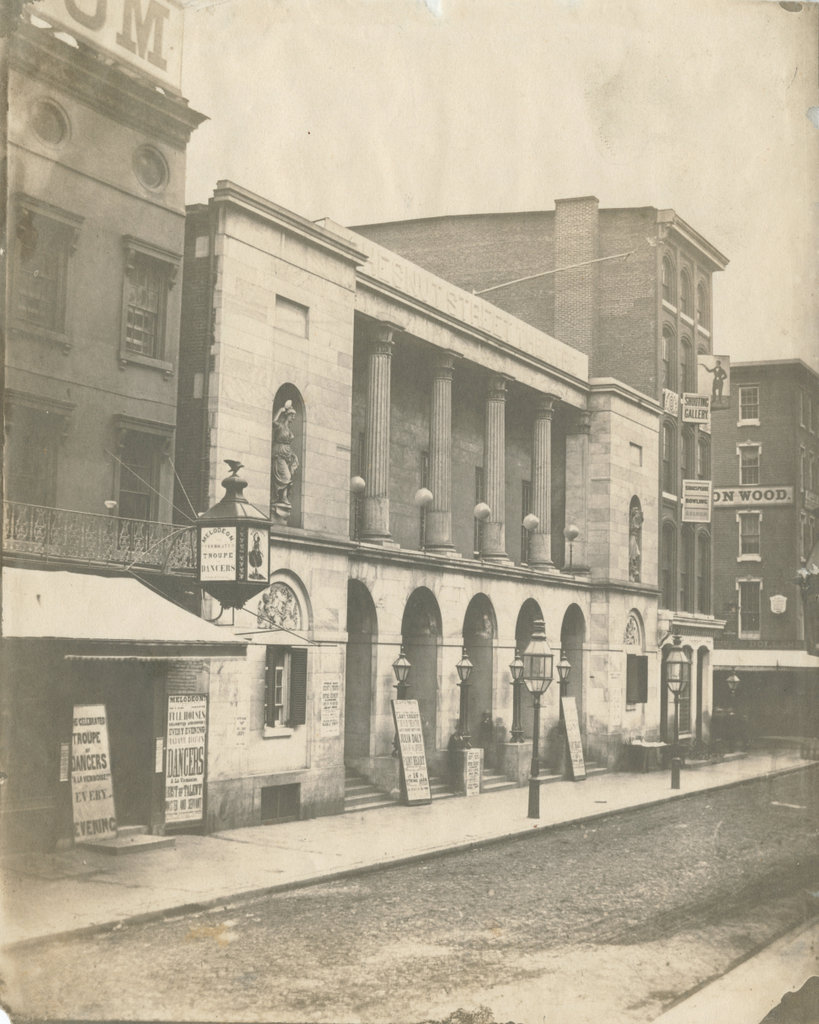
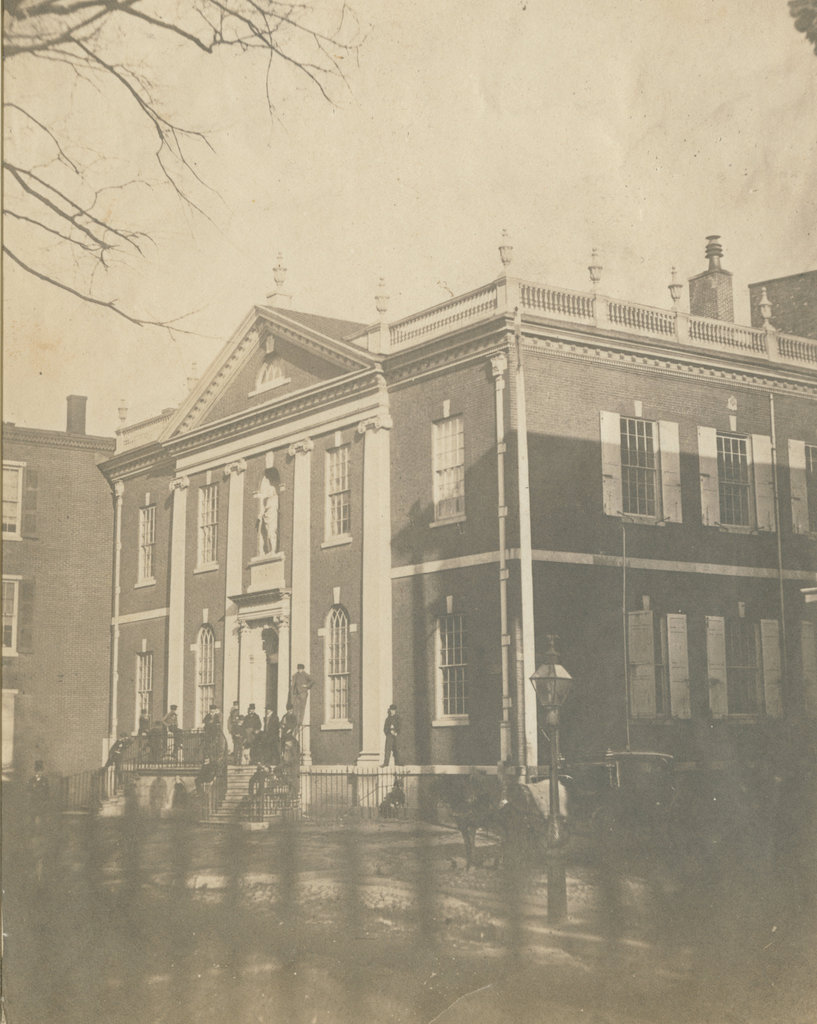
The Chestnut Street Theatre on the north side of Chestnut Street, just west of Sixth Street in Philadelphia, on April 30, 1855. Image courtesy of the Library Company of Philadelphia, James McClees Philadelphia Photograph Collection.
