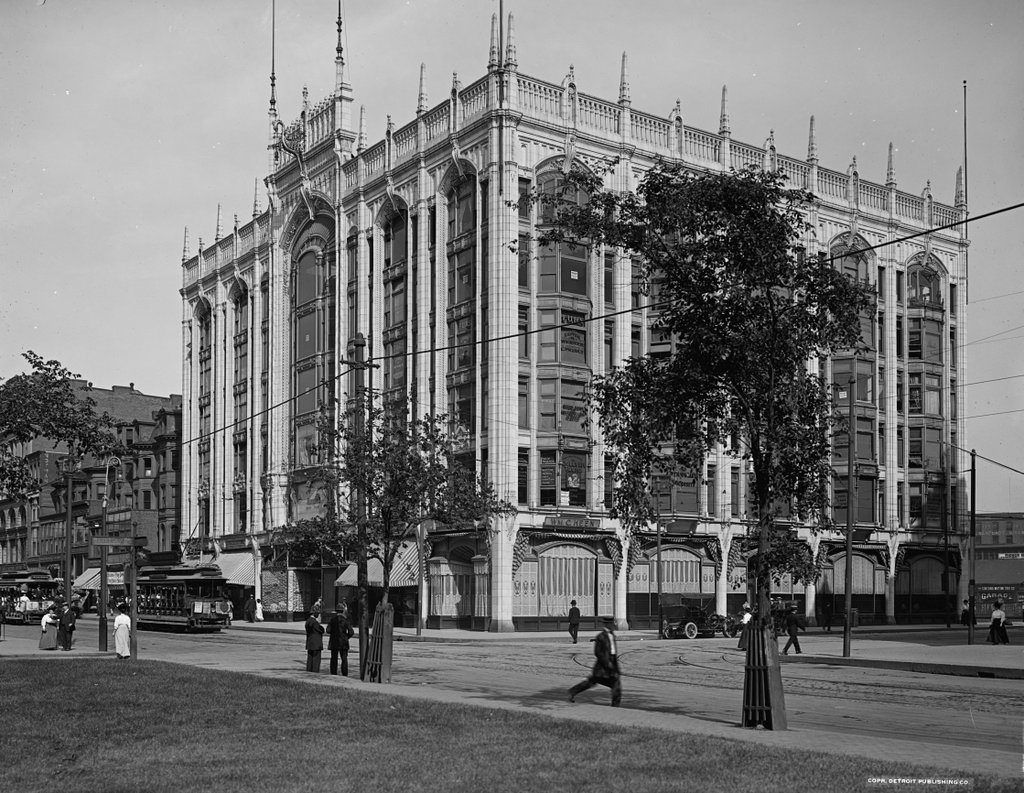
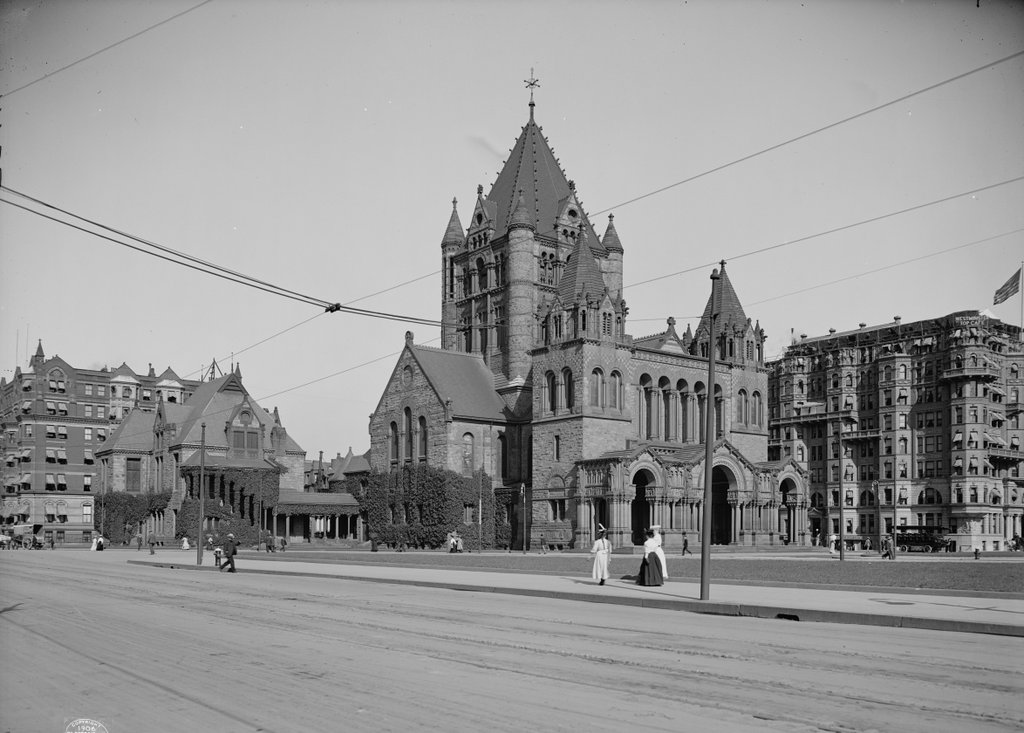
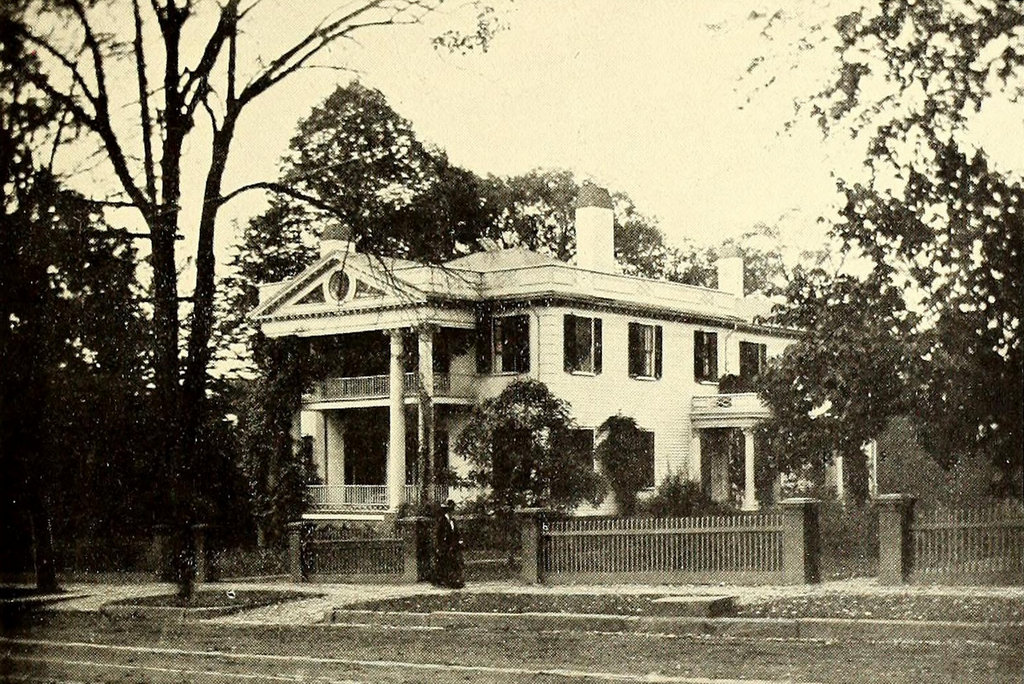
The Alexander House on State Street in Springfield, around 1905. Image from Springfield, Present and Prospective (1905).
