viewed him as being theologically liberal. However, as the divide grew between the two factions, Osgood ultimately favored the orthodox Trinitarian theology, alienating some of the most influential citizens of Springfield in the process. The majority of the church sided with Osgood, but the Unitarians were both vocal and wealthy, and included prominent businessmen such as merchant Jonathan Dwight, Sr. As a result, around 117 Unitarians separated from the First Church in 1819, forming the Third Congregational Society of Springfield. This name came from the fact that Chicopee, home of the Second Congregational Church, was still a part of Springfield at the time.
Later in 1819, the Unitarians moved into this newly-completed church building at the corner of State and Willow Streets. Both the land and the building had been donated by Jonathan Dwight, and the building was designed by local architect Simon Sanborn. It bore a strong resemblance to the new First Church building, which had been completed several weeks earlier at Court Square, and it reflected the Greek Revival style of architecture, which was becoming popular for churches and other public buildings during this era.
The first pastor of the Unitarian church was William B. O. Peabody, who was just 21 years old when he was ordained in October 1820. He served the church for the next 27 years, until his death in 1847, and during this time he also had a successful career as an author. He wrote several books, plus a number of poems and hymns, and he was also a regular contributor to the North American Review literary magazine. None of Peabody’s 19th century successors were able to match his longevity with the congregation, but the second-longest pastorate here in this church building was that of Francis Tiffany, who served from 1852 until 1864, when he left to accept a position as professor of English and rhetoric at Antioch College in Ohio. Like Peabody, he also became a published author, writing a biography of social reformer Dorothea Dix in 1890.
The Unitarians worshiped here in this building for nearby 50 years, but by the 1860s they had begun planning the construction of a new building further up the hill, opposite where the Springfield City Library now stands. In the process, they helped to start the career of Henry H. Richardson, who would become one of the most influential architects in American history. Although he did not have any major commissions at the time, Richardson was allowed to enter the design competition thanks to Chester W. Chapin, a railroad and bank executive who was a prominent member of the Unitarian church. Chapin’s son-in-law had attended college with Richardson, and this connection enabled the young architect to submit his plans for a new church, which were ultimately the ones chosen in the competition. The new building, known as the Church of the Unity, was completed in 1869, and Richardson’s work helped to establish his reputation as an architect.
The other building in the first photo, just to the right of the church, is the Springfield Bank. This brick, two-story Greek Revival structure was built around in 1814, the same year that the Springfield Bank was established as the first bank here in Springfield. It was one of the many business interests of Jonathan Dwight, who was one of its founders and its first president, serving from 1814 to 1817. The building was also the first home of the Springfield Institution for Savings, which was established in 1827. It was the first savings bank in Springfield, and it shared this building with the Springfield Bank until 1849, when it moved into the newly-completed Foot Block at the corner of Main and State Streets. In the meantime, the Springfield Bank remained here in this building until 1863, when it was reorganized as the Second National Bank. This new bank relocated three years later, and the old building later became a store owned by grain merchant John W. Wilder.
Only four years after the Unitarians moved up the hill to their new building, the old church burned down on the night of October 12, 1873. The site was later redeveloped with a large brick commercial building known as the Kirkham and Olmstead Block, which was in turn replaced by the two-story building that is now standing here. However, the old bank building survived well into the 20th century, despite being converted to other commercial use. The 1920 atlas shows it still standing, but it was demolished sometime before 1933, when the Art Deco-style Springfield Safe Deposit and Trust Company building was completed on the site. This building, now the Community Music School, is still here today, and is visible on the far right side of the 2017 photo.