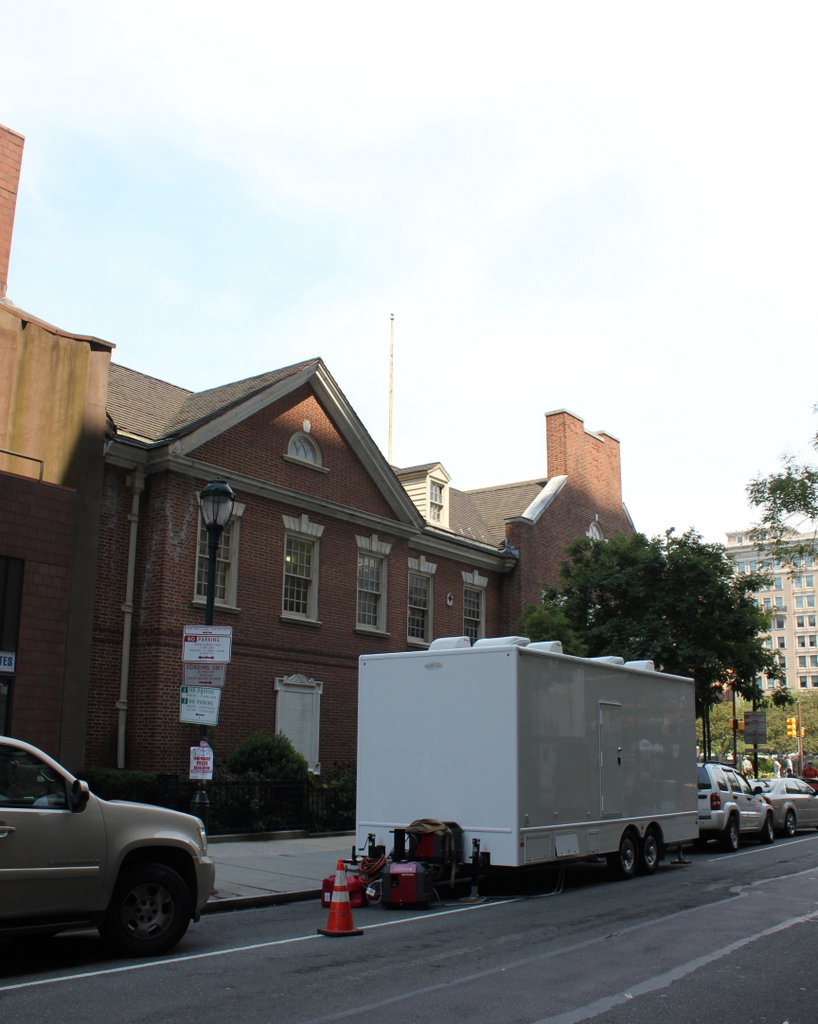
The scene in 2019:
During the colonial era, theater was not a significant part of American culture, particularly in the northern and middle colonies. In New England, the Puritans saw plays and acting as immoral, and here in Philadelphia the Quakers similarly disapproved, believing that going to theaters was a frivolous use of time and money. Some colonies, including Pennsylvania, even outlawed plays. However, this trend began to change after the American Revolution, and one of the first purpose-built theaters in the country was the Chestnut Street Theatre, which opened here in 1794.