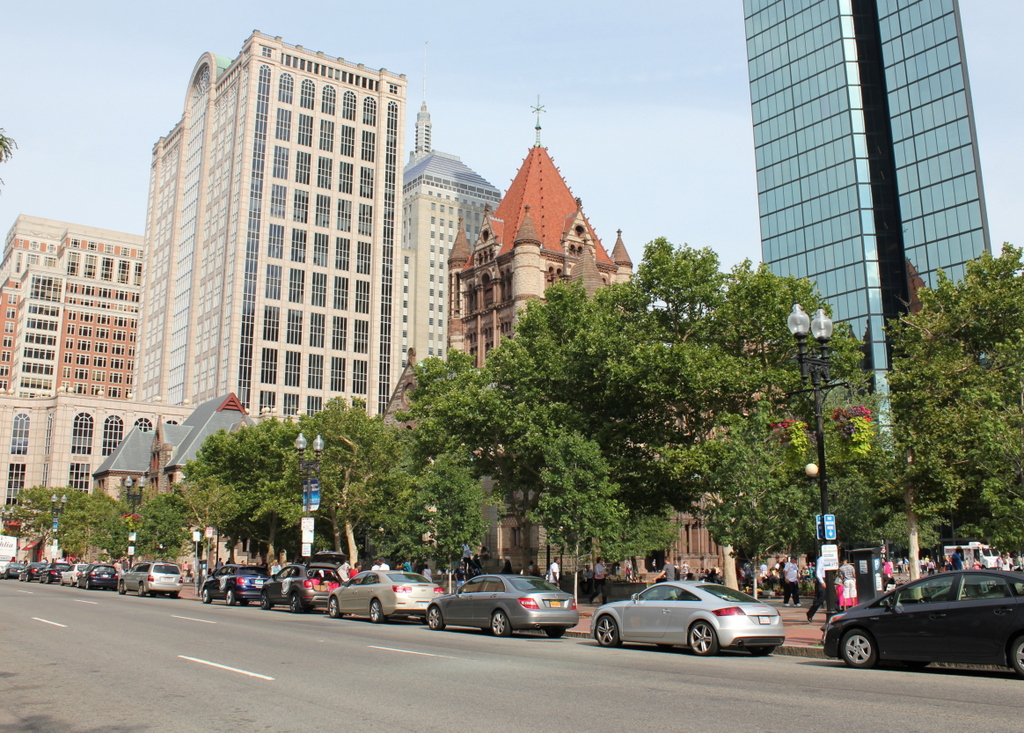
The site in 2015:
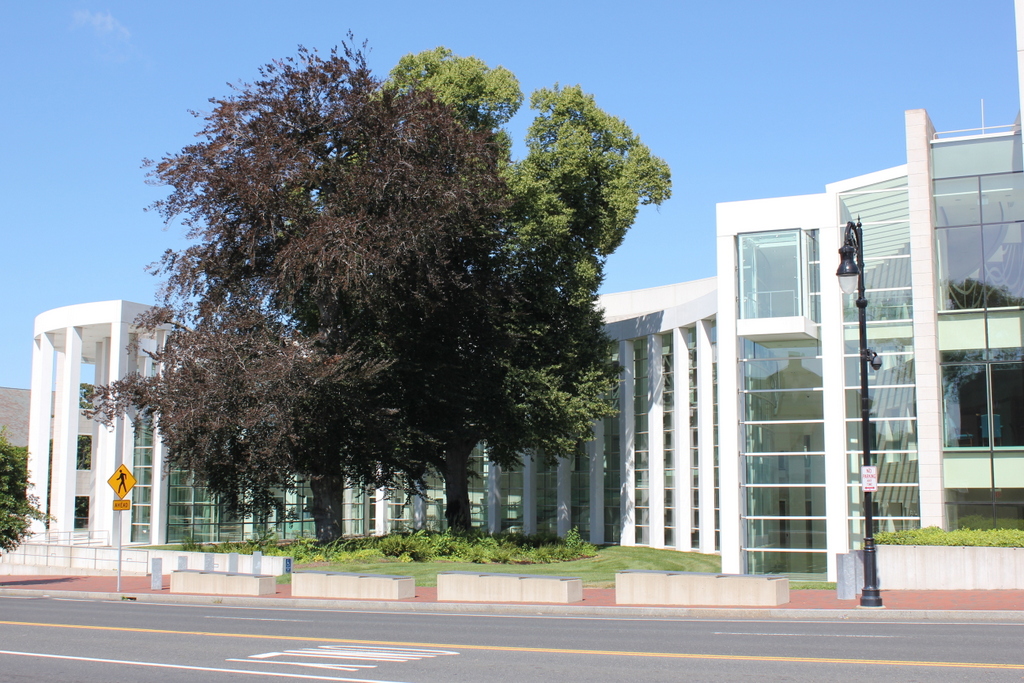

The Alexander House was one of many elegant homes that once lined this section of State Street between Chestnut Street and the Armory. Most of them have long since been replaced, but the Alexander House is still standing, just in a different location. Its history is explained in more detail in this post, which shows is current appearance around the corner from here, but it was built in 1811 and is one of the oldest existing buildings in the city.
Former owners of the house included portrait artist Chester Harding as well as former Springfield mayor Henry Alexander, Jr., for whom the house is named. However, its future was threatened in the early 2000s, when a new federal courthouse was proposed for this location. So, the house was moved about 100 yards away, behind the courthouse on Elliot Street. The large trees that once stood in front of the house couldn’t be moved, though, so architect Moshe Safdie literally built around them, designing the courthouse so that the trees could be saved as a central element.