At the time, Philadelphia was the capital city of both the United States and Pennsylvania, and the theater was located in the midst of these governmental buildings. The national capitol, Congress Hall, was diagonally across the street from the theater, and just beyond Congress Hall was Independence Hall, the seat of the state government. The Supreme Court met in a building on the other side of Independence Hall, and a block to the north of the theater was the President’s House, home of George Washington and later John Adams.
The original Chestnut Street Theatre burned in 1820, but it was rebuilt two years later. This new building, which is shown here in the first photo, was designed by prominent Philadelphia architect William Strickland, who was responsible for many important buildings in the city during the early 19th century. On the exterior, the theater featured classically-inspired elements such as the arched entryways on the ground level and the four columns on the upper floor. The columns were flanked by a pair of statues, representing Tragedy and Comedy, that were carved by sculptor William Rush. The interior of the theater featured three rows of boxes arranged in a semi-circle around the stage, and it could accommodate around 2,000 people. It was built with fire safety in mind, including large stairways and multiple exits with outward-swinging doors, and it was said that a full crowd could evacuate the building in under three minutes.
The theater opened on December 2, 1822, and the occasion was marked by the reading of a letter from poet Charles Sprague, followed by a performance of the comedy The School for Scandal. Several days later, the National Gazette reported on it, observing that it opened “to a crowded, brilliant and good humoured house. The spectators and the actors appeared to be in the best spirits and both performed their respective parts in the best manner.” The article went on to say that “Everything went on and off swimmingly and satisfactorily” and that “Several gentlemen who had been abroad, and some foreigners, were heard to say that the Theatre was the prettiest they had ever seen.”
The new Chestnut Street Theatre, which came to be known as “Old Drury,” remained a popular venue for plays and concerts throughout the first half of the 19th century. During this time, perhaps the most famous performer was Jenny Lind, a Swedish opera singer who toured America from 1850 to 1852. The tour was organized by P. T. Barnum, who used his showman skills to generate fanfare for her performances. She arrived in New York in September 1850, and a month later she came to Philadelphia, where her first performance in the city occurred here at the Chestnut Street Theatre on October 17. In order to meet the anticipated demand, the tickets were auctioned off. The first one sold for the astronomical price of $625, equivalent to around $20,000 today, but prices quickly dropped for the subsequent tickets. The second one sold for just $15, and before long they were selling for under $10. In the end, about 1,700 tickets were sold at the auction, at an average of $7 each.
The day after the concert, the Philadelphia Inquirer published an account of the event, including a description of the crowd inside the theater:
A more brilliant audience never assembled within its walls, and this is saying a great deal, for “Old Drury” ranked for many years as the very temple of taste, fashion, dramatic and musical triumph. The spectacle was, indeed, fairy-like. The splendid dresses, the bright eyes, the flushed cheeks, the eager expectation depicted on every countenance, the brilliant gas-lights, and the whisperings and buzzings of many voices, served to produce an unwonted excitement; and thus, long before the hour for the commencement of the entertainment, the blood seemed to flow more rapidly through the veins, even of the most passionless.
The excitement of this event notwithstanding, by the 1850s the Chestnut Street Theatre was past its prime. Its location was no longer as desirable as it had once been, and the building was considered too small by this point. The first photo was taken on April 30, 1855, a day before its final performance, as indicated by the playbills at the main entrance, which indicate that it will be the “last night but one” for the old theater. That evening’s entertainment consisted of the burletta The Loan of a Lover, followed by the comedy Faint Heart Never Won Fair Lady and the drama Sixteen String Jack. The leading performer was 21-year-old Philadelphia native Julia Daly, whose name appears prominently on the playbills. According to newspaper advertisements, admission started at 12.5 cents for the gallery. General admission was 25 cents, and reserved seats for 37.5 cents. Orchestra and private box seating was 50 cents, and the “Colored Gallery” was 25 cents.
Somewhat more ominously than the playbills, the first photo also includes several visible posters advertising for the public sale that would take place on May 2, the day after the final performance. The sale would include the theater’s scenery, wardrobe, machinery, and other items, along with building materials such as doors, windows, rafters, roofing, and even the marble facade. This included the four marble columns, which sold for $25 each.
The theater was demolished soon after the sale, and it was replaced by a commercial building. All of the other buildings in the first photo have since been demolished as well, and the site of the theater is now a bank, which was built in 1965. It was originally the First Pennsylvania Bank, but after a series of mergers it is now a Wells Fargo branch. Further in the distance, on the other side of Sixth Street, is part of the Independence National Historical Park, and just out of view on the far right is Congress Hall and Independence Hall.